Viliuisk encephalomyelitis
| Viliuisk encephalomyelitis | |
|---|---|
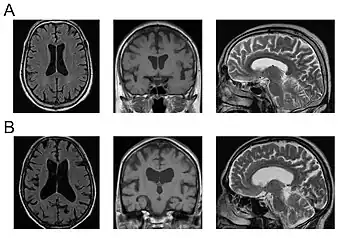 | |
| a,b)MRI of mild and severe chronic VE showing severity-dependent enlargement of the lateral and third ventricles | |
| Specialty | Neurological |
Viliuisk encephalomyelitis (VE) is a fatal progressive neurological disorder found only in the Sakha (Iakut/Yakut) population of central Siberia.[1][2] About 15 new cases are reported each year. VE is a very rare disease and little research has been conducted. The causative agents, origin of the disease, and involved candidate genes are currently unknown, but much research has been done in pursuit of the answers. Those inflicted with the disease survive for a period of only a few months to several years. VE follows three main courses of infection: an acute form, a sub-acute form subsiding into a progressive form, and a chronic form.[1]
Signs and symptoms
Initially, the infected patients experience symptoms such as: severe headaches, delirium, lethargy, meningism, bradykinesia, and incoordination.[1]
Cause
No causative agent has been found in blood, spinal fluid, or brain tissue.[1][3]Currently the mechanism of spread and infection is unknown despite the tedious epidemiological, clinical, and neurological studies that have been conducted.[4] Recent studies show horizontal disease transmission, or the transmission of a disease from one individual to another of the same generation. It appears that VE is an infectious disease; however, the incubation period would have to be very extensive[1] (in excess of five years).
Pathologic process
The acute form is the most rapid and most violent of all the stages. It begins with the characteristic rigidity of the muscles, accompanied by slurred speech, severe headaches, and exaggeration of cold-like symptoms. Patients usually die within weeks of the initial symptoms. Routine post-mortem examinations yield: severe inflammation of the brain lining, clusters of dead cells and tissue, and largely increased amounts of macrophages and lymphocytes.[5][6]
The progressive form is the most common case. Patients initially experience acute-like symptoms which are not as severe, and subside within a few weeks. Following the sub-acute phase, the patients experience a few mild symptoms including some behavioral changes, incoordination, and difficulty in speech. Eventually the disease developed fully and those infected were stricken with the characteristic symptoms of rigidity, slurred speech, and deterioration of cognitive functions.[5][6] Ultimately, brain function depreciates rapidly resulting in death.
Many patients who undergo the chronic form claim never to have had an acute attack. These patients endure varying measures of impairment and suffer mental deterioration for the remainder of their lives. Usually they live to be very old and succumb to other diseases.[5][6] In almost all cases there are changes characteristic of VE. Early onset shows an increased number of lymphocytes and increased protein concentration—which reduces over many years. These factors help neurologists determine the form of VE based on progression. The trademark changes in the brain include: thickened inflamed meninges, necrotic cortical lesions, increased number of lymphocytes, and neuronal death.[5][7]
Diagnosis
In terms of the diagnosis we find that lumbar puncture and cerebrospinal fluid examination are important[8]
Prognosis
A small percentage of patients die during the acute phase as result of a severe coma. In all cases the disease is fatal.
Epidemiology
As of 2007, fewer than 500 Yakut individuals have been infected with VE.[5] Viliuisk encephalomyelitis is classified as a progressive neurological disorder that ultimately ends in the death of the infected individual.
History
Research has concluded that Viliuisk encephalomyelitis has been present in the Viuli valley for many centuries among the Evenk populations of northern Siberia.[1][9] The disease had its debut through its first Yakut diagnosis a little over a century ago in villages of the Viuli region of Siberia. Not until after World War II did the Yakut people become aware of this mysterious killer. The locals and Northern Evenks referred to this illness as "Bokhoror" or "the stiffness" because of the typical rigidity of the limbs those infected individuals experienced. VE is currently isolated in the Yakut (Sakha) populations of Siberia, Russia. However, extensive migration might allow the disease to become a continental epidemic as it has already spread the infection radius many miles since its induction in the early 1900s.[1]
Fifty years ago it was believed that the Yakut people had extremely degraded immune systems as result of malnourishment and starvation from the World War. It was believed that this disease was docile and those with healthy immune systems could easily fight it off. This inclination appeared to be accurate until a case of a single Caucasian Russian woman. Supposedly, she infected herself as a means to end her own life. She injected herself with cerebrospinal fluid of a victim of VE, and died as a result of it. This is the first and only reported infection and death of a Caucasian.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Goldfarb, L.G.; Gajdusek, D.C. (1992). "Viliuisk Encephalomyelitis in the Iakut people of Siberia". Brain. 115 (4): 961–78. doi:10.1093/brain/115.4.961. PMID 1393513.
- ↑ Oleksyk, TK; Goldfarb, LG; Sivtseva, T; Danilova, AP; Osakovsky, VL; Shrestha, S; O'Brien, SJ; Smith, MW (2004). "Evaluating association and transmission of eight inflammatory genes with Viliuisk encephalomyelitis susceptibility". European Journal of Immunogenetics. 31 (3): 121–8. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2370.2004.00459.x. PMID 15182325.
- ↑ Green, AJ; Sivtseva, TM; Danilova, AP; et al. (August 2003). "Viliuisk encephalomyelitis: intrathecal synthesis of oligoclonal IgG". J. Neurol. Sci. 212 (1–2): 69–73. doi:10.1016/s0022-510x(03)00107-2. PMID 12810001. S2CID 27693647.
- ↑ Gajdusek DC, Goldfarb LG. Bibliography of Viliuisk Encephalomyelitis in the Iakut (Sakha) People of Siberia. 3rd edn. Bethesda, Maryland, USA: Laboratory of Ventral Nervous System Studies, National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, national Institutes of Health, 1992.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Stone, R (2002). "Infectious disease. Siberia's deadly stalker emerges from the shadows". Science. 296 (5568): 642–5. doi:10.1126/science.296.5568.642. PMID 11976423. S2CID 5104506.
- 1 2 3 McLean, CA; Masters, CL; Vladimirtsev, VA; Prokhorova, IA; Goldfarb, LG; Asher, DM; Vladimirtsev, AI; Alekseev, VP; Gajdusek, DC (1997). "Viliuisk encephalomyelitis--review of the spectrum of pathological changes". Neuropathology and Applied Neurobiology. 23 (3): 212–7. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2990.1997.tb01204.x. PMID 9223130. S2CID 13278776.
- ↑ Garruto, R.M.; Little, M.A.; James, G.D.; Brown, B.D. (1999). "natural experimental models: the global search for biomedical paradigms among traditional, modernizing, and modern populations". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA. 96 (18): 10536–43. Bibcode:1999PNAS...9610536G. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.18.10536. PMC 17924. PMID 10468644.
- ↑ Ellul, Mark; Solomon, Tom (1 April 2018). "Acute encephalitis – diagnosis and management". Clinical Medicine. 18 (2): 155–159. doi:10.7861/clinmedicine.18-2-155. ISSN 1470-2118. Archived from the original on 8 February 2023. Retrieved 9 October 2023.
- ↑ World Health Organization. Program for Investigation of Viliuisk Encephalomyelitis in Collaboration with the Institute of Health, National Academy of Sciences, Sakha (Yakut) Republic, and a Group of International Experts. Geneva: W.H.O.; 1998. pp. 1 – 13.
External links
- Viliuisk Encephalomyelitis in the Iakut People of Siberia Archived 2022-04-27 at the Wayback Machine