Parainfluenza
| Parainfluenza | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Specialty | Infectious disease |
| Symptoms | Fever, runny nose, cough[1] |
| Causes | Human parainfluenza viruses[2] |
| Treatment | Symptomatic and supportive[2] |
Parainfluenza is an infectious disease caused by human parainfluenza viruses.[2] It typically presents with symptoms of the common cold; fever, runny nose and cough.[1] There may also be a sore throat, sneezing, wheezing, ear pain, irritability and poor appetite.[1]
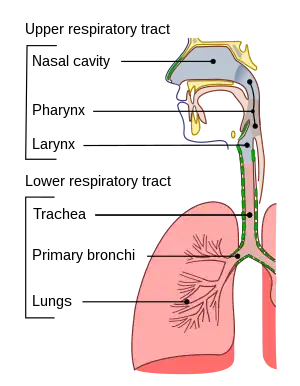
Spread occurs when an infected person is in close contact with another person, from the air by coughs and sneezes, or via contaminated surfaces.[3] It can spread to the larynx and trachea to cause croup.[2] Other complications include bronchitis, bronchiolitis and pneumonia.[1]
There is no vaccine for parainfluenza.[4] Treatment is symptomatic and supportive.[2] The primary methods of prevention are handwashing, not touching the eyes, nose or mouth with unwashed hands, and staying away from sick people.[4]
References
- 1 2 3 4 "Symptoms of Human Parainfluenza Virus (HPIV) Illnesses". www.cdc.gov. 1 April 2021. Archived from the original on 1 April 2022. Retrieved 29 April 2022.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Barlow, Gavin; Irving, William L.; Moss, Peter J. (2020). "20. Infectious disease". In Feather, Adam; Randall, David; Waterhouse, Mona (eds.). Kumar and Clark's Clinical Medicine (10th ed.). Elsevier. pp. 519–520. ISBN 978-0-7020-7870-5. Archived from the original on 2022-04-30. Retrieved 2022-04-29.
- ↑ "Human Parainfluenza Viruses (HPIVs)". www.cdc.gov. 1 April 2021. Archived from the original on 7 March 2022. Retrieved 29 April 2022.
- 1 2 "Preventing and Treating Human Parainfluenza Viruses (HPIV)". www.cdc.gov. 1 April 2021. Archived from the original on 10 December 2021. Retrieved 29 April 2022.