Aryepiglottic muscle
The aryepiglottic muscle or aryepiglotticus muscle is an intrinsic muscle of the larynx.[1]
| Aryepiglottic muscle | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Apex of arytenoid |
| Insertion | Lateral border of epiglottis |
| Artery | Laryngeal branch of superior thyroid artery |
| Nerve | Inferior laryngeal nerve (from the vagus nerve) |
| Actions | Closes the laryngeal inlet |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Pars aryepiglottica musculi arytaenoidei obliqui, musculus aryepiglotticus |
| TA98 | A06.2.08.011 |
| TA2 | 2204 |
| FMA | 46602 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
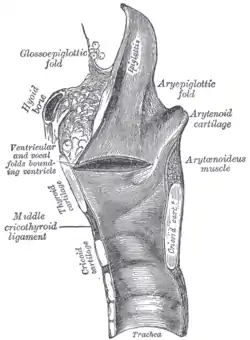
The muscle originates from the muscular process of arytenoid cartilage and inserts to the aryepiglottic fold and lateral border of the epiglottis. The aryepiglottic muscle is innervated by the inferior laryngeal nerve, a branch of the recurrent laryngeal nerve (itself a branch of the vagus nerve). The muscle adducts arytenoid cartilages and acts as a sphincter on the laryngeal inlet.[1][2]
Additional images
 Aryepiglottic muscle
Aryepiglottic muscle
External links
- lesson11 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (larynxmuscles)
References
- Allen, Evan; Murcek, Benjamin W. (2019), "Anatomy, Head and Neck, Larynx Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve", StatPearls, StatPearls Publishing, PMID 29261997, retrieved 2019-09-28
- Gray's anatomy : the anatomical basis of clinical practice. Standring, Susan (Forty-first ed.). [Philadelphia]. 2016. ISBN 9780702052309. OCLC 920806541.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) CS1 maint: others (link)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.