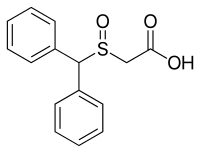
Modafinil acid
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(Diphenylmethanesulfinyl)acetic acid | |
| Other names
Modafinilic acid; Modafinil carboxylate; CRL-40467 | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.219.633 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C15H14O3S |
| Molar mass | 274.33 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Modafinil acid (code name CRL-40467), also known as modafinilic acid or modafinil carboxylate, is one of the two major metabolites of modafinil – the other being modafinil sulfone.[1][2] Modafinil acid is also a metabolite of the modafinil prodrug, adrafinil, and the (R)-(–)-enantiomer is a metabolite of armodafinil, the (R)-(–)-enantiomer of modafinil.[3] Modafinil acid seems to be inactive,[4] and similarly to modafinil sulfone, does not appear to contribute to the wakefulness-promoting/psychostimulant effects of modafinil.[5][6][7]
In the breakdown process of modafinil, modafinil is primarily hydrolyzed by an esterase or amidase enzyme into modafinil acid.[8] The apparent clearance of modafinil acid is significantly higher than that of modafinil, following the hypothesis that metabolism increases the polarity and the clearance of modafinil.[9]
References
- ↑ Dubey, S.; Ahi, S.; Reddy, I. M.; Kaur, T.; Beotra, A.; Jain, S. "A novel study of screening and confirmation of modafinil, adrafinil and their metabolite modafinilic acid under EI-GC-MS and ESI-LC-MS-MS ionization". Indian Journal of Pharmacology. 41 (6): 278–283. doi:10.4103/0253-7613.59928. ISSN 1998-3751. PMC 2846503. PMID 20407560.
- ↑ "Ultimate Modafinil Guide 2021". Nootropics UK - Modafinil UK. Retrieved 2021-11-04.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ↑ Sousa, Ana; Dinis-Oliveira, Ricardo Jorge (2020). "Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic of the cognitive enhancer modafinil: Relevant clinical and forensic aspects". Substance Abuse. 41 (2): 155–173. doi:10.1080/08897077.2019.1700584. ISSN 1547-0164. PMID 31951804.
- ↑ Wong, Y. Nancy; Wang, Lixia; Hartman, Linda; Simcoe, Donna; Chen, Yusong; Laughton, Watson; Eldon, Richard; Markland, Colin; Grebow, Peter (1998). "Comparison of the Single-Dose Pharmacokinetics and Tolerability of Modafinil and Dextroamphetamine Administered Alone or in Combination in Healthy Male Volunteers". The Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 38 (10): 971–978. doi:10.1002/j.1552-4604.1998.tb04395.x. ISSN 0091-2700. PMID 9807980. S2CID 32857213.
- ↑ Schwertner, Harvey A.; Kong, Suk Bin (2005). "Determination of modafinil in plasma and urine by reversed phase high-performance liquid-chromatography". Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis. 37 (3): 475–479. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2004.11.014. ISSN 0731-7085. PMID 15740906.
- ↑ Robertson, Philmore; Hellriegel, Edward T. (2003). "Clinical Pharmacokinetic Profile of Modafinil". Clinical Pharmacokinetics. 42 (2): 123–137. doi:10.2165/00003088-200342020-00002. ISSN 0312-5963. PMID 12537513. S2CID 1266677.
- ↑ Robertson, P (2002). "Effect of modafinil on the pharmacokinetics of ethinyl estradiol and triazolam in healthy volunteers". Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics. 71 (1): 46–56. doi:10.1067/mcp.2002.121217. ISSN 0009-9236. PMID 11823757.
- ↑ Wu, Ke-hua; Guo, Tao; Deng, Chen-hui; Guan, Zheng; Li, Liang; Zhou, Tian-yan; Lu, Wei (2012). "Population pharmacokinetics of modafinil acid and estimation of the metabolic conversion of modafinil into modafinil acid in 5 major ethnic groups of China". Acta Pharmacologica Sinica. 33 (11): 1401–1408. doi:10.1038/aps.2012.124. ISSN 1671-4083. PMC 4011351. PMID 23103618.
- ↑ "Modafinil As A Physical Performance Enhancer". Retrieved 2017-02-22.