Instruments used in general surgery
Surgical instruments can vary widely by the field of surgery that they are used in. In general instruments can be divided into five classes by function:
- Cutting and dissecting instruments:
- Scalpels, scissors, and saws are the most traditional
- Elevators can be both cutting and lifting/retracting
- Although the term dissection is broad, energy devices such as diathermy/cautery are often used as more modern alternatives.
- Grasping or holding instruments:
- Classically this included forceps and clamps predominantly
- Roughly, forceps can be divided into traumatic (tissue crushing) and atraumatic (tissue preserving, such as Debakey's)
- Numerous examples are available for different purposes by field
- Hemostatic instruments:
- This includes instruments utilized for the cessation of bleeding
- Artery forceps are a classic example in which bleeding is halted by direct clamping of a vessel
- Sutures are often used, aided by a needle holder
- Cautery and related instruments are used with increasing frequency in high resource countries
- Retractors:
- Surgery is often considered to be largely about exposure
- A multitude of retractors exist to aid in exposing the body's cavities accessed during surgery
- These can broadly be hand held (often by a junior assistant) or self retaining
- Elevators can be both cutting and lifting/retracting
- Tissue unifying instruments and materials:
- This would include instruments that aid in tissue unification (such as needle holders or staple applicators)
- And the materials themselves
Instruments used in surgery are:[1][2][3][4][5][6][7][8][9][10][11]
| Instrument class | Image | Uses | Specific instruments | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Articulator |  |
Galotti articulator | ||
| Bone chisel |  |
Cutting instrument | ||
| Pin cutter |  |
To cut the pins after they are used to place bone in correct place | ||
| Bone distractor |  |
Clamps and distractors | ||
| llizarov apparatus |  |
Accessories and implants | ||
| Intramedullary kinetic bone distractor | Clamps and distractors | |||
| Bone drill | To drill inside the bone | |||
| Elevator | Accessories and implants | |||
| Bone mallet | Accessories | |||
| Bone rasp | Cutting instruments | |||
| Bone saw | Cutting instruments | |||
| Bone skid | ||||
| Bone splint | ||||
| Bone button | ||||
| Caliper | To measure | Castroviejo caliper | ||
| Cannula |  |
Accessories and implants | Spackmann Cannula | |
| Cautery |  |
To cauterize and seal vessels and bone, using electricity | ||
| Curette |  |
for scraping or debriding biological tissue or debris in a biopsy, excision, or cleaning procedure Cutting instrument | ||
| Depressor | ||||
| Dilator |  |
Accessories and implants | ||
| Dissecting knife | cutting instrument | |||
| surgical Pinzette |  |
Grasping/holding | ||
| Dermatome | 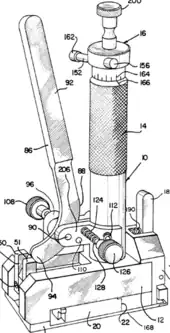 |
To take off a top layer of skin to implant over another area. | ||
| Forceps, Dissecting |  |
Grasping/holding. Usually used in skin closure or small wounds | Adson | |
| Forceps, Tissue |  |
Grasping/holding tissue | Allis | |
| Penetrating towel clamp |  |
Used to secure towels or reduce bone fragments | Backhaus penetating towel clamp | |
| Acanthulus or Acanthabolos | Thorn removal | |||
| Bone forceps | Grasping/holding | |||
| Carmalt forceps | haemostatic forceps | kalabasa | ||
| Cushing forceps | grasping/holding | Non-toothed dissecting forceps | ||
| Dandy forceps | haemostatic forceps | |||
| DeBakey forceps |  |
grasping/holding | Non-toothed dissecting forceps designed for use on blood vessels, organs, or delicate tissue | |
| Doyen intestinal clamp | clamps and distractors | Non-crushing clamp designed for use on the intestines | ||
| Epilation forceps | ||||
| Tiberio forceps | haemostatic forceps | |||
| Kelly forceps |  |
hemostatic forceps | ||
| Kocher forceps |  |
hemostatic forceps | ||
| Mosquito forceps |  |
hemostatic forceps | ||
| Hook | retractor | |||
| Nerve hook | retractor | |||
| Obstetrical hook | retractor | |||
| Skin hook | retractor | |||
| Lancet (scalpel) |  |
cutting | ||
| Lythotome | ||||
| Lythotript | ||||
| Mallet | ||||
| Partsch mallet | ||||
| Mammotome |  |
|||
| Needle holder |  |
grasping/holding | Castroviejo Crilewood Mayo-Hegar Olsen-Hegar | |
| Occluder | ||||
| Osteotome |  |
cutting | ||
| Epker osteotome | cutting | |||
| Periosteal elevator |  |
cutting and lifting | ||
| Joseph elevator | cutting | |||
| Molt periosteal elevator | cutting | |||
| Obweg periosteal elevator | cutting | |||
| Septum elevator | cutting | |||
| Tessier periosteal elevator | cutting | |||
| Periodontal probe | ||||
| Probe Dental explorer | ||||
| Retractor |  |
retractor | ||
| Deaver retractor |  |
Deep wound retraction | ||
| Gelpi retractor | self-retaining retractor. Used for superficial wound exposure | |||
| Weitlaner retractor | self-retaining retractor. Used for superficial wound exposure | |||
| USA-Army/Navy retractor | retractor | |||
| O'Connor-O'Sullivan | retractor | |||
| Mathieu Retractor | retractor | |||
| Jackson Tracheal Hook | retractor | |||
| Crile Retractor | retractor | |||
| Meyerding Finger Retractor | retractor | |||
| Little Retractor | retractor | |||
| Love Nerve Retractor | retractor | |||
| Green Retractor | retractor | |||
| Goelet Retractor | retractor | |||
| Cushing Vein Retractor | retractor | |||
| Langenbeck Retractor | retractor | |||
| Richardson Retractor | retractor | |||
| Richardson-Eastmann Retractor | retractor | |||
| Kelly Retractor | retractor | |||
| Parker Retractor | retractor | |||
| Parker-Mott Retractor | retractor | |||
| Roux Retractor | retractor | |||
| Mayo-Collins Retractor | retractor | |||
| Ribbon Retractor | retractor | |||
| Alm Retractor | retractor | |||
| Self Retaining Retractors | West, Travers and Norfolk & Norwich | |||
| Weitlaner Retractor | ||||
| Beckman-Weitlaner Retractor | ||||
| Beckman-Eaton Retractor | ||||
| Beckman Retractor | ||||
| Adson Retractor | ||||
| Rib spreader | ||||
| Rongeur | cutting instrument | |||
| Ultrasonic scalpel | cutting | |||
| Laser scalpel |  |
cutting | ||
| Scissors |  |
cutting | ||
| Iris scissors | cutting | |||
| Kiene scissors | cutting | |||
| Metzenbaum scissors |  |
To dissect delicate tissue | cutting | |
| Mayo scissors |  |
To cut suture, bandages, or dressings | cutting | |
| Tenotomy scissors | cutting | |||
| Spatula | ||||
| Speculum |  |
To retract the walls of the vagina | Graves vaginal speculum | |
| Mouth speculum | retractor | |||
| Rectal speculum | retractor | |||
| Sim's vaginal speculum |  |
To retract the walls of the vagina | ||
| Cusco's vaginal speculum |  |
retractor | ||
| Sponge bowl | accessories and implants | |||
| Sterilization tray | accessories and implants | |||
| Sternal saw | cutting | |||
| Suction tube and Yankeur suction tip |  |
accessories and implants | ||
| Surgical elevator |  |
|||
| Surgical hook |  |
retractor | ||
| Surgical blade #15 |  |
Used to cut vessels or make small incisions | ||
| Surgical mesh |  |
accessories and implants | ||
| Surgical needle |  |
accessories and implants | ||
| Surgical snare | ||||
| Surgical sponge | ||||
| Curettes |  |
|||
| GIA stapler |  |
Used to make a gastrointestinal anastamosis | Linear stapler | |
| Surgical tray | ||||
| Suture |  |
|||
| Tongue depressor |  |
|||
| Tonsillotome | ||||
| Towel clamp |  |
clamp | ||
| Towel forceps | clamp | |||
| Backhaus towel forceps |  |
|||
| Lorna towel clamp | Non-penatrating towel clamp | |||
| Tracheotome | ||||
| Tissue expander | accessories and implant | |||
| Subcutaneous inflatable balloon expander | accessories and implants | |||
| Trephine |  |
cutting instrument | ||
| Trocar |  Disposable trocar family |
Access instrument. Used to create an opening into a space without opening the abdominal cavity. A camera then inserted through one to view the inside of the space while instruments are inserted through the others to manipulate the organs. | ||
| Ultrasonic energy device | Surgical device using electrical energy that's converted to mechanical ultrasound energy typically used to dissect tissue but also seals small vessels and tissue bundles. | |||
| Vessel Sealing Device |  Vessel sealing device |
Vessel sealing device used to weld vessels together prior to cutting. These devices used bipolar radio frequency energy to create heat that welds the tissue. | Advanced Bipolar Energy | |
References
- ↑ "ilizarov.com (English)". Archived from the original on 2013-01-26. Retrieved 2008-06-04.
- ↑ Children with Tracheostomies Resource Guide, by Marilyn K. Kertoy, p. 15 (Google book search)
- ↑ Rob Toreki (1 December 2004). "Cannulas". The Glassware Gallery. Interactive Learning ←Paradigms Incorporated.
- ↑ "Practical approach to nephrostomy". Archived from the original on 2005-11-03. Retrieved 2008-06-04.
- ↑ See Mr R McElroy for details of various operations and the unintended effects of chemical cauterization
- ↑ Ring, Malvin (July 2001). "How a Dentist's Name Became a Synonym for a Life-saving Device: The Story of Dr. Charles Stent". Journal of the History of Dentistry. 49 (2): 77–80. PMID 11484317. Archived from the original on 2005-04-28. Retrieved 2008-04-01.
- ↑ How do they get the hole through a hypodermic needle?
- ↑ Bonfils-Roberts, E (May 1972). "The Rib Spreader: A Chapter in the History of Thoracic Surgery" (PDF). Chest. 61 (5): 469–474. doi:10.1378/chest.61.5.469. ISSN 0012-3692. PMID 4558402. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2008-12-17. Retrieved 2008-04-22.
- ↑ "General Instrument Sourcebook - KMedic" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-18. Retrieved 2011-02-10.
- ↑ Russell, R. C. G.; Bulstrode, C. J. K.; Williams, N. S. (25 April 2000). Bailey & Love's SHORT PRACTICE OF SURGERY (23rd ed.). ISBN 0-340-75949-6.
- ↑ Gould, George M. (1934). Gould's Pocket Pronouncing Medical Dictionary (10th (rev) ed.). P. Blakiston's Son & Co., Inc.
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.