Araçuaí
Araçuaí is a Brazilian municipality located in the northeast of the state of Minas Gerais in the Jequitinhonha River valley. The Araçuaí River, a tributary of the Jequitinhonha, flows through it. Its population as of 2020 was estimated to be 36,712 people living in a total area of 2,235 km2. The city belongs to the mesoregion of Jequitinhonha and to the microregion of Araçuaí. The city is the seat of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Araçuaí. The elevation of the municipal seat is 307 meters. It became a municipality in 1870.
Araçuaí | |
|---|---|
 Monument at the city entrance | |
 Flag  Seal | |
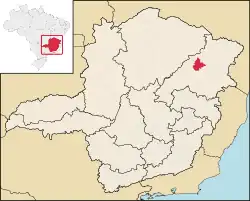 Location in the state of Minas Gerais | |
 Araçuaí Location in Brazil | |
| Coordinates: 16°51′00″S 42°04′12″W | |
| Country | Brazil |
| State | Minas Gerais |
| Mesoregion | Jequitinhonha |
| Microregion | Araçuaí |
| Incorporated (municipality) | 21 September 1871 |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Tadeu Barbosa de Oliveira |
| Area | |
| • Total | 2,236.279 km2 (863.432 sq mi) |
| Population (2020 [2]) | |
| • Total | 36,712 |
| • Density | 16/km2 (43/sq mi) |
| Demonym | araçuaiense[3] |
| Time zone | UTC−3 (BRT) |
| CEP postal code | 39600-000 |
| Area code | 33 |
| Website | aracuai.mg.gov.br |
Araçuaí Micro-region
Araçuaí is a statistical micro-region with 08 municipalities: Araçuaí, Caraí, Coronel Murta, Itinga, Novo Cruzeiro, Padre Paraíso, Ponto dos Volantes and Virgem da Lapa. In 2000 the population was 145,679 inhabitants in an area of 10,299.30 km2. The population density was 14.14 inhabitants/km2 (2000).
The economy is based on cattle raising (31,000 head), services, and subsistence agriculture, with the main crops being mangoes rice, beans, sugarcane, and corn. In 2005 there were 2558 rural producers but only 28 tractors. 7,600 persons were dependent on agriculture. As of 2005 there were 19 public and 6 private health clinics, with 7 carrying out diagnosis and complete therapy. There was one private hospital with 96 beds. Educational needs were met by 45 primary schools, 7 middle schools and 7 nursery schools. There were 1375 automobiles in 2006, giving a ratio of 26 inhabitants per automobile (there were 2851 motorcycles). There were 3 banks in 2007.[4]
Neighboring municipalities are: Virgem da Lapa, Coronel Murta, Itinga, Ponto dos Volantes, Padre Paraíso, Carai and Novo Cruzeiro. The distance to Belo Horizonte is 678 km. The distance to the nearest major population center, Teófilo Otoni is 210 km.[5] [6]
Social Indicators
Araçuaí is ranked low on the MHDI and was one of the poorest municipalities in the state and in the country in 2000.
- MHDI: .687 (2000)
- State ranking: 602 out of 853 municipalities
- National ranking: 3,208 out of 5,138 municipalities in 2000
- Life expectancy: 67
- Literacy rate: 76
- Combined primary, secondary and tertiary gross enrolment ratio: .760
- Per capita income (monthly): R$131.00 [7]
- Degree of urbanization: 57.29
- Percentage of urban residences connected to sewage system: 19.40
- Infant mortality rate: 16.95 [8]
The above figures can be compared with those of Poços de Caldas, which had an MHDI of .841, the highest in the state of Minas Gerais. The highest in the country was São Caetano do Sul in the state of São Paulo with an MHDI of .919. The lowest was Manari in the state of Pernambuco with an MHDI of .467 out of a total of 5504 municipalities in the country as of 2004. At last count Brazil had 5,561 municipalities so this might have changed at the time of this writing.[7]
References
- "IBGE - Cidades e Estados" [IBGE - Cities and States] (in Portuguese). Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics (IBGE). 2017. Retrieved 2019-07-11.
- IBGE 2020
- "IBGE - Brasil em Síntese". Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics (IBGE). Retrieved 2019-11-13.
- IBGE Archived June 11, 2008, at the Wayback Machine
- "Guia de Distancias entre cidades de Minas Gerais". Aondefica. Retrieved 2019-12-28.
- "Citybrazil". Archived from the original on 2008-05-01. Retrieved 2008-07-25.
- Frigoletto Archived 2011-07-06 at the Wayback Machine
- Indicadores de Saúde Archived July 6, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
