Saccharopinuria
| Saccharopinuria | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Hyperlysinemia type II[1] |
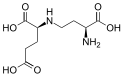 | |
| Saccharopine | |
Saccharopinuria (an excess of saccharopine in the urine), also called saccharopinemia, saccharopine dehydrogenase deficiency or alpha-aminoadipic semialdehyde synthase deficiency,[2] is a variant form of hyperlysinemia.[3] It is caused by a partial deficiency of the enzyme saccharopine dehydrogenase, which plays a secondary role in the lysine metabolic pathway. Inheritance is thought to be autosomal recessive, but this cannot be established as individuals affected by saccharopinuria typically have only a 40% reduction in functional enzyme.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ RESERVED, INSERM US14-- ALL RIGHTS. "Orphanet: Saccharopinuria". www.orpha.net. Retrieved 16 April 2019.
- 1 2 Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM): 268700
- ↑ Higashino, K. (1998). "Saccharopinuria (a variant form of familial hyperlysinemia)". Ryoikibetsu Shokogun Shirizu (18 Pt 1): 191–194. PMID 9590025.
External links
- Saccharopinuria; Alpha-aminoadipic semialdehyde synthase deficiency at NIH's Office of Rare Diseases
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.