Hepatozoon
| Hepatozoon | |
|---|---|
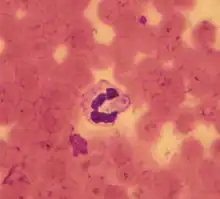 | |
| A gamont of Hepatozoon canis in a blood smear from a naturally infected dog | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Clade: | SAR |
| Infrakingdom: | Alveolata |
| Phylum: | Apicomplexa |
| Class: | Conoidasida |
| Order: | Eucoccidiorida |
| Suborder: | Adeleorina |
| Family: | Hepatozoidae Wenyon, 1926 |
| Genus: | Hepatozoon Miller, 1908 |
| Selected species | |
|
Hepatozoon americanum | |
Hepatozoon is a genus of Apicomplexa alveolates which incorporates over 300 species obligate intraerythrocytic parasites. Species have been described from all groups of tetrapod vertebrates, as well as a wide range of haematophagous arthropods, which serve as both the vectors and definitive hosts of the parasite. By far the most biodiverse and prevalent of all haemogregarines, the genus is distinguished by its unique reciprocal trophic lifecycle which lacks the salivary transmission between hosts commonly associated with other apicomplexans. While particularly prevalent in amphibians and reptiles, the genus is more well known in veterinary circles for causing a tick-borne disease called hepatozoonosis in some mammals.
Lifecycle
Members of the genus Hepatozoon possess particularly complex lifecycles which vary considerably among species. Sexual reproduction and sporogenic development occur within the haemocoel of the invertebrate host, which is subsequently consumed by the vertebrate host. The sporozoites then migrate to the liver of the vertebrate, where they undergo multiple fission (asexual reproduction) to produce merozoites. The meronts are released into the bloodstream where they form gametocytes, the final stage of development within the vertebrate host. The gamonts are large, conspicuous organisms which occupy a significant portion of the erythrocyte, and are easily visible on simple blood films. When the invertebrate vector feeds on the blood of the infected vertebrate, the gamonts are taken up into the gut once more, where they undergo gametogenesis and the cycle begins once more.
This simplified lifecycle is, of course, insufficient for species which infect vertebrate and invertebrate hosts which do not directly feed on one another, necessitating an even more complex cycle. For instance, Hepatozoon sipedon infects mosquitoes and snakes, but since snakes do not typically feed on mosquitoes, a third, intermediate host is required, in this case a frog. The frog ingests the infected mosquito, and the snake acquires the infection by feeding on the now-infected frog. Another mosquito can then feed on the snake, thus continuing the lifecycle.
Hepatozoonosis, therefore, results when an animal eats an infected tick - the disease is not spread by tick bites. Species include Hepatozoon muris and Hepatozoon canis,[2] which typically infects mice and dogs, respectively, and Hepatozoon atticorae, which is found in birds.
References
- ↑ Maia, João P.; Crottini, Angelica; Harris, David James (2014). "Microscopic and molecular characterization of Hepatozoon domerguei (Apicomplexa) and Foleyella furcata (Nematoda) in wild endemic reptiles from Madagascar". Parasite. 21: 47. doi:10.1051/parasite/2014046. ISSN 1776-1042. PMC 4165108. PMID 25224723.

- ↑ Nash, DVM, MS, Holly. "Hepatozoon canis".
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)