Foville's syndrome
| Foville's syndrome | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Pons | |
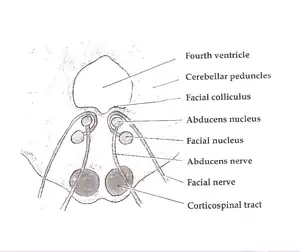
Foville's syndrome is caused by the blockage of the perforating branches of the basilar artery in the region of the brainstem known as the pons.[1] It is most frequently caused by vascular disease or tumors involving the dorsal pons.
Structures affected by the infarct are the dorsal pons(pontine tegmentum) which comprises paramedian pontine reticular formation (PPRF), nuclei of cranial nerves VI and VII, corticospinal tract, medial lemniscus, and the medial longitudinal fasciculus. There is involvement of the fifth to eighth cranial nerves, central sympathetic fibres (Horner syndrome) and horizontal gaze palsy.
Signs and symptoms
This produces ipsilateral horizontal gaze palsy and facial nerve palsy and contralateral hemiparesis, hemisensory loss, and internuclear ophthalmoplegia.
Cause
The reason for Foville's syndrome is pontine infarction, however, tumors in the pons have occured as well[2]
Diagnosis

In terms of the diagnosis of this condition we fine the following is done:[2]
- MRI angiography
- CT angiography
- Cardiac evaluation
Treatment
In the management of Foville's syndrome the following is done:[2]
- Antiplatelet therapy]]]]
- Statin therapy
- Evaluation by physical therapists/occupational therapists
- Cessation of smoking (if individual smokes)
History
Foville's syndrome was initially described by Achille-Louis Foville, a French physician, in 1859.[3]
References
- ↑ "Foville syndrome". GPnotebook.
- 1 2 3 Khazaal, Ossama; Marquez, Destiny L.; Naqvi, Imama A. (2022). "Foville Syndrome". StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Archived from the original on 12 July 2022. Retrieved 24 July 2022.
- ↑ Foville, ALF (1859). "Note sur une paralysie peu connue de certains muscles de l'oeil, et sa liaison avec quelques points de l'anatomie de la physiologie de la protubérance annulaire". Gazette Hebdomadaire de Médecine et de Chirurgie. 6: 146.
External links
| Classification |
|---|