July 2019 lunar eclipse
A partial lunar eclipse occurred on the 16 and 17 July 2019. The Moon was covered 65.31% by the Earth's umbral shadow at maximum eclipse.
| Partial Lunar Eclipse July 16, 2019 | |
|---|---|
 Near greatest eclipse from Tilehurst, England, 21:30 UTC | |
 This chart shows the right-to-left hourly motion of the moon through the earth's shadow. | |
| Series (and member) | 139 (22 of 81) |
| Gamma | -0.643 |
| Magnitude | 0.6531 |
| Duration (hr:mn:sc) | |
| Partial | 2:57:56 |
| Penumbral | 5:33:43 |
| Contacts | |
| P1 | 18:43:53 UTC |
| U1 | 20:01:43 |
| Greatest | 21:30:44 |
| U4 | 22:59:39 |
| P4 | 0:17:36 |
This was the last umbral lunar eclipse until May 2021.
Visibility
It was visible over most of Asia, Australia, Africa, Europe, and South America.[1]
 |
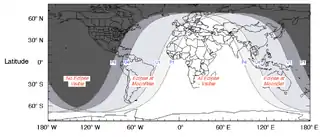 Visibility map |
Gallery
 Hefei, China, 19:56 UTC
Hefei, China, 19:56 UTC Mariupol, Ukraine, 20:25 UTC
Mariupol, Ukraine, 20:25 UTC Tashkent, Uzbekistan, 21:05 UTC
Tashkent, Uzbekistan, 21:05 UTC Moscow, Russia, 21:11 UTC
Moscow, Russia, 21:11 UTC Novate Milanese, Italy, 21:17 UTC
Novate Milanese, Italy, 21:17 UTC Bandung, Indonesia, 21:20 UTC
Bandung, Indonesia, 21:20 UTC.jpg.webp) Farasan Island, Saudi Arabia, 21:25 UTC
Farasan Island, Saudi Arabia, 21:25 UTC Paris, France, 21:27 UTC
Paris, France, 21:27 UTC Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 21:30 UTC
Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 21:30 UTC Munich, Germany, 21:36 UTC
Munich, Germany, 21:36 UTC Prague, Czech Republic, 21:39 UTC
Prague, Czech Republic, 21:39 UTC.jpg.webp) Manuel B. Gonnet, Argentina, 21:43 UTC
Manuel B. Gonnet, Argentina, 21:43 UTC.jpg.webp) London, England, 21:47 UTC
London, England, 21:47 UTC Sayada, Tunisia, 21:55 UTC
Sayada, Tunisia, 21:55 UTC Virovitica, Croatia, 22:12 UTC
Virovitica, Croatia, 22:12 UTC Banjarmasin, Indonesia, Near Moonset, 22:17 UTC
Banjarmasin, Indonesia, Near Moonset, 22:17 UTC.jpg.webp) Krško, Slovenia, 22:19 UTC
Krško, Slovenia, 22:19 UTC Szanda, Hungary, 22:23 UTC
Szanda, Hungary, 22:23 UTC Wrocław, Poland, 22:27 UTC
Wrocław, Poland, 22:27 UTC_1.jpg.webp) Logroño, Spain, 22:32 UTC
Logroño, Spain, 22:32 UTC
Related eclipses
Tzolkinex
- Preceded: Lunar eclipse of 4 June 2012
- Followed: Lunar eclipse of 28 August 2026
Tritos
- Preceded: Lunar eclipse of 16 August 2008
- Followed: Lunar eclipse of 15 June 2030
Inex
- Preceded: Lunar eclipse of 6 August 1990
- Followed: Lunar eclipse of 26 June 2048
Triad
- Preceded: Lunar eclipse of 14 September 1932
- Followed: Lunar eclipse of 17 May 2106
Eclipses of 2019
- A partial solar eclipse on 6 January.
- A total lunar eclipse on 21 January.
- A total solar eclipse on 2 July.
- A partial lunar eclipse on 16 July.
- An annular solar eclipse on 26 December.
Lunar year series
| Lunar eclipse series sets from 2016–2020 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Descending node | Ascending node | |||||||
| Saros | Date | Type Viewing |
Gamma | Saros | Date Viewing |
Type Chart |
Gamma | |
| 109 | 2016 Aug 18 |
Penumbral |
1.56406 | 114 |
2017 Feb 11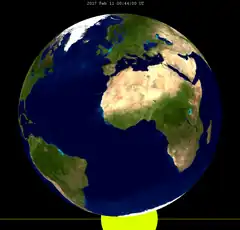 |
Penumbral |
−1.02548 | |
119 |
2017 Aug 07 |
Partial |
0.86690 | 124 |
2018 Jan 31 |
Total |
−0.30143 | |
129_(43696968392)_(cropped).jpg.webp) |
2018 Jul 27 |
Total |
0.11681 | 134_(cropped).jpg.webp) |
2019 Jan 21 |
Total |
0.36842 | |
139 |
2019 Jul 16 |
Partial |
−0.64300 | 144 |
2020 Jan 10 |
Penumbral |
1.07270 | |
| 149 | 2020 Jul 05 |
Penumbral |
−1.36387 | |||||
| Last set | 2016 Sep 16 | Last set | 2016 Mar 23 | |||||
| Next set | 2020 Jun 05 | Next set | 2020 Nov 30 | |||||
Saros cycle
Lunar Saros series 139, repeating every 18 years and 11 days, has a total of 79 lunar eclipse events including 42 umbral lunar eclipses (15 partial lunar eclipses and 27 total lunar eclipses)..
| Greatest | First | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
The greatest eclipse of the series will occur on 2199 Nov 02, lasting 102 minutes.[2] |
Penumbral | Partial | Total | Central |
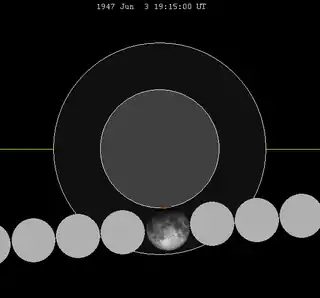
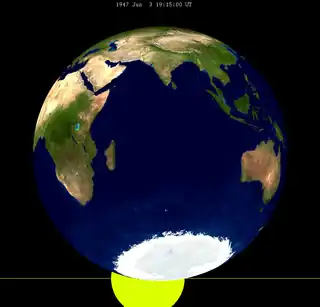
| 1658 Dec 09 | 1947 Jun 03 | 2073 Aug 17 | 2109 Sep 09 | |
| Last | ||||
| Central | Total | Partial | Penumbral | |
| 2488 Apr 26 | 2542 May 30 | 2686 Aug 25 | 3065 Apr 13 | |
| 1911 May 13 | 1929 May 23 | 1947 Jun 03 | |||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| 1965 Jun 14 | 1983 Jun 25 | 2001 Jul 05 | |||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| 2019 Jul 16 | 2037 Jul 27 | 2055 Aug 07 | |||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| 2073 Aug 17 | 2091 Aug 29 | ||||
Half-Saros cycle
A lunar eclipse will be preceded and followed by solar eclipses by 9 years and 5.5 days (a half saros).[3] This lunar eclipse is related to two total solar eclipses of Solar Saros 146.
| 11 July 2010 | 22 July 2028 |
|---|---|
 |
 |
References
- "Lunar eclipse july 2019 timing of all countries". bindassnews.com. Archived from the original on 7 May 2019. Retrieved 7 May 2019.
- Listing of Eclipses of cycle 139
- Mathematical Astronomy Morsels, Jean Meeus, p.110, Chapter 18, The half-saros
External links
- Partial Lunar Eclipse 2019
- Saros cycle 139
- Hermit eclipse: 2019-07-16
- 2019 Jul 16 chart: Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
_(cropped).jpg.webp)