Aminorex
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.164.420 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
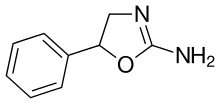
| Formula | C9H10N2O |
| Molar mass | 162.192 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Aminorex (Menocil, Apiquel, aminoxaphen, aminoxafen, McN-742) is a weight loss (anorectic) stimulant drug. It was withdrawn from the market after it was found to cause pulmonary hypertension.[1] In the U.S., it is an illegal Schedule I drug, meaning it has high abuse potential, no accepted medical use, and a poor safety profile.
Aminorex, in the 2-amino-5-aryl oxazoline class, was developed by McNeil Laboratories in 1962.[2] It is closely related to 4-methylaminorex. Aminorex has been shown to have locomotor stimulant effects, lying midway between dextroamphetamine and methamphetamine. Aminorex effects have been attributed to the release of catecholamines.[3] It can be produced as a metabolite of the worming medication levamisole, which is sometimes used as a cutting agent of illicitly produced cocaine.[4][5]
History
It was discovered in 1962 by Edward John Hurlburt,[6] and was quickly found in 1963 to have an anorectic effect in rats. It was introduced as a prescription appetite suppressant in Germany, Switzerland and Austria in 1965, but was withdrawn in 1972 after it was found to cause pulmonary hypertension in approximately 0.2% of patients, and was linked to a number of deaths.[3][7]
Synthesis
The synthesis was first reported in a structure-activity relationship study of 2-amino-5-aryl-2-oxazolines, where aminorex was found to be approximately 2.5 times more potent than D-amphetamine sulfate in inducing anorexia in rats, and was also reported to have CNS stimulant effects.
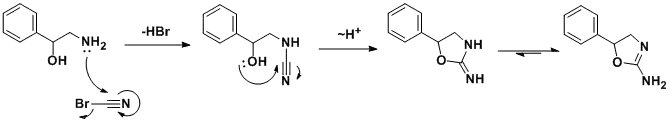
The racemic synthesis involves addition/cyclization reaction of 2-amino-1-phenylethanol with cyanogen bromide.[8] A similar synthesis has been also published.[9] In a search for a cheaper synthetic route, a German team developed an alternative route[10] which, by using chiral styrene oxide, allows an enantiopure product.
See also
References
- ↑ Gaine SP, Rubin LJ, Kmetzo JJ, Palevsky HI, Traill TA (November 2000). "Recreational use of aminorex and pulmonary hypertension". Chest. 118 (5): 1496–7. doi:10.1378/chest.118.5.1496. PMID 11083709. Archived from the original on 2013-01-12.
- ↑ US 3161650, "2-Amino-5-Aryloxazoline Products"
- 1 2 Fishman AP. (Jan 1991). "Aminorex to fen/phen - An epidemic foretold". Circulation. 99 (1): 156–161. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.99.1.156. ISSN 0009-7322. PMID 9884392.
- ↑ Ho EN, Leung DK, Leung GN, Wan TS, Wong AS, Wong CH, Soma LR, Rudy JA, Uboh C, Sams R (April 2009). "Aminorex and rexamino as metabolites of levamisole in the horse". Analytica Chimica Acta. 638 (1): 58–68. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2009.02.033. PMID 19298880.
- ↑ Bertol E, Mari F, Milia MG, Politi L, Furlanetto S, Karch SB (July 2011). "Determination of aminorex in human urine samples by GC-MS after use of levamisole". Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis. 55 (5): 1186–9. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2011.03.039. PMID 21531521.
- ↑ US 3115494, "2-amino-5, 6-dihydro-4ii-1, 3-oxazines and a process for their preparation"
- ↑ Weigle, DS (June 2003). "Pharmacological therapy of obesity: past, present, and future". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 88 (6): 2462–9. doi:10.1210/jc.2003-030151. PMID 12788841.
- ↑ Poos GI, Carson JR, Rosenau JD, Roszowski AP, Kelley NM, McGowin J (May 1963). "2-Amino-5-aryl-2-oxazolines. Potent New Anorectic Agents". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 6 (3): 266–272. doi:10.1021/jm00339a011. PMID 14185981.
- ↑ Ueda S, Terauchi H, Yano A, Ido M, Matsumoto M, Kawasaki M (Jan 2004). "4,5-Disubstituted-1,3-oxazolidin-2-imine derivatives: a new class of orally bioavailable nitric oxide synthase inhibitor". Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 14 (2): 313–316. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2003.11.010. PMID 14698148.
- ↑ DE Patent 2101424 2-amino-5-phenyl-2-oxazoline preparation