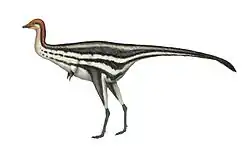
Camptodontornis
Camptodontornis is an extinct genus of enantiornithine bird which existed in what is now Chaoyang in Liaoning Province, China during the early Cretaceous period (Aptian age). It is known from a well-preserved skeleton including a skull found in the Jiufotang Formation of Liaoning Province. Its original generic name was "Camptodontus" (meaning "bent tooth"); it was named by Li Li, En-pu Gong, Li-dong Zhang, Ya-jun Yang and Lian-hai Hou in 2010. However, the name had previously been used for a genus of beetle (Dejean, 1826).[1] The type species is "Camptodontus" yangi.[2] Demirjian (2019) coined a replacement generic name Camptodontornis.[3] The status of C. yangi as a distinct species is disputed, with Wang et al. (2015) considering it to be a probable synonym of Longipteryx chaoyangensis.[4]
| Camptodontornis Temporal range: Early Cretaceous, | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Dinosauria |
| Clade: | Saurischia |
| Clade: | Theropoda |
| Clade: | Avialae |
| Clade: | †Enantiornithes |
| Family: | †Longipterygidae |
| Genus: | †Camptodontornis Demirjian, 2019 |
| Species: | †C. yangi |
| Binomial name | |
| †Camptodontornis yangi (Li et al., 2010) | |
References
- Dejean, (1826). Spec. gén. Coléopt., 2, 476.
- Li Li; En-pu Gong; Li-dong Zhang; Ya-jun Yang & Lian-hai Hou (2010). "A new enantiornithine bird (aves) from the Early Cretaceous of Liaoning, China". Acta Palaeontologica Sinica. 49 (4): 524–531. CNKI:SUN:GSWX.0.2010-04-012.
- Vahe Demirjian (2019). "Camptodontornis gen. nov., a replacement name for the bird genus Camptodontus Li, Gong, Zhang, Yang, and Hou, 2010, a junior homonym of Camptodontus Dejean, 1826". Zootaxa. 4612 (3): 440. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.4612.3.10. PMID 31717059. S2CID 190899508.
- Xuri Wang; Caizhi Shen; Sizhao Liu; Chunling Gao; Xiaodong Cheng; Fengjiao Zhang (2015). "New material of Longipteryx (Aves: Enantiornithes) from the Lower Cretaceous Yixian Formation of China with the first recognized avian tooth crenulations". Zootaxa. 3941 (4): 565–578. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.3941.4.5. PMID 25947529.







.png.webp)


.jpg.webp)




