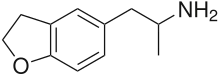
5-APDB
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H15NO |
| Molar mass | 177.247 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
5-(2-Aminopropyl)-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran (5-APDB, 3-Desoxy-MDA, EMA-4) is a putative entactogen drug of the phenethylamine and amphetamine classes.[1] It is an analogue of MDA where the heterocyclic 3-position oxygen from the 3,4-methylenedioxy ring has been replaced by a methylene bridge.[1] 6-APDB is an analogue of 5-APDB where the 4-position oxygen has been replaced by a methylene bridge instead.[1] 5-APDB was developed by a team led by David E. Nichols at Purdue University as part of their research into non-neurotoxic analogues of MDMA.[1]
In animal studies, 5-APDB's effects generalize most closely to non-stimulant MDMA analogues such as MBDB and MMAI, while producing no substitution for LSD or amphetamine.[1] In vitro studies show that 5-APDB acts as a highly selective serotonin releasing agent (SSRA), with IC50 values of 130 nM, 7,089 nM, and 3,238 nM for inhibiting the reuptake of serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, respectively.[1] In contrast, 6-APDB is more balanced on the three monoamine neurotransmitters and acts more similarly to MDA and MDMA.[1]
Methoxy-substituted analogues of 5-APDB and 6-APDB have also been made and substituted for DOM in animal tests, although they were around one tenth as potent as DOM.[2][3]
Legal status
China
As of October 2015 5-APDB is a controlled substance in China.[4]
UK
On June 10, 2013 5-APDB and a number of analogues were classified as Temporary Class Drugs in the UK following an ACMD recommendation.[5] This means that sale and import of the named substances are criminal offences and are treated as for class B drugs.[6]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Monte AP, Marona-Lewicka D, Cozzi NV, Nichols DE (November 1993). "Synthesis and pharmacological examination of benzofuran, indan, and tetralin analogues of 3,4-(methylenedioxy)amphetamine". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 36 (23): 3700–6. doi:10.1021/jm00075a027. PMID 8246240.
- ↑ Nichols, DE; Hoffman, AJ; Oberlender, RA; Riggs, RM (1986). "Synthesis and evaluation of 2,3-dihydrobenzofuran analogues of the hallucinogen 1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-methylphenyl)-2-aminopropane: drug discrimination studies in rats". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 29 (2): 302–4. doi:10.1021/jm00152a022. PMID 3950910.
- ↑ Nichols, DE; Snyder, SE; Oberlender, R; Johnson, MP; Huang, XM (1991). "2,3-Dihydrobenzofuran analogues of hallucinogenic phenethylamines". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 34 (1): 276–81. doi:10.1021/jm00105a043. PMID 1992127.
- ↑ "关于印发《非药用类麻醉药品和精神药品列管办法》的通知" (in Chinese). China Food and Drug Administration. 27 September 2015. Archived from the original on 1 October 2015. Retrieved 1 October 2015.
- ↑ "Temporary class drug order report on 5-6APB and NBOMe compounds". UK Home Office. 4 Jun 2013. Retrieved 2013-06-13.
- ↑ "'NBOMe' and 'Benzofury' banned". UK Home Office. 4 Jun 2013. Retrieved 2013-06-13.