Needle thoracostomy
| Needle thoracostomy | |
|---|---|
| Other names: Needle decompression[1] | |
 | |
| 12.3 GA / 8 Fr, 14 GA / 6.3 Fr, and 16 GA / 5 Fr needles used for the procedure | |
| Specialty | Emergency medicine |
| Indications | Tension pneumothorax[1] |
| Steps | 1) Select and clean site[1] 2) Insert a large hollow needle and catheter just above the rib[1] 3) Remove the needle, leaving the catheter in place[2] |
| Success | Rush of air, improved vital signs[3] |
| Complications | Bleeding, infection, lung or diaphragm injury[1] |
Needle thoracostomy (NT) is a procedure used in the initial treatment of a suspected tension pneumothorax.[1] It is generally followed by placement of a chest tube.[1] Finger thoracostomy; however, may be preferred over needle thoracostomy.[4] It is a type of thoracostomy, along with chest tubes and catheter thoracostomy.[2]
Typically the procedure is carried out in the 2nd intercostal space mid clavicular line or the 4th intercostal space anterior axillary line.[1][5] If sufficient time is present, the area may be cleaned with chlorhexidine and local anesthetic injected.[1] A 12, 14, or 16 gauge hollow needle and catheter is than placed just above the rib.[1] Once air returns, the needle is removed while the catheter is left in the chest.[2]
Successful placement will often result in a rush of air and improved vital signs.[3] A chest X-ray is than carried out to verify improvement.[2] Complications may include bleeding, infection, and heart, lung, or diaphragm injury.[1][6] If someone did not previously have a pneumothorax, one may develop.[1]
Technique
.jpg.webp)
Typically the procedure is carried out in the 2nd intercostal space mid clavicular line or the 4th intercostal space anterior axillary line.[1][7] The 4th intercostal space anterior axillary line may have a higher chance of success.[7] If there is sufficient time, the area may be cleaned with chlorhexidine and local anesthetic injected.[1] A 12, 14, or 16 gauge hollow needle and catheter is than placed just above the rib.[1] Longer needs (>8 cm) are better than shorter ones (5 cm).[1] Once air returns, the needle is removed while the catheter is left in the chest.[2]
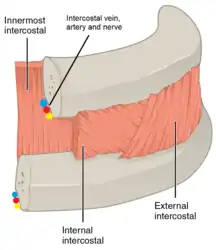 Part of the thorax with skin and muscle cut away to show the location of the intercostal vein, artery, and nerve
Part of the thorax with skin and muscle cut away to show the location of the intercostal vein, artery, and nerve_(Radiopaedia_37730)_(cropped).png.webp) Intercostal space
Intercostal space
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 "How To Do Needle Thoracostomy - Pulmonary Disorders". Merck Manuals Professional Edition. Archived from the original on 20 June 2022. Retrieved 9 August 2022.
- 1 2 3 4 5 King, Christopher; Henretig, Fred M. (2008). Textbook of Pediatric Emergency Procedures. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 355, 365. ISBN 978-0-7817-5386-9. Archived from the original on 2022-08-10. Retrieved 2022-08-09.
- 1 2 Nagelhout, John J.; Plaus, Karen (11 February 2009). Nurse Anesthesia E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 976. ISBN 978-0-323-08101-6. Archived from the original on 10 August 2022. Retrieved 9 August 2022.
- ↑ "Needle Thoracentesis". fpnotebook.com. Archived from the original on 15 December 2021. Retrieved 9 August 2022.
- ↑ Laan, DV; Vu, TD; Thiels, CA; Pandian, TK; Schiller, HJ; Murad, MH; Aho, JM (April 2016). "Chest wall thickness and decompression failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis comparing anatomic locations in needle thoracostomy". Injury. 47 (4): 797–804. doi:10.1016/j.injury.2015.11.045. PMID 26724173.
- ↑ Wernick, Brian; Hon, HeidiH; Mubang, RonnieN; Cipriano, Anthony; Hughes, Ronson; Rankin, DemichaD; Evans, DavidC; Burfeind, WilliamR; Hoey, BrianA; Cipolla, James; Galwankar, SagarC; Papadimos, ThomasJ; Stawicki, StanislawP; Firstenberg, MichaelS (2015). "Complications of needle thoracostomy: A comprehensive clinical review". International Journal of Critical Illness and Injury Science. 5 (3): 160. doi:10.4103/2229-5151.164939.
- 1 2 Laan, DV; Vu, TD; Thiels, CA; Pandian, TK; Schiller, HJ; Murad, MH; Aho, JM (April 2016). "Chest wall thickness and decompression failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis comparing anatomic locations in needle thoracostomy". Injury. 47 (4): 797–804. doi:10.1016/j.injury.2015.11.045. PMID 26724173.
External links
- Taming the SRU Archived 2020-07-16 at the Wayback Machine