Eugeroic
| Eugeroic | |
|---|---|
| Drug class | |
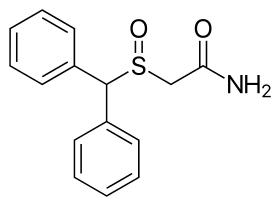 The chemical structure of modafinil, the prototypical drug of this class. | |
| Class identifiers | |
| Synonyms | wakefulness-promoting agent wakefulness-promoting drug |
| Use | Promote wakefulness and alertness |
| ATC code | N06B |
| In Wikidata | |
Eugeroics (originally "eugrégorique" or "eugregoric"),[1] also known as wakefulness-promoting agents and wakefulness-promoting drugs, are a class of drugs that promote wakefulness and alertness.[2][3] They are medically indicated for the treatment of certain sleep disorders including excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS) in narcolepsy or obstructive sleep apnea (OSA).[2][3] Eugeroics are also often prescribed off-label for the treatment of EDS in idiopathic hypersomnia,[4] a rare and often debilitating sleep disorder which currently has no official treatments approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). In contrast to classical psychostimulants, such as methylphenidate and amphetamine, which are also used in the treatment of these disorders, eugeroics typically do not produce euphoria, and, consequently, have a lower addictive potential.[2][3]
Modafinil and armodafinil are each thought to act as selective, weak, atypical dopamine reuptake inhibitors (DRI),[2][3] whereas adrafinil acts as a prodrug for modafinil. Other eugeroics include solriamfetol, which acts as a norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (NDRI), and pitolisant, which acts as a histamine 3 (H3) receptor antagonist/inverse agonist.
Examples
Marketed
- Armodafinil (Nuvigil)
- Modafinil (Provigil)
- Pitolisant (Wakix)[5]
- Solriamfetol (Sunosi)[6]
Discontinued
Never marketed
- Flmodafinil (CRL-40,940)
- Fluorafinil (CRL-40,941)
- Fluorenol
- Methylbisfluoromodafinil
In development
- Selective orexin receptor agonists (two are currently under development by Takeda, danavorexton and TAK-994)[7]
References
- ↑ Milgram, Norton W.; Callahan, Heather; Siwak, Christina (2006). "Adrafinil: A Novel Vigilance Promoting Agent". CNS Drug Reviews. 5 (3): 193–212. doi:10.1111/j.1527-3458.1999.tb00100.x. ISSN 1080-563X.
- 1 2 3 4 "Provigil: Prescribing information" (PDF). United States Food and Drug Administration. Cephalon, Inc. January 2015. Retrieved 16 August 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 "Nuvigil: Prescribing information" (PDF). United States Food and Drug Administration. Cephalon, Inc. April 2015. Retrieved 16 August 2015.
- ↑ "Practice Parameters for the Treatment of Narcolepsy and other Hypersomnias of Central Origin" (PDF). American Academy of Sleep Medicine (AASM). September 2007.
- ↑ "How WAKIX Works | WAKIX® (pitolisant) tablets". wakix.com. Retrieved 2020-01-03.
- ↑ "What is SUNOSI® (solriamfetol) Treatment ? | SUNOSI® for Patients". www.sunosi.com. Retrieved 2020-01-03.
- ↑ "New Data Presented at World Sleep Congress Demonstrate Early Signs of Efficacy for TAK-925, a Selective Orexin Type-2 Receptor (OX2R) Agonist, in Patients with Narcolepsy Type 1". www.takeda.com. Retrieved 2019-12-06.