August 2007 lunar eclipse
A total lunar eclipse occurred on 28 August 2007, lasting just over 90 minutes. The Moon entered the Earth's penumbra at 7:53:40 UTC. The first partial phase began in earnest at 8:51:16 UTC when the Moon entered the Earth's umbra. It exited the penumbra at 13:20:57 UTC.
| Total Lunar Eclipse 28 August 2007 | |
|---|---|
 Viewed from Wollongong, Australia at 9:48 UTC, shortly before totality | |
 The moon's path through the Earth's southern shadow. | |
| Series (and member) | 128 (40 of 71) |
| Gamma | -0.2145 |
| Magnitude | -1.481 |
| Duration (hr:mn:sc) | |
| Totality | 1:30:01 |
| Partial | 3:32:12 |
| Penumbral | 5:27:17 |
| Contacts (UTC) | |
| P1 | 7:53:40 |
| U1 | 8:51:16 |
| U2 | 9:52:21 |
| Greatest | 10:37:21 |
| U3 | 11:22:22 |
| U4 | 12:23:28 |
| P4 | 13:20:57 |
 The Moon's hourly motion across the Earth's shadow in the constellation of Aquarius | |
It is a relatively rare central eclipse where the Moon passes in front of the center of the Earth's shadow. It was the last central lunar eclipse of Saros series 128 as well as the "longest and deepest lunar eclipse to be seen in 7 years". In the total lunar eclipse of 16 July 2000 the moon passed within two arc minutes of the center of the Earth's shadow. In comparison, this still very deep eclipse was off-center by over 12 minutes of arc.[1] The next total lunar eclipse of a longer duration was on 15 June 2011.
The lunar eclipse was the second one in 2007. The first one occurred on 3 March 2007.
Viewing

Viewing from Oceania is favoured for the eclipse, because at the moment of greatest eclipse (10:37:22 UTC), the Moon was at the zenith of French Polynesia. The Pacific regions of Canada and the continental United States (including all of Alaska) witnessed the whole event, along with most of eastern Australia, New Zealand and all the Pacific Island regions (except New Guinea), and the tip of the Chukchi Peninsula that includes the town of Uelen, Russia. The majority of the Americas observed an abbreviated eclipse, with moonset occurring at some time during the eclipse. Siberia, far eastern Russia, eastern South Asia, China, the rest of eastern and southeastern Asia, New Guinea, and the rest of Australia missed out on the beginning of the eclipse, because the eclipse occurred at or close to moonrise in those regions.[2]
Luzon (except Visayas and Mindanao) in the Philippines, particularly Metro Manila, missed the rare eclipse entirely, due to clouds in the area due to the rainy season, which saddened many eclipse watchers in the area, but the eclipse was sighted by other amateur astronomers in other parts of the country as the lunar eclipse seen in clear skies. The eclipse was also missed in New Guinea, especially Port Moresby because of clouds. Greenland, Europe (including western Russia), Africa, western Asia, western Central Asia, and western South Asia missed the eclipse completely.
 This simulated view of the Earth from the center of the Moon during the lunar eclipse shows where the eclipse is visible on Earth. |
Map

Relation to other lunar eclipses
Eclipses of 2007
- A total lunar eclipse on 3 March.
- A partial solar eclipse on 19 March.
- A total lunar eclipse on 28 August.
- A partial solar eclipse on 11 September.
This eclipse at the Moon's ascending node was the second of two lunar eclipses to occur in 2007. The first at the descending node was on 3 March 2007.
Lunar year series
| Lunar eclipse series sets from 2006–2009 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Descending node | Ascending node | |||||||
| Saros # and photo |
Date Viewing |
Type Chart |
Gamma | Saros # and photo |
Date Viewing |
Type Chart |
Gamma | |
113.jpg.webp) |
2006 Mar 14 |
penumbral |
1.0211 | 118 |
2006 Sep 7 |
partial |
−0.9262 | |
123 |
2007 Mar 03 |
total |
0.3175 | 128 |
2007 Aug 28 |
total |
−0.2146 | |
133 |
2008 Feb 21 |
total |
−0.3992 | 138 |
2008 Aug 16 |
partial |
0.5646 | |
143 |
2009 Feb 09 |
penumbral |
−1.0640 | 148 |
2009 Aug 06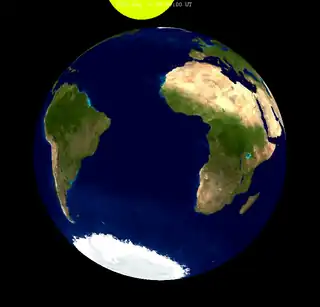 |
penumbral |
1.3572 | |
| Last set | 2005 Apr 24 | Last set | 2005 Oct 17 | |||||
| Next set | 2009 Dec 31 | Next set | 2009 Jul 07 | |||||
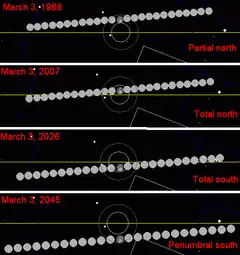
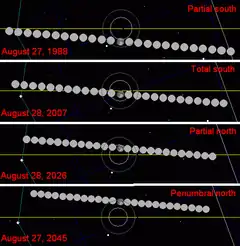
Metonic cycle (19 years)
The Metonic cycle repeats nearly exactly every 19 years and represents a Saros cycle plus one lunar year. Because it occurs on the same calendar date, the earth's shadow will be in nearly the same location relative to the background stars.
|
|
 |
 |
Saros series
Lunar saros series 128, repeating every 18 years and 11 days, has a total of 71 lunar eclipse events including 57 umbral eclipses (42 partial lunar eclipses and 15 total lunar eclipses). Solar Saros 135 interleaves with this lunar saros with an event occurring every 9 years 5 days alternating between each saros series.
| Greatest | First | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 The greatest eclipse of the series occurred on 1953 Jul 26, lasting 108 minutes.[3] |
Penumbral | Partial | Total | Central |
| 1304 Jun 18 | 1430 Sep 2 | 1845 May 21 | 1899 Jun 23 | |
| Last | ||||
| Central | Total | Partial | Penumbral | |
| 2007 Aug 28 | 2097 May 21 | 2440 May 17 | 2566 Aug 2 | |
| 1917 Jul 4 | 1935 Jul 16 | 1953 Jul 26 | |||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
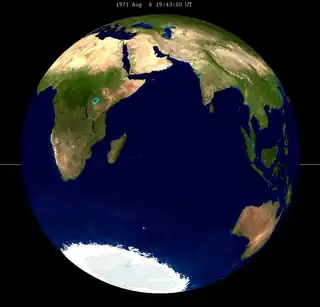
| 1971 Aug 6 | 1989 Aug 17 | 2007 Aug 28 | |||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| 2025 Sep 7 | 2043 Sep 19 | 2061 Sep 29 | |||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| 2079 Oct 10 | 2097 Oct 21 | ||||
 |
 |
 |
 | ||
Lunar Saros 128 contains 15 total lunar eclipses between 1845 and 2097 (in years 1845, 1863, 1881, 1899, 1917, 1935, 1953, 1971, 1989, 2007, 2025, 2043, 2061, 2079 and 2097). Solar Saros 135 interleaves with this lunar saros with an event occurring every 9 years 5 days alternating between each saros series.
Half-Saros cycle
A lunar eclipse will be preceded and followed by solar eclipses by 9 years and 5.5 days (a half saros).[4] This lunar eclipse is related to two annular solar eclipses of Solar Saros 135.
| 22 August 1998 | 1 September 2016 |
|---|---|
 |
 |
Photo gallery
 From the Oregon Coast. |
 From Swifts Creek, Australia. (3 minute intervals) |
 From Bakersfield, California. |
 From Nagayo, Nagasaki, 10:33 UTC.
From Nagayo, Nagasaki, 10:33 UTC. A wider angle shows stars around the moon.
A wider angle shows stars around the moon. A full sky view (moon on left) shows the Milky Way (across the center), which is usually invisible under a full moon.
A full sky view (moon on left) shows the Milky Way (across the center), which is usually invisible under a full moon. From Melbourne, Australia.
From Melbourne, Australia.
See also
- List of lunar eclipses and List of 21st-century lunar eclipses
- File:2007-08-28 Lunar Eclipse Sketch.gif Chart
Notes
- Visibility Map for Total Lunar Eclipse of 16 July 2000
- Visibility Map for Total Lunar Eclipse of 28 August 2007
- Listing of Eclipses of cycle 128
- Mathematical Astronomy Morsels, Jean Meeus, p.110, Chapter 18, The half-saros

_(cropped).jpg.webp)
