Buprofezin
Buprofezin is an insecticide used for control of insect pests such as mealybugs, leafhoppers and whitefly on vegetable crops. It is a growth regulator, acting as an inhibitor of chitin synthesis.[2] It is banned in some countries due to its negative environmental impacts, being especially toxic to aquatic organisms as well as non-target insects, though is of low toxicity to humans and other mammals.[3]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
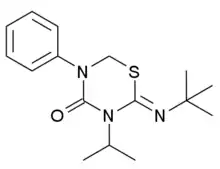
| IUPAC name
(2Z)-3-Isopropyl-2-[(2-methyl-2-propanyl)imino]-5-phenyl-1,3,5-thiadiazinan-4-one | |
| Other names
Buprofezin | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 8625926 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.125.182 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H23N3OS | |
| Molar mass | 305.44 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling:[1] | |
  | |
| Warning | |
| H373, H410 | |
| P260, P273, P314, P391, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- "Buprofezin". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 26 December 2021.
- Liu TX, Chen TY. Effects of the chitin synthesis inhibitor buprofezin on survival and development of immatures of Chrysoperla rufilabris (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae). J Econ Entomol. 2000 Apr;93(2):234-9. PMID 10826167
- Qureshi IZ, Bibi A, Shahid S, Ghazanfar M. Exposure to sub-acute doses of fipronil and buprofezin in combination or alone induces biochemical, hematological, histopathological and genotoxic damage in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Aquat Toxicol. 2016 Oct;179:103-14. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2016.08.012. PMID 27595653
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.