Chronica Hungarorum
Chronica Hungarorum (Latin for "Chronicle of the Hungarians") (Hungarian: A magyarok krónikája), also known as the Thuróczy Chronicle, is the title of a 15th-century Latin-language Hungarian chronicle written by Johannes de Thurocz by compiling several earlier works in 1488. It served as the primary source for the history of medieval Hungary for centuries.[1]
 The first page of the Augsburg edition of the Chronica Hungarorum by Johannes Thuróczy from 1488, better known as the "Thuróczy Chronicle". For the first time in history, gold paint was used for this print. This edition is stored in the National Széchény Library in Budapest in Hungary. | |
| Author | Johannes Thuróczy |
|---|---|
| Original title | Chronica Hungarorum |
| Country | Kingdom of Hungary |
| Language | Latin |
| Subjects | History of the Hungarians |
| Genre | Chronicle |
| Published | 1488 |
| Media type | |
History
The historical knowledge of future generations of people was based on the Thuróczy Chronicle, because it was the most complete medieval Hungarian history at that time, and the chronicle itself was the result of historiographical construction by the predecessor Hungarian chronicles over the previous centuries in since the time of the Ancient Gesta. According to Thuróczy, he worked from contemporary works of the time of King Charles I (1301–1342) and King Louis I (1342–1382), which also based on older chronicles. The basic premise of the Hungarian medieval chronicle tradition that the Huns, i.e. the Hungarians coming out twice from Scythia, the guiding principle was the Hun-Hungarian continuity.[2]
No one doubts that the mother of the Huns, namely the Hungarians, was Scythia: Even at the beginning of their exodus from Scythia, the famous fighting virtue glowed in them, and now, in our day, their swords are flashing over the head of the enemy.
King Matthias of Hungary was happy to be described as "the second Attila".[4] In the prologue of his chronicle, Thuróczy set the goal of glorifying Attila, which was undeservedly neglected, moreover, he introduced the famous "Scourge of God" characterization to the later Hungarian writers, because the earlier chronicles remained hidden for a long time. Thuróczy worked hard to endear Attila, the Hun king with an effort far surpassing his predecessor chroniclers. He made Attila a model for his victorious ruler, King Matthias of Hungary (1458–1490) who had Attila's abilities, with this he almost brought "the hammer of the world" to life.[2]
The chronicle describes the history of Hungarians from the earliest times to 1487. The chronicle contains hand-colored woodcuts depicting 41 Hungarian kings and leaders. The Augsburg edition of the Chronica Hungarorum from 1488 is the first known print made with gold paint.
The images are listed together with the title of the chapter in the same order as their appearance in the chronicle.
| Illustration | Description |
|---|---|
.jpg.webp) The Great Coats of Arms of King Matthias Corvinus of Hungary |
The Great Coats of Arms of King Matthias Corvinus of Hungary
|
 Saint Ladislaus Chases the Cuman Warrior Who Kidnapped a Girl |
Saint Ladislaus Chases the Cuman Warrior Who Kidnapped a Girl
|
The Prologue of Master Johannes Thuróczy to the First Book of the Chronicle of the Hungarians  Page With Golden Frame |
Preface
|
The Arrival of the Huns Into Pannonia and the Battle of Tárnok Valley  Battle of the Tárnok Valley |
Battle of Tárnok Valley
|
The Battle Near a Place Named Zeiselmauer  Battle of Zeiselmauer |
Battle of Zeiselmauer
|
Election of King Attila, His Morals and Weapons He Used Against the Enemy  King Attila |
King Attila
|
The Famous and Great Battle of King Attila Which Was Fought on the Catalaunum Plain  Battle of the Catalaunian Plains |
Battle of the Catalaunian Plains
|
About the First Captain, the White Horse, the Golden Saddle and the Golden Brake  Árpád, the First Captain |
Árpád, the First Captain
|
About the First Captain, the White Horse, the Golden Saddle and the Golden Brake  The Hungarians defeat Svatopluk |
The Hungarians Defeat Svatopluk
|
The Second Captain  Szabolcs, the Second Captain |
Szabolcs, the Second Captain
|
The Third Captain  Gyula, the Third Captain |
Gyula, the Third Captain
|
The Fourth Captain  Kund, the Fourth Captain |
Kund, the Fourth Captain
|
The Fifth Captain  Lehel, the Fifth Captain |
Lehel, the Fifth Captain
|
The Sixth Captain  Vérbulcsú, the Sixth Captain |
Vérbulcsú, the Sixth Captain
|
The Seventh Captain  Örs, the Seventh Captain |
Örs, the Seventh Captain
|
The Hungarians Are Destroying Bulgaria  Hungarian Campaign Against Bulgaria |
Hungarian Campaign Against Bulgaria
|
The Birth and Reign of Saint Stephen, the First King of the Hungarians  King Saint Stephen and Prince Saint Emeric |
King Saint Stephen and Prince Saint Emeric
|
Battle of King Saint Stephen Against Koppány, Duke of Somogy  Battle of King Saint Stephen Against Koppány |
Battle of King Saint Stephen Against Koppány
|
The Death of King Saint Stephen and the Election of King Peter  King Peter |
King Peter
|
Expulsion of Peter and Election of Aba as King  King Samuel Aba |
King Samuel Aba
|
The Coronation of King Andrew Who Was Called Endre the First  King Andrew I |
King Andrew I
|
The Coronation and Engagement of King Solomon  King Solomon |
King Solomon
|
The Coronation, Life and Reign of King Béla the First  King Béla I |
King Béla I
|
The King’s Fraud, the Two Campaigns of the Princes and Their Victory  The Battle of King Solomon and Prince Géza Against the Greeks |
The Battle of King Solomon and Prince Géza Against the Greeks
|
How Géza the First Was Crowned As King After the Defeat and Running Away of King Solomon  King Géza I |
King Géza I
|
The Coronation and Campaigns of Saint Ladislaus the First, Brother of Géza and Son of King Béla the First .jpg.webp) King Saint Ladislaus |
King Saint Ladislaus
|
The Coronation of Coloman, Son of King Géza the First, Grandson of King Béla the First .jpg.webp) King Coloman |
King Coloman
|
After the Death of King Coloman, His Son, Stephen the Second Was Crowned As King .jpg.webp) King Stephen II |
King Stephen II
|
The Reign of Béla the Second the Blind, He Is the Son of Prince Álmos, Grandson of Lampert, Great-Grandson of King Béla the First _B%C3%A9la_kir%C3%A1ly.jpg.webp) King Béla the Blind |
King Béla the Blind
|
The Coronation and the Deeds of King Géza the Second, the First-Born Son of King Béla the Blind  King Géza II |
King Géza II
|
The Coronation and the Deeds of King Géza the Second, the First-Born Son of King Béla the Blind  The Battle of the Fischa |
The Battle of the Fischa
|
The Coronation of King Stephen the Third, Who Was the Son of Géza the Second and the Grandson of King Béla The Blind. Prince Ladislaus, the Second Son of King Béla the Blind Usurs the Crown  King Stephen III |
King Stephen III
|
The Coronation of King Béla the Third, Who Was the Brother of Stephen the Third and the Son of Géza the Second  King Béla III |
King Béla III
|
The Coronation of King Emeric, Who Was the Son of King Béla the Third  King Emeric |
King Emeric
|
The Coronation of King Ladislaus the Third, Who Was the Son of King Emeric  King Ladislaus III |
King Ladislaus III
|
The Coronation of King Andrew the Second, Father of Saint Elizabeth, He Was the Son of King Béla the Third and Was Also Called Andrew of Jerusalem  King Andrew II |
King Andrew II
|
The Coronation of King Béla the Fourth, He Was the Son of King Andrew the Second. Also the First Arrival of the Tatars and the Terrible Destruction of Hungary .jpg.webp) King Béla IV |
King Béla IV
|
The War of King Béla With Ottokar, King of Bohemia  The Battle of Kressenbrunn |
The Battle of Kressenbrunn
|
The Coronation of King Stephen the Fifth, Son of King Béla the Fourth  King Stephen V |
King Stephen V
|
The Coronation of King Ladislaus the Fourth, Son of King Stephen the Fifth, Who Is Called Ladislaus the Cuman _L%C3%A1szl%C3%B3_kir%C3%A1ly.jpg.webp) King Ladislaus the Cuman |
King Ladislaus the Cuman
|
The Coronation of King Andrew the Third, the Grandson of King Andrew the Second, He Was Also Called Andrew the Venetian  King Andrew III |
King Andrew III
|
Ladislaus, that is King Wenceslaus Leaves Hungary and Returns to Bohemia  King Wenceslaus |
King Wenceslaus
|
Bringing Otto, Prince of Bavaria to Hungary, His Coronation, Captivity and Expulsion, All This Is the Work of Some Barons Against Charles the Child  King Otto |
King Otto
|
The Arrival of Friar Cardinal Gentilis to Hungary and the Crowning of Charles as King .jpg.webp) King Charles I |
King Charles I
|
The Unfortunate Campaign of King Charles Against Voivode Basarab of Wallachia  The Battle of Posada |
The Battle of Posada
|
The Coronation, Life and Campaigns of King Louis 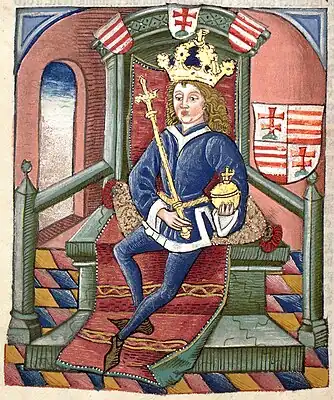 King Louis I |
King Louis I
|
The Campaign Against the Croatians  The Campaign of King Louis I Against the Croatians |
The Campaign of King Louis I Against the Croatians |
The Battle of Voivode Stephen Against the Army of Louis, Husband of Joanna Around Naples  The Battle of Stephen Lackfi Against Louis of Taranto Around Naples |
The Battle of Stephen Lackfi Against Louis of Taranto Around Naples
|
The Coronation of Queen Mary and This Following Hate  Queen Mary |
Queen Mary
|
The Coronation of King Charles .jpg.webp) King Charles II |
King Charles II
|
The Coronation of King Sigismund .jpg.webp) King Sigismund |
King Sigismund
|
Punishment of Ban John Horvati  Campaign of King Sigismund Against the Rebel Lords |
Campaign of King Sigismund Against the Rebel Lords
|
King Sigismund’s Wars Against the Hussites and the Burning of John Hus  The Wars of King Sigismund Against the Hussites |
The Wars of King Sigismund Against the Hussites
|
The Campaign of the Hungarians in the Region of Bosnia  The Campaign of Hungarians Against Bosnia |
The Campaign of Hungarians Against Bosnia
|
The Coronation of King Albert and the Plundering in the City of Buda .jpg.webp) King Albert |
King Albert
|
The Birth and Crowning of Ladislaus the Child, and Taking of the Crown  King Ladislaus V |
King Ladislaus V
|
The Coronation of King Vladislaus, and the Internal Strife That Followed  King Vladislaus I |
King Vladislaus I
|
The Battle of Lord Voivode John Around Belgrade  The Battle of John Hunyadi Around Belgrade |
The Battle of John Hunyadi Around Belgrade
|
The Transylvanian Campaign and Battle of Lord Voivode John  The Battle of Szeben |
The Battle of Szeben
|
The Battle of Lord Voivode John Which He Fought at the Iron Gate  The Battle of John Hunyadi at the Iron Gate |
The Battle of John Hunyadi at the Iron Gate
|
Lord Voivode John Avenges the Grief on the Turks, Six Lucky Battles  The Long Campaign of John Hunyadi |
The Long Campaign of John Hunyadi
|
The Campaign and Destruction of King Vladislaus in the Area of Rumelia, Around the City of Varna, Close to the Sea  The Battle of Varna |
The Battle of Varna
|
Election of Lord Voivode John as Governor and His Revenge Against Voivode Dracul  John Hunyadi |
John Hunyadi
|
The Battle of Lord Governor at the Blackbird's Field  The Battle of Kosovo |
The Battle of Kosovo
|
The Emperor of the Turks Is Sieging Nándorfehérvár  The Siege of Belgrade |
The Siege of Belgrade
|
The Election of Lord Count Matthias as King .jpg.webp) King Matthias Corvinus |
King Matthias Corvinus
|
Appendix at the end of the chronicle from Master Roger: A mournful song about the destruction of the Tatars in Hungary.
| Illustration | Description |
|---|---|
The Arrival of Tatars in Hungary During the Time of King Béla the Fourth  First Mongol invasion of Hungary |
First Mongol Invasion of Hungary
|
See also
References
- "Johannes Thuróczy: Chronica Hungarorum". Bibliotheca Corvina Virtualis – National Széchényi Library, Budapest, Hungary.
- Dr. Szabados, György (1998). "A krónikáktól a Gestáig – Az előidő-szemlélet hangsúlyváltásai a 15–18. században" [From the chronicles to the Gesta - Shifts in emphasis of the pre-time perspective in the 15th–18th centuries]. Irodalomtörténeti Közlemények, 102 (5-6) (PDF) (in Hungarian). MTA Irodalomtudományi Intézet (Institute for Literary Studies of Hungarian Academy of Sciences). pp. 615–641. ISSN 0021-1486.
- Johannes Thuróczy: Chronica Hungarorum http://thuroczykronika.atw.hu/pdf/Thuroczy.pdf
- Malcolm, Noel (2019). Useful Enemies: Islam and The Ottoman Empire in Western Political Thought, 1450-1750. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0198830139.
In Hungary, King Matthias Corvinus (r.1458–90) was happy to be described as 'the second Attila', and the tradition of identifying the Hungarians with 'Scythian' Huns, already present in the writings of earlier Hungarian chroniclers but greatly strengthened in his reign, would continue for hundreds of years.
Further reading
- Dr. Szabados, György (1998). "A krónikáktól a Gestáig – Az előidő-szemlélet hangsúlyváltásai a 15–18. században" [From the chronicles to the Gesta - Shifts in emphasis of the pre-time perspective in the 15th–18th centuries]. Irodalomtörténeti Közlemények, 102 (5-6) (PDF) (in Hungarian). MTA Irodalomtudományi Intézet (Institute for Literary Studies of Hungarian Academy of Sciences). pp. 615–641. ISSN 0021-1486.
External links
- Thuróczy, Johannes (1488). Chronica Hungarorum (PDF) (in Latin). Augsburg.
- "Johannes Thuróczy: Chronica Hungarorum". Bibliotheca Corvina Virtualis – National Széchényi Library, Budapest, Hungary. Augsburg: Erhard Ratdolt, at the expense of Theobald Feger (Buda). 1488.
Miklós Jankovich purchased it on March 24, 1823. It made its way to the Hungarian national library with the Jankovich collection in the 1830s.
- "Johannes Thuróczy: Chronica Hungarorum". Bibliotheca Corvina Virtualis – National Széchényi Library, Budapest, Hungary. Augsburg: Erhard Ratdolt, at the expense of Theobald Feger (Buda). 1488.
Joseph, Palatine of Hungary purchased it at an auction in Vienna in February 1845, and then he donated it to National Széchényi Library on March 14, 1845.
- Thuróczy, Johannes (1490). Chronica Hungarorum (in German). Bavaria.
- Thuróczy, János (1918). A magyarok krónikája [Chronicle of the Hungarians] (in Hungarian). Translated by Horváth, János. Magyar Helikon.
- Thuróczy, János (1957). Magyar krónika (Thuróczy krónika 4. és 5. könyve, 1382–1487-ig tartó időszak) [Hungarians Chronicle (Book 4 and 5 from the Thuróczy Chronicle, Period of 1382–1487)] (PDF) (in Hungarian). Translated by Geréb, László. Magyar Helikon.





.jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp)