Perichondritis
| Perichondritis | |
|---|---|
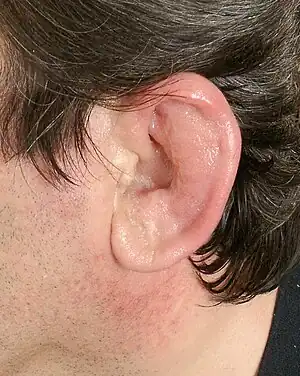 | |
| Perichondritis of the pinna | |
| Specialty | Otorhinolaryngology |
| Differential diagnosis | Otitis externa[1] |
Perichondritis is inflammation of the perichondrium, a layer of connective tissue surrounding cartilage.[2] The most common form is perichondritis of the ear involves the pinna of the ear. Less commonly the larynx may be involved, known as laryngeal perichondritis. Complications may include deformation of the ear.
It may occur due to infection of a traumatic or surgical wound or the spread of inflammation into depth.[3] The bacteria involved is usually Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Risk factors include a compromised immune status.
Treatment is with intravenous antibiotics.
Signs and symptoms
Signs in those with embedded earring are similar (pain, swelling, and redness). Fluctuant swelling may indicate an abscess that should be drained (typically associated with chondritis).[3]
Diagnosis
Differential diagnosis
Perichondritis can be differentiated from cellulitis of the pinna, in that the first usually does not involve the earlobe.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ Wolfson, Allan B.; Hendey, Gregory W.; Ling, Louis J.; Rosen, Carlo L. (2009). Harwood-Nuss' Clinical Practice of Emergency Medicine. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. PT428. ISBN 978-0-7817-8943-1. Archived from the original on 2020-08-01. Retrieved 2020-12-14.
- ↑ "Perichondritis" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- 1 2 3 Rodríguez, Javier Ignacio; Thöne, Natalie; Duque, Josefina; Brañes, Rocío (2019-05-31). "Infected transcartilaginous ear piercings. A case report and review of the literature". ARS MEDICA Revista de Ciencias Médicas. 44 (2): 23–25. doi:10.11565/arsmed.v44i2.1550. ISSN 0719-1855. Archived from the original on 2019-06-05. Retrieved 2020-12-14.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |