Triazolopyridine
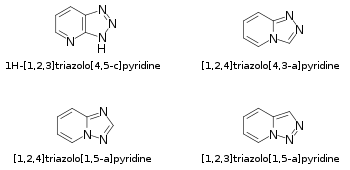
Chemical structures of selected examples of triazolopyridine isomers and their IUPAC names
Triazolopyridines are a class of heterocyclic chemical compounds with a triazole ring fused to a pyridine ring. There are multiple isomers which differ by the location of the nitrogen atoms and the nature of the ring fusion.
The term triazolopyridine can also refer to a class of antidepressant drugs whose chemical structure includes a trazolopyridine-derived ring system.[1] One example is trazodone.[2]
Other pharmaceutical drugs that contain a triazolopyridine ring system include filgotinib, tucatinib, and enarodustat. In addition, the reagents used in organic chemistry HATU, HOAt, and PyAOP[3] are triazolopyridine derivatives.
References
- ↑ "Triazolopyridine antidepressant". dictionary.com.
- ↑ J P Feighner (1980). "Trazodone, a triazolopyridine derivative, in primary depressive disorder". J Clin Psychiatry. 41 (7): 250–255. PMID 6993447.
- ↑ Jacques Coste, Patrick Jouin (April 15, 2003). "(7-Azabenzotriazol-1-yloxy)tris(pyrrolidino)phosphonium Hexafluorophosphate". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rn00199.
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.