Bennington Battlefield State Historic Site
The Bennington Battlefield is the Rensselaer County, New York, location where the Battle of Bennington occurred on the 16th of August 1777. It is located on New York State Route 67 in Walloomsac, New York, a historic route between Bennington, Vermont and the Hudson River. Here, New Hampshire, Vermont and Massachusetts militia under General John Stark rebuffed a British attempt led by Colonel Friedrich Baum to capture American stores. It was declared a National Historic Landmark in 1961.[1][3] A portion of the battlefield is preserved in the Bennington Battlefield State Historic Site. The American Battlefield Trust and its partners have acquired and preserved more than 23 acres of the battlefield not already part of the state historic site.[4]
Bennington Battlefield | |
 The Bennington Battlefield State Historic Site in Walloomsac, New York, where the Battle of Bennington occurred on 16 August 1777. | |
  | |
| Location | NY 67, Walloomsac, NY |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 42°56′19″N 73°18′16″W |
| Area | 1,250 acres (510 ha)[1] |
| NRHP reference No. | 66000564 |
| Significant dates | |
| Added to NRHP | October 15, 1966[2] |
| Designated NHL | January 20, 1961[3] |
Description
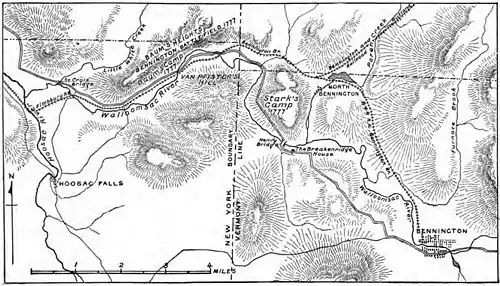
The main portion of the Bennington Battlefield is located about 2.5 miles (4.0 km) west of the New York-Vermont border, on the north side of the Walloomsac River. The river valley is flanked by a series of hills with steeply ridged sides. The state historic site encompasses the top of one of these hills as well as some of its surrounding terrain; it is at this site that some of the most concentrated fighting took place. The modern Route 67 no longer exactly follows the alignment of the road in 1777, but a bridge crossing on a nearby secondary street is believed to be located near a key crossing site at the time. Most of the hillside terrain is now wooded, while portions of the river floodplain are in agricultural use (as they were in 1777), and the hilltop of the state historic site has been cleared. A 19th-century railroad right-of-way, also following the river, is a significant intrusion on the battlefield landscape.[1]
Prior to the Battle of Bennington, British troops (mainly Hessians) under the command of Colonel Baum occupied this particular hilltop, with additional detachments guarding the bridge, the ridge on the south side of the river, and a stream crossing north of the river and east of the hill. The American troops led by General Stark were able to reconnoiter these positions and sneak up on them, executing a surprise attack. Baum's forces were eventually routed, and he was slain. Hessian reinforcements arrived near the end of the first phase of the battle, and were eventually also put to chase, with the battlefield extending as far as a mile further down the river valley. The battle was a serious blow to the campaign of British General John Burgoyne depriving him of a needed supplies and a significant portion of his army as he made his push toward Albany, New York. and set the stage for his subsequent surrender at Saratoga.[1]
 An American flag and historical marker at the entrance to the historic site
An American flag and historical marker at the entrance to the historic site (Top down) American, New York State, Prisoner of War and New York State Office of Parks Recreation and Historic Preservation flags fly atop the hill at the battlefield
(Top down) American, New York State, Prisoner of War and New York State Office of Parks Recreation and Historic Preservation flags fly atop the hill at the battlefield A topographical map depicting the area at the time of the battle
A topographical map depicting the area at the time of the battle A plaque erected by the state of New Hampshire commemorating the achievements of John Stark and the New Hampshire militia
A plaque erected by the state of New Hampshire commemorating the achievements of John Stark and the New Hampshire militia A plaque erected by the Commonwealth of Massachusetts commemorating the achievements of the volunteer militia
A plaque erected by the Commonwealth of Massachusetts commemorating the achievements of the volunteer militia A plaque erected by the state of Vermont commemorating the achievements of the Vermont militia and their comrades
A plaque erected by the state of Vermont commemorating the achievements of the Vermont militia and their comrades The site grounds
The site grounds A historical plaque erected at the entrance to the site describing the battle
A historical plaque erected at the entrance to the site describing the battle
See also
- List of New York State Historic Sites
- List of National Historic Landmarks in New York
- Bennington Monument, which also commemorates the battle
References
- Richard Greenwood (November 24, 1975). "National Register of Historic Places Inventory-Nomination: Bennington Battlefield" (pdf). National Park Service. and Accompanying 10 photos from 1967 and 1975 (1.28 MB)
- "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places. National Park Service. January 23, 2007.
- "Bennington Battlefield". National Historic Landmark summary listing. National Park Service. September 8, 2007. Archived from the original on August 21, 2009.
- "Bennington Battlefield". American Battlefield Trust. Retrieved June 19, 2023.