Cholangiography
Cholangiography is the imaging of the bile duct (also known as the biliary tree) by x-rays and an injection of contrast medium.[1]
| Cholangiography | |
|---|---|
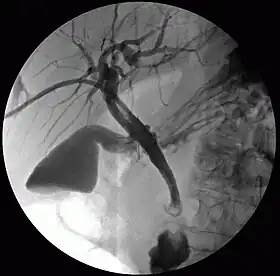 Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography | |
| ICD-9-CM | 87.5 |
| MeSH | D002758 |
| OPS-301 code | 3-13c |
Types
There are at least four types of cholangiography:
- Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography (PTC): Examination of liver and bile ducts by x-rays. This is accomplished by the insertion of a thin needle into the liver carrying a contrast medium to help to see blockage in liver and bile ducts.
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP). Although this is a form of imaging, it is both diagnostic and therapeutic, and is often classified with surgeries rather than with imaging.
- Primary cholangiography (or perioperative): Done in the operation room during a biliary drainage intervention.
- Secondary cholangiography: Done after a biliary drainage intervention.
In both cases fluorescent fluids are used to create contrasts that make the diagnosis possible. Cholangiography has largely replaced the previously used method of intravenous cholangiography (IVC).
- Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) is another cholangiography method.
References
- "Cholangiography | Gallbladder cancer | Cancer Research UK". www.cancerresearchuk.org. Retrieved 2021-01-04.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.