Belotecan
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
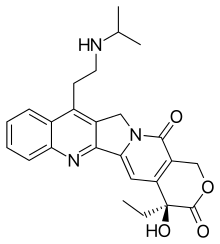
| Formula | C25H27N3O4 |
| Molar mass | 433.508 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Belotecan is a drug used in chemotherapy. It is a semi-synthetic camptothecin analogue indicated for small-cell lung cancer and ovarian cancer, approved in South Korea under the trade name Camtobell, presented in 2 mg vials for injection.[1] The drug has been marketed by ChongKunDang Pharmaceuticals[2] since 2003.[3]
Mechanism of action
Belotecan blocks topoisomerase I with a pIC50 of 6.56,[4] stabilizing the cleavable complex of topoisomerase I-DNA, which inhibits the religation of single-stranded DNA breaks generated by topoisomerase I; lethal double-stranded DNA breaks occur when the topoisomerase I-DNA complex is encountered by the DNA replication machinery, DNA replication is disrupted, and the tumor cell undergoes apoptosis. Topoisomerase I is an enzyme that mediates reversible single-strand breaks in DNA during DNA replication.[5]
References
- ↑ "Camtobell Inj. 2mg". Chong Kun Dang pharmaceutical Corp. Archived from the original on 12 November 2016.
- ↑ "Camtobell Inj. 2mg". Chong Kun Dang pharmaceutical Corp. Archived from the original on 12 November 2016.
- ↑ Sahoo U, ed. (2012). Clinical Research in Asia: Opportunities and Challenges. Oxford: Woodhead Publishing Limited. p. 152. ISBN 978-1-908818-13-3.
New drugs approved in South Korea
- ↑ "Belotecan". drugcentral.org. UNM School of Medicine. 2016-07-31. Retrieved 2016-11-12.
- ↑ Li F, Jiang T, Li Q, Ling X (2017). "Camptothecin (CPT) and its derivatives are known to target topoisomerase I (Top1) as their mechanism of action: did we miss something in CPT analogue molecular targets for treating human disease such as cancer?". American Journal of Cancer Research. 7 (12): 2350–2394. PMC 5752681. PMID 29312794.