Pustulosis palmaris et plantaris
| Pustulosis palmaris et plantaris | |
|---|---|
| Other names: Pustulosis of palms and soles,[1] Palmoplantar pustulosis, Persistent palmoplantar pustulosis, Pustular psoriasis of the Barber type, and Pustular psoriasis of the extremities | |
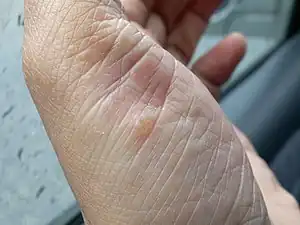 | |
| Pustulosis palmaris et plantaris | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
| Risk factors | SAPHO syndrome |
Pustulosis palmaris et plantaris is a chronic recurrent type of localized pustular psoriasis on the palms and soles only, characterized histologically by intraepidermal pustules filled with neutrophils.[2]: 411, 628 [3]
It can occur as part of the SAPHO syndrome.[4]
Treatment
Systematic reviews show evidence to support the use of systemic retinoids alone and in combination with photochemotherapy to improve symptoms of chronic palmoplantar pustulosis, with a combination more effective than one alone. There is also evidence to support topical steroids under hydrocolloid occlusion dressings, low dose ciclosporin, tetracyclines, and Grenz-Ray Therapy. There is no evidence to support the use of hydroxyurea in chronic palmoplantar pustulosis.[5]
Treatment with guselkumab, an anti–interleukin 23 monoclonal antibody has shown a decrease in the size of the area affected and severity.[6]
Additional images
.jpg.webp) Palmoplantar pustulosis
Palmoplantar pustulosis.jpg.webp) Palmoplantar pustulosis
Palmoplantar pustulosis.jpg.webp) Palmoplantar pustulosis
Palmoplantar pustulosis
See also
References
- ↑ Rapini RP, Bolognia JL, Jorizzo JL (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. ISBN 978-1-4160-2999-1.
- ↑ Freedberg IM, Fitzpatrick TB (2003). Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-07-138076-0.
- ↑ James, William D.; Elston, Dirk; Treat, James R.; Rosenbach, Misha A.; Neuhaus, Isaac (2020). "10. Seborrheic dermatitis, psoriasis, recalcitrant palmopustular eruptions, pustular dermatitis, and erythroderma". Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology (13th ed.). Edinburgh: Elsevier. pp. 203–204. ISBN 978-0-323-54753-6. Archived from the original on 2022-06-04. Retrieved 2022-06-02.
- ↑ Matzaroglou C, Velissaris D, Karageorgos A, Marangos M, Panagiotopoulos E, Karanikolas M (November 2009). "SAPHO Syndrome Diagnosis and Treatment: Report of Five Cases and Review of the Literature". The Open Orthopaedics Journal. 3: 100–6. doi:10.2174/1874325000903010100. PMC 2790148. PMID 19997538.
- ↑ Chalmers, Robert; Hollis, Sally; Leonardi-Bee, Jo; Griffiths, Christopher EM; Marsland Bsc MRCP, Alexander (2006-01-25). "Interventions for chronic palmoplantar pustulosis". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (1): CD001433. doi:10.1002/14651858.cd001433.pub2. ISSN 1465-1858. PMID 16437433.
- ↑ Terui T, Kobayashi S, Okubo Y, Murakami M, Zheng R, Morishima H, et al. (July 2019). "Efficacy and Safety of Guselkumab in Japanese Patients With Palmoplantar Pustulosis: A Phase 3 Randomized Clinical Trial". JAMA Dermatology. 155 (10): 1153. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.1394. PMC 6613288. PMID 31268476.
External links
| Classification |
|---|