Poecilostomatoida
Poecilostomatoida are an suborder of copepods. Although it was previously considered a separate order,[1][2] recent research showed it to be nested within the Cyclopoida[3]
| Poecilostomatoida | |
|---|---|
 | |
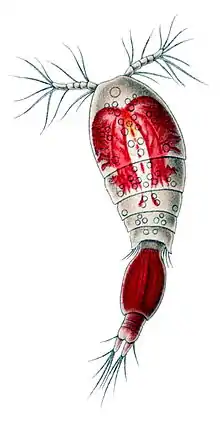
| Sapphirina darwinii with egg cases | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Copepoda |
| Order: | Cyclopoida |
| Suborder: | Poecilostomatoida Thorell, 1859 |
| Families | |
|
See text | |
Description
The classification of these copepods has been established on the basis of the structure of the mouth. In poecilostomatoids the mouth is represented by a transverse slit, partially covered by the overhanging labrum which resembles an upper lip. Although there is variability in the form of the mandible among poecilostomatoids, it can be generalized as being falcate (sickle-shaped).[1][2]
The antennules are frequently reduced in size and the antennae modified to terminate in small hooks or claws that are used in attachment to host organisms.[1][2]
Life cycle
As with many crustaceans, larval development is metamorphic with immature forms differing greatly from those of adults. Embryos are carried in paired or single sacs attached to first abdominal somite (as seen in the illustration of the female Sapphirina darwinii above right).[4][5]
Ecology
Most poecilostomatoid copepods are ectoparasites of saltwater fish or invertebrates (including among the latter mollusks and echinoderms). They usually attach to the external surface of the host, in the throat-mouth cavity, or the gills.[1][2][6][7] One family of poecilostomatoid copepods, however, have evolved an endoparasitic mode of life and live deep within their hosts' bodies rather than merely attaching themselves to exterior and semi-exterior surface tissue.[1][2]
In addition to typical marine environments, poecilostomatoid copepods may be found in such very particular habitats as anchialine caves and deep sea vents (both hydrothermal vents and cold seeps). Here, many primitive associated copepods belonging to the Poecilostomatoida and Siphonostomatoida and have been found.[7] Representatives of one Poecilostomatoida family have successfully made the transition to freshwater habitats and host animals therein.[1][2]
List of families
There are over sixty families currently recognized within the group:[8]
- Abrsiidae
- Anchimolgidae
- Anomoclausiidae
- Antheacheridae
- Anthessiidae
- Bomolochidae
- Bradophilidae
- Catiniidae
- Chondracanthidae
- Clausidiidae
- Clausiidae
- Corallovexiidae
- Corycaeidae
- Echiurophilidae
- Entobiidae
- Erebonasteridae
- Ergasilidae
- Eunicicolidae
- Gadilicolidae
- Gastrodelphyidae
- Herpyllobiidae
- Intramolgidae
- Iveidae
- Jasmineiricolidae
- Kelleriidae
- Lamippidae
- Leaniricolidae
- Lichomolgidae
- Lubbockiidae
- Macrochironidae
- Makrostrotidae
- Mesoglicolidae
- Myicolidae
- Mytilicolidae
- Nereicolidae
- Octopicolidae
- Oncaeidae
- Paralubbockiidae
- Philichthyidae
- Philoblennidae
- Phyllodicolidae
- Pionodesmotidae
- Polyankyliidae
- Pseudanthessiidae
- Rhynchomolgidae
- Sabelliphilidae
- Saccopsidae
- Sapphirinidae
- Serpulidicolidae
- Shiinoidae
- Spiophanicolidae
- Splanchnotrophidae
- Strepidae
- Synapticolidae
- Synaptiphilidae
- Taeniacanthidae
- Telsidae
- Thamnomolgidae
- Tuccidae
- Umazurcolidae
- Urocopiidae
- Vahiniidae
- Ventriculinidae
- Xarifiidae
- Xenocoelomatidae
References
- A. G. Humes & G. A. Boxshall (1996). "A revision of the lichomolgoid complex (Copepoda: Poecilostomatoida), with the recognition of six new families". Journal of Natural History. 30 (2): 175–227. doi:10.1080/00222939600771131.
- Joel W. Martin & George E. Davis (2001). An Updated Classification of the Recent Crustacea (PDF). Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County. p. 132.
- Khodami, S; McArthur, JV; Blanco-Bercial, L; Martinez Arbizu (2017). "Molecular Phylogeny and Revision of Copepod Orders (Crustacea: Copepoda)". Scientific Reports. 7 (1): 9164. Bibcode:2017NatSR...7.9164K. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-06656-4. PMC 5567239. PMID 28831035.
- J. K. Lowry (October 2, 1999). "Crustacea, the Higher Taxa: Description, Identification, and Information Retrieval". Archived from the original on March 20, 2019. Retrieved January 22, 2007.
- "Introduction to Copepods" (PDF). University of Connecticut. Archived from the original (PDF) on May 13, 2008.
- Masahiro Dojiri & Roger F. Cressey (1987). "Revision of the Taeniacanthidae (Copepoda: Poecilostomatoida) parasitic on fishes and sea urchins". Smithsonian Contributions to Zoology. 447 (447): 1–250. doi:10.5479/si.00810282.447.i. hdl:10088/5504.
- "Introduction to Copepods" (PDF). University of Connecticut. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2008-05-13. Retrieved 2007-01-22.
- Geoff Boxshall, & T. Chad Walter (2019). T. Chad Walter & Geoff Boxshall (ed.). "Poecilostomatoida". World Copepoda database. World Register of Marine Species. Retrieved May 19, 2019.
External links
 Data related to Poecilostomatoida at Wikispecies
Data related to Poecilostomatoida at Wikispecies Media related to Poecilostomatoida at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Poecilostomatoida at Wikimedia Commons
