List of aminorex analogues
This is a list of aminorex analogues. Aminorex itself is a stimulant drug with a 5-phenyl-2-amino-oxazoline structure. It was developed in the 1960s as an anorectic,[1][2][3] but withdrawn from sale after it was discovered that extended use produced pulmonary hypertension, often followed by heart failure, which resulted in a number of deaths.[4] A designer drug analogue 4-methylaminorex appeared on the illicit market in the late 1980s but did not attract significant popularity due to its steep dose-response curve and tendency to produce seizures.[5][6][7][8] Pemoline, the 4-keto derivative of aminorex, had been discovered several years earlier,[9] and derivatives of this type appeared to be effective stimulants with comparatively low toxicity.[10][11] Pemoline was sold for around 25 years as a therapy for ADHD and relief of fatigue, before being withdrawn from the market in 2005 because of rare but serious cases of liver failure.[12][13][14][15] More recently in around 2014 another derivative 4,4'-dimethylaminorex started to be sold illicitly, but again swiftly lost popularity due to a spate of fatal overdose cases.[16][17][18] A number of related compounds are known, and new derivatives have continued to appear on the designer drug market.[19][20][21][22][23][24]
List of substituted aminorex derivatives
| Structure | Common name | Chemical name | CAS number |
|---|---|---|---|
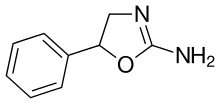 |
Aminorex | 5-phenyl-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine | 2207-50-3 |
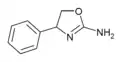 |
Rexamino | 4-phenyl-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine | 52883-35-9 |
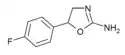 |
4'-Fluoroaminorex (4'-FAR) | 5-(4-fluorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine | 2967-77-3 |
| Clominorex | 5-(4-chlorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine | 3876-10-6 | |
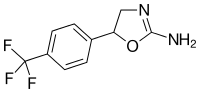 |
Fluminorex | 5-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine | 720-76-3 |
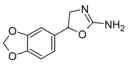 |
Methylenedioxyaminorex | 5-(3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine | 3865-98-3 |
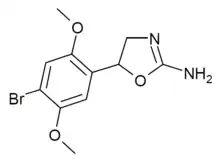 |
2C-B-aminorex (2C-B-AR) | 5-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine | |
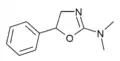 |
N,N-Dimethylaminorex (N,N-DMAR) | N,N-dimethyl-5-phenyl-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine | 32968-41-5 |
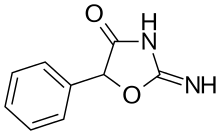 |
Pemoline | 2-amino-5-phenyl-1,3-oxazol-4(5H)-one | 2152-34-3 |
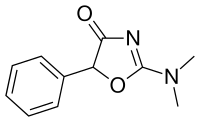 |
Thozalinone | 2-(dimethylamino)-5-phenyl-1,3-oxazol-4(5H)-one | 655-05-0 |
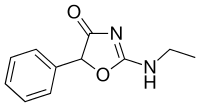 |
Fenozolone | 2-ethylamino-5-phenyl-1,3-oxazol-4-one | 15302-16-6 |
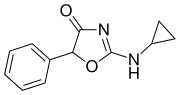 |
Cyclazodone | 2-(cyclopropylamino)-5-phenyl-1,3-oxazol-4-one | 14461-91-7 |
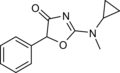 |
N-Methylcyclazodone | 2-(cyclopropyl(methyl)amino)-5-phenyl-1,3-oxazol-4-one | 14461-92-8 |
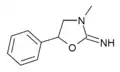 |
3-Methylaminorex | 3-methyl-5-phenyl-2-oxazolidinimine | 75343-73-6 |
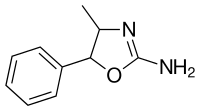 |
4-Methylaminorex (4-MAR) | 4-methyl-5-phenyl-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine | 3568-94-3 |
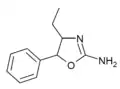 |
4-Ethylaminorex (4-EAR) | 4-ethyl-5-phenyl-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine | 1364933-63-0 |
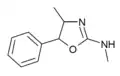 |
4,N-Dimethylaminorex (4,N-DMAR) | 4,5-dihydro-N,4-dimethyl-5-phenyl-2-oxazolamine | 2207-49-0 |
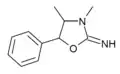 |
3,4-Dimethylaminorex (3,4-DMAR) | 3,4-dimethyl-5-phenyl-2-oxazolidinimine | 82485-31-2 |
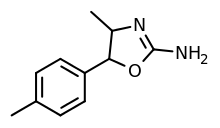 |
4,4'-Dimethylaminorex (4,4'-DMAR) | 4-methyl-5-(4-methylphenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine | 1445569-01-6 |
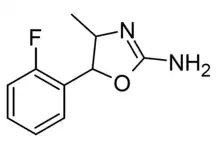 |
2'-Fluoro-4-methylaminorex (2'-F-4-MAR) | 4-methyl-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine | |
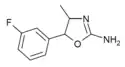 |
3'-Fluoro-4-methylaminorex (3'-F-4-MAR) | 4-methyl-5-(3-fluorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine | |
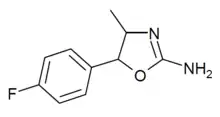 |
4'-Fluoro-4-methylaminorex (4'-F-4-MAR) | 4-methyl-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine | 1364933-64-1 |
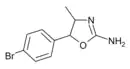 |
4'-Bromo-4-methylaminorex (4B-MAR) | 4-methyl-5-(4-bromophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine | |
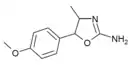 |
4'-Methoxy-4-methylaminorex (4'-MeO-4-MAR) | 4-methyl-5-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine | 1445570-65-9 |
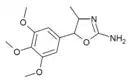 |
3',4',5'-Trimethoxy-4-methylaminorex (TM-4-MAR) | 4-methyl-5-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine | 1445571-92-5 |
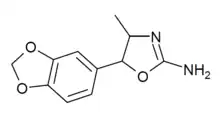 |
3',4'-Methylenedioxy-4-methylaminorex (MDMAR) | 4-methyl-5-(3,4-methylenedioyphenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine | 1445573-16-9 |
See also
References
- ↑ Meschino JA, Poos GI. 2-amino-5,6-dihydro-4H-1,3-oxazines and a process for their preparation. US Patent 3115494, 1961
- ↑ Poos GI. 2-amino-5-aryloxazoline products. US Patent 3161650, 1962
- ↑ Poos GI, Carson JR, Rosenau JD, Roszowski AP, Kelley NM, McGowin J (May 1963). "2-Amino-5-aryl-2-oxazolines. Potent New Anorectic Agents". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 6 (3): 266–272. doi:10.1021/jm00339a011. PMID 14185981.
- ↑ Gurtner HP. Aminorex and pulmonary hypertension. A review. Cor Vasa. 1985;27(2-3):160-71. PMID 3928246
- ↑ Davis FT, Brewster ME. A fatality involving U4Euh, a cyclic derivative of phenylpropanolamine. J Forensic Sci. 1988 Mar;33(2):549-53. PMID 3373171
- ↑ Bunker CF, Johnson M, Gibb JW, Bush LG, Hanson GR. Neurochemical effects of an acute treatment with 4-methylaminorex: a new stimulant of abuse. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 May 3;180(1):103-11. PMID 1973111
- ↑ Gaine SP, Rubin LJ, Kmetzo JJ, Palevsky HI, Traill TA. Recreational use of aminorex and pulmonary hypertension. Chest. 2000 Nov;118(5):1496-7. PMID 11083709
- ↑ Meririnne E, Kajos M, Kankaanpää A, Koistinen M, Kiianmaa K, Seppälä T. Rewarding properties of the stereoisomers of 4-methylaminorex: involvement of the dopamine system. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2005 Aug;81(4):715-24. PMID 15982727
- ↑ Schmidt L, Scheffler H. Central nervous system stimulant. US Patent 2892753, 1957
- ↑ "Hardy RA, Howell CF, Quinones NQ. Method of producing central nervous system stimulation and anorexia. US Patent 3313688, 1964". Archived from the original on 2021-05-31. Retrieved 2019-06-14.
- ↑ "Guidicelli DP, Najer H. 5-phenyl-2-cyclopropylamino-4-oxazolinone, and process for making the same. US Patent 3609159, 1967". Archived from the original on 2021-05-31. Retrieved 2019-06-14.
- ↑ Marotta PJ, Roberts EA. Pemoline hepatotoxicity in children. J Pediatr. 1998 May;132(5):894-7. PMID 9602211
- ↑ Safer DJ, Zito JM, Gardner JE. Pemoline hepatotoxicity and postmarketing surveillance. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2001 Jun;40(6):622-9. PMID 11392339
- ↑ Etwel FA, Rieder MJ, Bend JR, Koren G (2008). "A surveillance method for the early identification of idiosyncratic adverse drug reactions". Drug Saf. 31 (2): 169–80. doi:10.2165/00002018-200831020-00006. PMID 18217792. S2CID 19964105.
- ↑ Shader RI. Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies (REMS), Pemoline, and What Is a Signal? Clin Ther. 2017 Apr;39(4):665-669. Shader, Richard I. (2017). "Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies (REMS), Pemoline, and What is a Signal?". Clinical Therapeutics. 39 (4): 665–669. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2017.03.008. PMID 28366595.
- ↑ Brandt SD, Baumann MH, Partilla JS, Kavanagh PV, Power JD, Talbot B, Twamley B, Mahony O, O'Brien J, Elliott SP, Archer RP, Patrick J, Singh K, Dempster NM, Cosbey SH. Characterization of a novel and potentially lethal designer drug (±)-cis-para-methyl-4-methylaminorex (4,4'-DMAR, or 'Serotoni'). Drug Test Anal. 2014 Jul-Aug;6(7-8):684-95. doi:10.1002/dta.1668 PMID 24841869
- ↑ Coppola M, Mondola R. 4,4'-DMAR: chemistry, pharmacology and toxicology of a new synthetic stimulant of abuse. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2015 Jul;117(1):26-30. doi:10.1111/bcpt.12399 PMID 25819702
- ↑ Maier J, Mayer FP, Luethi D, Holy M, Jäntsch K, Reither H, Hirtler L, Hoener MC, Liechti ME, Pifl C, Brandt SD, Sitte HH. The psychostimulant (±)-cis-4,4'-dimethylaminorex (4,4'-DMAR) interacts with human plasmalemmal and vesicular monoamine transporters. Neuropharmacology. 2018 Aug;138:282-291. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.06.018 PMID 29908239
- ↑ Russell BR, Beresford RA, Schmierer DM, McNaughton N, Clark CR. Stimulus properties of some analogues of 4-methylaminorex. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1995 Jun-Jul;51(2-3):375-8. PMID 7667356
- ↑ Zheng Y, Russell B, Schmierer D, Laverty R. The effects of aminorex and related compounds on brain monoamines and metabolites in CBA mice. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1997 Jan;49(1):89-96. PMID 9120777
- ↑ McLaughlin G, Morris N, Kavanagh PV, Power JD, Twamley B, O'Brien J, Talbot B, Dowling G, Mahony O, Brandt SD, Patrick J, Archer RP, Partilla JS, Baumann MH. Synthesis, characterization, and monoamine transporter activity of the new psychoactive substance 3',4'-methylenedioxy-4-methylaminorex (MDMAR). Drug Test Anal. 2015 Jul;7(7):555-64. doi:10.1002/dta.1732 PMID 25331619
- ↑ Maier J, Mayer FP, Brandt SD, Sitte HH. DARK Classics in Chemical Neuroscience: Aminorex Analogues. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2018 Oct 17;9(10):2484-2502. doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.8b00415 PMID 30269490
- ↑ Fabregat-Safont D, Carbón X, Ventura M, Fornís I, Hernández F, Ibáñez M. Characterization of a recently detected halogenated aminorex derivative: para-fluoro-4-methylaminorex (4'F-4-MAR). Sci Rep. 2019 Jun 5;9(1):8314. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-44830-y PMID 31165778
- ↑ Rickli A, Kolaczynska K, Hoener MC, Liechti ME. Pharmacological characterization of the aminorex analogs 4-MAR, 4,4'-DMAR, and 3,4-DMAR. Neurotoxicology. 2019 May;72:95-100. doi:10.1016/j.neuro.2019.02.011 PMID 30776375