Sikh gurus
The Sikh gurus (Punjabi: ਸਿੱਖ ਗੁਰੂ; Devanagari: सिख गुरु) are the spiritual masters of Sikhism, who established the religion over the course of about two and a half centuries, beginning in 1469.[2] The year 1469 marks the birth of Guru Nanak, the founder of Sikhism. He was succeeded by nine other human gurus until, in 1708, the Guruship was finally passed on by the tenth guru to the holy Sikh scripture, Guru Granth Sahib, which is now considered the living Guru by the followers of the Sikh faith.[3]


| Part of a series on |
| Sikhism |
|---|
 |
Etymology and definition
Guru (/ˈɡuːruː/, UK also /ˈɡʊruː, ˈɡʊər-/; Sanskrit: गुरु, Punjabi: ਗੁਰੂ, IAST: guru) is a Sanskrit term for a "teacher, guide, expert, or master" of certain knowledge or field.[4] Bhai Vir Singh, in his dictionary of Guru Granth Sahib describes the term Guru as a combination of two separate units: "Gu;(ਗੁ)" meaning darkness and "Rū;(ਰੂ)" which means light.[5] Hence, Guru is who brings light into darkness or in other words, the one who enlightens. Bhai Vir Singh's definition provides further insight about Sikhi itself and explains why Guru Granth Sahib is considered the living Guru. The word Sikh is derived from the Sanskrit term shishya[6] (Punjabi: ਸਿੱਖ) which means a disciple or a student. Thus, Sikhs have a student–teacher relationship with their Gurus since their teachings, written in Guru Granth Sahib, serve as a guide for the Sikhs.
According to Sikh beliefs, all the Gurus contained the same light or soul and their physical body was a vessel for containing the same essence. When one Guru passed, the successor inherited this light and that is why the Gurus are also referred to as mahalla (house).[7]
The gurus
| No. | Name | Portrait | Birth date | Guruship | Birthplace | Clan | Faith born as | Father | Mother | Date of death | Reason | Place of death |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Guru Nanak |  |
14 April 1469 [note 1] | Since birth | Nankana Sahib, Punjab, Delhi Sultanate | Bedi Khatri | Hindu | Kalyan Das Bedi | Mata Tripta | 22 September 1539 (aged 70) | Natural causes | Kartarpur, Punjab, Mughal Empire |
| 2 | Guru Angad |  |
31 March 1504 | 7 September 1539 | Muktsar, Punjab, Mughal Empire | Trehan Khatri | Hindu | Baba Pheru Mal | Mata Ramo | 29 March 1552 (aged 47) | Natural causes | Khadur Sahib, Punjab, Mughal Empire |
| 3 | Guru Amar Das |  |
5 May 1479 | 26 April 1552 | Amritsar, Punjab, Mughal Empire | Bhalla Khatri | Hindu | Tej Bhan Bhalla | Mata Lachmi | 1 September 1574 (aged 95) | Natural causes | Goindval, Lahore Subah, Mughal Empire |
| 4 | Guru Ram Das |  |
24 September 1534 | 1 September 1574 | Lahore, Punjab, Mughal Empire | Sodhi Khatri | Hindu | Baba Har Das | Mata Daya | 1 September 1581 (aged 46) | Natural causes | Goindval, Lahore Subah, Mughal Empire |
| 5 | Guru Arjan |  |
15 April 1563 | 1 September 1581 | Goindval, Punjab, Mughal Empire | Sodhi Khatri | Sikh | Guru Ram Das | Mata Bhani | 30 May 1606 (aged 43) | Execution by Mughal Emperor Jahangir | Lahore, Lahore Subah, Mughal Empire |
| 6 | Guru Hargobind |  |
19 June 1595 | 25 May 1606 | Amritsar, Lahore Subah, Mughal Empire | Sodhi Khatri | Sikh | Guru Arjan | Mata Ganga | 28 February 1644 (aged 48) | Natural causes | Kiratpur Sahib, Lahore Subah, Mughal Empire |
| 7 | Guru Har Rai |  |
16 January 1630 | 3 March 1644 | Kiratpur Sahib, Lahore Subah, Mughal Empire | Sodhi Khatri | Sikh | Baba Gurditta | Mata Nihal Kaur | 6 October 1661 (aged 31) | Natural causes | Delhi, Delhi Subah, Mughal Empire |
| 8 | Guru Har Krishan |  |
7 July 1656 | 7 October 1661 | Kiratpur Sahib, Lahore Subah, Mughal Empire | Sodhi Khatri | Sikh | Guru Har Rai | Mata Krishan Kaur | 30 March 1664 (aged 7) | Smallpox | Delhi, Delhi Subah, Mughal Empire |
| 9 | Guru Tegh Bahadur |  |
1 April 1621 | 20 March 1664 | Amritsar, Lahore Subah, Mughal Empire | Sodhi Khatri | Sikh | Guru Hargobind | Mata Nanaki | 11 November 1675 (aged 54) | Execution by Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb | Delhi, Delhi Subah, Mughal Empire |
| 10 | Guru Gobind Singh |  |
5 January 1666 | 11 November 1675 | Patna Sahib, Bihar Subah, Mughal Empire | Sodhi Khatri | Sikh | Guru Tegh Bahadur | Mata Gujri | 7 October 1708 (aged 41) | Assassinated by Jamshed Khan and Wasil Beg on order of Wazir Khan | Hazur Sahib, Bidar Subah, Mughal Empire |
| 11 | Guru Granth Sahib |  |
29 August 1604 (date of completion of compilation of the first draft [Adi Granth]) |
20 October 1708 | Amritsar, Lahore Subah, Mughal Empire (place of compilation) |
The central holy scripture of Sikhism, regarded as the final, sovereign and eternal Guru. | ||||||
Timeline

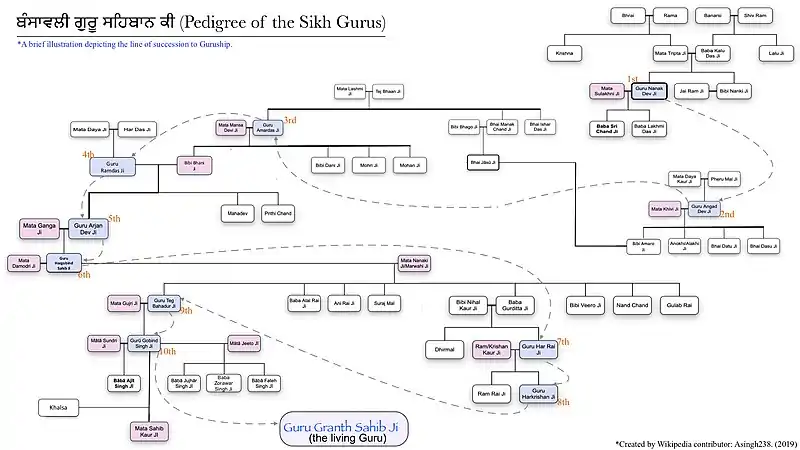
Pedigrees

See also
Notes
- Officially observed on Katak Puranmashi (October–November)
- Listed names and relations might vary from source to source since different aspects of Sikh history have been written by many different individuals over the course of past six centuries
References
- The Sikhs. E.J. Brill. p. 38. ISBN 9004095543.
- Sen, Sailendra (2013). A Textbook of Medieval Indian History. Primus Books. pp. 186–187. ISBN 978-9-38060-734-4.
- The Sikhs : faith, philosophy & folk. Lustre Press. 1998. ISBN 978-8174360373.
- Stefan Pertz (2013), The Guru in Me - Critical Perspectives on Management, GRIN Verlag, ISBN 978-3638749251, p. 2–3.
- Singh, Veer (1964). Sri Guru Granth Kosh. p. 122.
- Parrinder, Geoffrey (30 August 1983). World religions : from ancient history to the present. Facts on File. ISBN 978-0-87196-129-7.
- Sikh history from Persian sources : translations of major texts. J. S. Grewal, Irfan Habib, Indian History Congress. Session. New Delhi: Tulika. 2001. p. 5. ISBN 81-85229-17-1. OCLC 47024480.
The author of the Dabistan refers to the belief of the Sikhs in the unity of Guruship. The spirit of Guru Nanak entered the bodies of his successors - Guru Angad, Guru Amar Das, Guru Ram Das and Guru Arjan. That was why each Guru was referred to as mahal: Guru Nanak as the first mahal, Guru Angad as the second mahal, and in this way Guru Arjan as the fifth mahal. A Sikh who does not regard Guru Arjan as Baba Nanak is not a true Sikh. The firm belief of the Sikhs is that all the Gurus are Nanak. Indeed, Bhai Gurdas underscores the unity of Guruship from Guru Nanak to Guru Hargobind in one of his Vaars. This is reiterated in another Vaar in which the metaphors of light and water are used to emphasize that they all are the same.The idea of the unity of Guruship emphasized by Bhai Gurdas legitimized the succession of Guru Hargobind to face the rival claim of Prithi Chand and his descendants.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: others (link)