Zygoma fracture
| Zygoma fracture | |
|---|---|
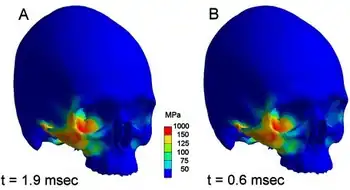 | |
| a,b)Regions coloured red are above the assumed failure of bone (150 MPa) and represent a zygomatic fracture (T=maximum stress pattern after impact) | |
| Frequency | Lua error in Module:PrevalenceData at line 5: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). |
A zygoma fracture (zygomatic fracture) is a form of facial fracture caused by a fracture of the zygomatic bone.[1][2] A zygoma fracture is often the result of facial trauma such as violence, falls or automobile accidents.
Symptoms include flattening of the face, trismus (reduced opening of the jaw) and lateral subconjunctival hemorrhage.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ Demetriades, Demetrios; Newton, Edward (2011). Color Atlas of Emergency Trauma. Cambridge University Press. p. 40. ISBN 9781139502719. Archived from the original on 1 April 2023. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
- ↑ Weinzweig, Jeffrey (2010). Plastic Surgery Secrets Plus E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 308. ISBN 978-0323085908. Archived from the original on 1 April 2023. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
- ↑ Snow, James Byron; Ballenger, John Jacob (2009). Ballenger's Otorhinolaryngology: Head and Neck Surgery. PMPH-USA. p. 688. ISBN 9781550093377. Archived from the original on 1 April 2023. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.