Climate of Finland
The climate of Finland is influenced most by its latitude: Finland is located between 60 and 70 N. Because of Finland's northern location, winter is the longest season. Only on the south coast and in the southwest is summer as long as winter. On average, winter lasts from early January to late February in the outermost islands in the archipelago and the warmest locations along the southwestern coast – notably in Hanko – and from early October to mid May in the most elevated locations, such as northwestern Lapland and the lowest valleys in northeastern Lapland. This means that southern portions of the country are snow-covered about three to four months of the year, and the northern for about seven months. The long winter causes about half of the annual 500 to 600 millimetres (19.7 to 23.6 in) precipitation in the north to fall as snow. Precipitation in the south amounts to about 600 to 700 millimetres (23.6 to 27.6 in) annually. Like that of the north, it occurs all through the year, though not so much of it is snow.[1]

In Köppen climate classification Finland belongs to the Df group (continental subarctic or boreal climates). The southern coast is Dfb (humid continental mild summer, wet all year), and the rest of the country is Dfc (subarctic with cool summer, wet all year).[2][3]
The climate of Finland has characteristics of both maritime and continental climate. The Atlantic Ocean to the west and the Eurasian continent to the east interact to modify the climate of the country. The warm waters of the Gulf Stream and the North Atlantic Drift Current, which continuously warm the region, play a big role in the climate of Norway, Sweden and Finland; if it weren't for these currents, the winters in Scandinavia and Fennoscandia would be much colder. Westerly winds bring the warm air currents into the Baltic areas and to the country's shores, moderating winter temperatures, especially in the south and southwest in cities like Helsinki and Turku where winter highs tend to be between 0 and 5 °C (32 and 41 °F) but a cold snap like the one that occurred in mid-January 2016 can cause temperatures to plunge well below −20 °C (−4 °F). These winds, because of clouds associated with weather systems accompanying the westerlies, also decrease the amount of sunshine received during the summer. By contrast, the continental high pressure system situated over the Eurasian continent counteracts the maritime influences, occasionally causing severe winters and high temperatures in the summer.
Temperature
The warmest annual average temperature in Southwestern Finland is 6.5 °C (43.7 °F). From there the temperature decreases gradually towards north and east. The Suomenselkä and Maanselkä drainage divides rise higher than the surrounding areas, and the climate there is cooler than at same latitudes elsewhere in Finland.[4] The Barents Sea between Finland and the North Pole is open even in winter, so northerly airflows are not as cold as in Siberia or Alaska.[5]
The highest temperature ever recorded is 37.2 °C (99.0 °F) (Liperi, July 29, 2010).[6] The lowest, −51.5 °C (−60.7 °F) (Kittilä, January 28, 1999). The annual average temperature is relatively high in the southwestern part of the country (5.0 to 7.5 °C or 41.0 to 45.5 °F), with quite mild winters and warm summers, and low in the northeastern part of Lapland (Finland) (0 to −4 °C or 32 to 25 °F).
Temperature extremes for every month:[7]
| Climate data for Finland | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 10.9 (51.6) |
11.8 (53.2) |
17.5 (63.5) |
25.5 (77.9) |
31.0 (87.8) |
33.8 (92.8) |
37.2 (99.0) |
33.8 (92.8) |
28.8 (83.8) |
21.1 (70.0) |
16.6 (61.9) |
11.3 (52.3) |
37.2 (99.0) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −51.5 (−60.7) |
−49.0 (−56.2) |
−44.3 (−47.7) |
−36.0 (−32.8) |
−24.6 (−12.3) |
−7.7 (18.1) |
−5.0 (23.0) |
−10.8 (12.6) |
−18.7 (−1.7) |
−31.8 (−25.2) |
−42.0 (−43.6) |
−47.0 (−52.6) |
−51.5 (−60.7) |
| Source: http://ilmatieteenlaitos.fi/lampotilaennatyksia | |||||||||||||
Record highs and lows
| Record highs by month | |||
| Month | Temp. | Date | Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| January | +10.9 °C (51.6 °F) | January 6, 1973 | Mariehamn, Åland |
| February | +11.8 °C (53.2 °F) | February 28, 1943 | Ilmala, Helsinki, Uusimaa |
| March | +17.5 °C (63.5 °F) | March 27, 2007 | Helsinki-Vantaa Airport, Vantaa, Uusimaa |
| April | +25.5 °C (77.9 °F) | April 27, 1921 | Jyväskylä, Central Finland |
| May | +31.0 °C (87.8 °F) | May 30/31, 1995 | Lapinjärvi, Uusimaa |
| June | +33.8 °C (92.8 °F) | June 24, 1934 | Ähtäri, Central Finland |
| July | +37.2 °C (99.0 °F) | July 29, 2010 | Joensuu Airport, Liperi, North Karelia[6] |
| August | +33.8 °C (92.8 °F) | August 7, 2010 | Heinola, Päijät-Häme,[8] Puumala, South Savo[9] |
| August 8, 2010 | Lahti, Päijät-Häme[8] | ||
| September | +28.8 °C (83.8 °F) | September 6, 1968 | Rauma, Satakunta |
| October | +21.1 °C (70.0 °F) | October 14, 2018 | Oulu Airport, North Ostrobothnia |
| November | +16.6 °C (61.9 °F) | November 6, 2020 | Mariehamn Airport, Jomala, Åland[10] |
| December | +11.3 °C (52.3 °F) | December 20, 2015 | Pori and Kokemäki, Satakunta[11] |
| Record lows by month | |||
| Month | Temp. | Date | Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| January | −51.5 °C (−60.7 °F) | January 28, 1999 | Kittilä, Pokka, Lapland |
| February | −49.0 °C (−56.2 °F) | February 5, 1912 | Sodankylä, Lapland |
| March | −44.3 °C (−47.7 °F) | March 1, 1971 | Salla, Tuntsa, Lapland |
| April | −36.0 °C (−32.8 °F) | April 2/9, 1912 | Kuusamo, Northern Ostrobothnia; Sodankylä, Lapland |
| May | −24.6 °C (−12.3 °F) | May 1, 1971 | Enontekiö, Kalmankaltio, Lapland |
| June | −7.7 °C (18.1 °F) | June 1, 2023 | Saana, Kilpisjärvi, Enontekiö, Lapland |
| July | −5.0 °C (23.0 °F) | July 1/12, 1958 | Enontekiö, Kilpisjärvi, Lapland |
| August | −10.8 °C (12.6 °F) | August 26, 1980 | Salla, Naruskajärvi, Lapland |
| September | −18.7 °C (−1.7 °F) | September 26, 1968 | Sodankylä, Vuotso, Lapland |
| October | −31.8 °C (−25.2 °F) | October 25, 1968 | Sodankylä, Lapland |
| November | −42.0 °C (−43.6 °F) | November 30, 1915 | Sodankylä, Lapland |
| December | −47.0 °C (−52.6 °F) | December 21, 1919 | Pielisjärvi, North Karelia |
- Measurements are made at the height of 2 metres. A record cold of sorts for June, −9.1 °C (15.6 °F) was measured on June 2, 2023 in Koivuniemi, Virolahti, Kymenlaakso. However, the measurement was made at ground level, so it could not be accepted as a record.[12][13]
Climate data
| Climate data for Helsinki (1991–2020 normals, records 1900–present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 8.5 (47.3) |
10.3 (50.5) |
15.1 (59.2) |
21.9 (71.4) |
27.6 (81.7) |
31.7 (89.1) |
33.2 (91.8) |
31.2 (88.2) |
26.2 (79.2) |
17.6 (63.7) |
13.4 (56.1) |
10.5 (50.9) |
33.2 (91.8) |
| Average high °C (°F) | −0.7 (30.7) |
−1.3 (29.7) |
2.3 (36.1) |
8.1 (46.6) |
14.6 (58.3) |
18.8 (65.8) |
21.9 (71.4) |
20.5 (68.9) |
15.4 (59.7) |
9.2 (48.6) |
4.4 (39.9) |
1.4 (34.5) |
9.6 (49.3) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −3.1 (26.4) |
−3.8 (25.2) |
−0.7 (30.7) |
4.4 (39.9) |
10.4 (50.7) |
14.9 (58.8) |
18.1 (64.6) |
16.9 (62.4) |
12.3 (54.1) |
6.6 (43.9) |
2.4 (36.3) |
−0.7 (30.7) |
6.5 (43.7) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −5.6 (21.9) |
−6.3 (20.7) |
−3.6 (25.5) |
1.1 (34.0) |
6.4 (43.5) |
11.2 (52.2) |
14.5 (58.1) |
13.5 (56.3) |
9.3 (48.7) |
4.2 (39.6) |
0.4 (32.7) |
−2.9 (26.8) |
3.5 (38.3) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −34.3 (−29.7) |
−31.5 (−24.7) |
−24.5 (−12.1) |
−16.3 (2.7) |
−4.8 (23.4) |
0.7 (33.3) |
5.4 (41.7) |
2.8 (37.0) |
−4.5 (23.9) |
−11.6 (11.1) |
−18.6 (−1.5) |
−29.5 (−21.1) |
−34.3 (−29.7) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 53 (2.1) |
38 (1.5) |
34 (1.3) |
34 (1.3) |
38 (1.5) |
60 (2.4) |
57 (2.2) |
81 (3.2) |
56 (2.2) |
73 (2.9) |
69 (2.7) |
58 (2.3) |
653 (25.7) |
| Average rainy days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 19 | 16 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 14 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 16 | 17 | 19 | 176 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 38 | 70 | 138 | 194 | 284 | 297 | 291 | 238 | 150 | 93 | 36 | 29 | 1,858 |
| Average ultraviolet index | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Source 1: FMI climatological normals for Finland 1991–2020[14] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: record highs and lows[15] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Tampere (1981–2010 normals, precipitation 1981-2010, extremes 1900–present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 8.0 (46.4) |
9.4 (48.9) |
14.9 (58.8) |
24.2 (75.6) |
28.4 (83.1) |
31.7 (89.1) |
33.1 (91.6) |
32.1 (89.8) |
24.8 (76.6) |
18.4 (65.1) |
11.1 (52.0) |
9.6 (49.3) |
33.1 (91.6) |
| Average high °C (°F) | −3.4 (25.9) |
−3.5 (25.7) |
1.2 (34.2) |
8.2 (46.8) |
15.4 (59.7) |
19.5 (67.1) |
22.2 (72.0) |
19.9 (67.8) |
14.0 (57.2) |
7.5 (45.5) |
1.5 (34.7) |
−1.9 (28.6) |
8.4 (47.1) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −6.4 (20.5) |
−6.9 (19.6) |
−2.8 (27.0) |
3.3 (37.9) |
9.7 (49.5) |
14.1 (57.4) |
16.9 (62.4) |
15.0 (59.0) |
9.8 (49.6) |
4.6 (40.3) |
0.6 (33.1) |
−4.5 (23.9) |
4.4 (39.9) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −9.7 (14.5) |
−10.6 (12.9) |
−6.6 (20.1) |
−1.3 (29.7) |
3.8 (38.8) |
8.6 (47.5) |
11.7 (53.1) |
10.4 (50.7) |
5.9 (42.6) |
1.9 (35.4) |
−3.0 (26.6) |
−7.6 (18.3) |
0.3 (32.5) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −37.0 (−34.6) |
−36.8 (−34.2) |
−29.6 (−21.3) |
−19.6 (−3.3) |
−7.3 (18.9) |
−2.8 (27.0) |
1.8 (35.2) |
−0.4 (31.3) |
−6.7 (19.9) |
−14.8 (5.4) |
−22.5 (−8.5) |
−34.2 (−29.6) |
−37.0 (−34.6) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 41 (1.6) |
29 (1.1) |
31 (1.2) |
32 (1.3) |
41 (1.6) |
66 (2.6) |
75 (3.0) |
72 (2.8) |
58 (2.3) |
60 (2.4) |
51 (2.0) |
42 (1.7) |
598 (23.5) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 32.3 (12.7) |
31.4 (12.4) |
29.5 (11.6) |
13.9 (5.5) |
1.6 (0.6) |
0.1 (0.0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
3.3 (1.3) |
13.1 (5.2) |
27.2 (10.7) |
152.4 (60) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 22 | 18 | 16 | 12 | 12 | 13 | 15 | 15 | 14 | 17 | 21 | 22 | 197 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 90 | 87 | 82 | 70 | 63 | 66 | 69 | 76 | 82 | 87 | 91 | 92 | 80 |
| Source 1: weatheronline.co.uk[16] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: FMI (precipitation, record highs and lows)[17] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Turku (1991-2020 normals, extremes 1900-present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 8.5 (47.3) |
10.2 (50.4) |
15.8 (60.4) |
24.5 (76.1) |
30.0 (86.0) |
32.0 (89.6) |
35.9 (96.6) |
32.6 (90.7) |
27.8 (82.0) |
18.9 (66.0) |
14.0 (57.2) |
11.0 (51.8) |
35.9 (96.6) |
| Average high °C (°F) | −1.1 (30.0) |
−1.2 (29.8) |
2.6 (36.7) |
9.1 (48.4) |
15.5 (59.9) |
19.5 (67.1) |
22.6 (72.7) |
21.1 (70.0) |
15.7 (60.3) |
8.8 (47.8) |
3.6 (38.5) |
0.7 (33.3) |
9.7 (49.5) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −3.8 (25.2) |
−4.5 (23.9) |
−1.3 (29.7) |
4.1 (39.4) |
10.0 (50.0) |
14.4 (57.9) |
17.5 (63.5) |
16.2 (61.2) |
11.3 (52.3) |
5.7 (42.3) |
1.5 (34.7) |
−1.5 (29.3) |
5.8 (42.5) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −6.5 (20.3) |
−7.1 (19.2) |
−4.7 (23.5) |
−0.2 (31.6) |
4.6 (40.3) |
9.3 (48.7) |
12.5 (54.5) |
11.6 (52.9) |
7.4 (45.3) |
2.8 (37.0) |
−0.9 (30.4) |
−4.1 (24.6) |
2.1 (35.8) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −35.5 (−31.9) |
−35.2 (−31.4) |
−32.8 (−27.0) |
−21.0 (−5.8) |
−6.6 (20.1) |
−2.2 (28.0) |
1.8 (35.2) |
0.2 (32.4) |
−6.9 (19.6) |
−15.0 (5.0) |
−22.3 (−8.1) |
−33.8 (−28.8) |
−35.5 (−31.9) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 58 (2.3) |
42 (1.7) |
39 (1.5) |
32 (1.3) |
35 (1.4) |
55 (2.2) |
74 (2.9) |
73 (2.9) |
59 (2.3) |
73 (2.9) |
71 (2.8) |
73 (2.9) |
684 (27.1) |
| Average precipitation days | 11 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 7 | 8 | 8 | 10 | 9 | 11 | 13 | 12 | 113 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 40 | 75 | 134 | 204 | 284 | 276 | 287 | 230 | 155 | 89 | 38 | 27 | 1,839 |
| Source: Climatological statistics for the normal period 1991–2020[18] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Oulu (1991-2020 normals, records 1921 - present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 9.3 (48.7) |
7.8 (46.0) |
11.5 (52.7) |
23.9 (75.0) |
29.9 (85.8) |
32.3 (90.1) |
33.3 (91.9) |
30.5 (86.9) |
25.4 (77.7) |
21.1 (70.0) |
11.2 (52.2) |
8.2 (46.8) |
33.3 (91.9) |
| Average high °C (°F) | −4.8 (23.4) |
−4.7 (23.5) |
−0.4 (31.3) |
5.8 (42.4) |
12.6 (54.7) |
17.9 (64.2) |
21.1 (70.0) |
18.9 (66.0) |
13.2 (55.8) |
5.8 (42.4) |
0.5 (32.9) |
−2.7 (27.1) |
6.9 (44.5) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −8.2 (17.2) |
−8.4 (16.9) |
−4.4 (24.1) |
1.6 (34.9) |
8.0 (46.4) |
13.7 (56.7) |
16.7 (62.1) |
14.6 (58.3) |
9.6 (49.3) |
3.3 (37.9) |
−1.6 (29.1) |
−5.3 (22.5) |
3.3 (38.0) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −11.9 (10.6) |
−12.1 (10.2) |
−8.3 (17.1) |
−2.5 (27.5) |
3.4 (38.1) |
9.3 (48.7) |
12.4 (54.3) |
10.6 (51.1) |
6.0 (42.8) |
0.6 (33.1) |
−4.2 (24.4) |
−8.8 (16.2) |
−0.5 (31.2) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −37.5 (−35.5) |
−41.5 (−42.7) |
−32 (−26) |
−21.4 (−6.5) |
−9.1 (15.6) |
−6.1 (21.0) |
3.6 (38.5) |
−1.5 (29.3) |
−8.0 (17.6) |
−20.6 (−5.1) |
−33 (−27) |
−37.2 (−35.0) |
−41.5 (−42.7) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 32 (1.3) |
29 (1.1) |
26 (1.0) |
23 (0.9) |
40 (1.6) |
51 (2.0) |
80 (3.1) |
62 (2.4) |
49 (1.9) |
51 (2.0) |
43 (1.7) |
39 (1.5) |
525 (20.5) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 33 (13) |
46 (18) |
43 (17) |
7 (2.8) |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 4 (1.6) |
17 (6.7) |
150 (59) |
| Average precipitation days | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 8 | 8 | 10 | 10 | 8 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 104 |
| Average relative humidity (%) (daily average) | 87 | 86 | 82 | 73 | 67 | 66 | 71 | 76 | 82 | 86 | 90 | 89 | 80 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 24 | 69 | 137 | 208 | 273 | 296 | 283 | 212 | 133 | 69 | 28 | 8 | 1,740 |
| Average ultraviolet index | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Source 1: FMI[19] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: FMI (record highs and lows 1961–present)[20]
FMI(record highs and lows 1921–1961)[21] Source 3: Finland. Oulu climate (average monthly UV index)[22] | |||||||||||||
Wind
The most common wind direction in Finland is from southwest, but the low pressure areas typical for these latitudes cause great variations in wind speed and direction.[1]
Storm, defined as at least one Finnish coastal station reporting at least 21 m/s as a 10-minutes average wind speed, is observed on Finnish seas on average 19 days a year. Strong winds are most frequent between October and January.[23]
Snow
The first snow cover is observed on average in September in Lapland, and in November in Southern and western areas. Permanent snow cover time starts typically around Christmas in the Southwestern corner, but before mid-November in most of Lapland. The maximum snow depth is usually found around March.[24]
Snow and supercooled droplets can accumulate in tree crowns and cause damage to trees. The trunks of pine trees can break under the weight of a snow-loaded crown, and deciduous trees can bend permanently. The snow load of a tree is typically 100–150 kg per one meter tree trunk, but the heaviest measured snow load of a spruce was over 3000 kilograms.[25]
Snowmelt contributes to spring floods. In north, the peak flow of rivers always happens in spring, in the south 70–80% of floods happen in spring. In the south, maximum flow happens in mid-April, in the north, in mid-May.[26]
It is predicted that as the Barents Sea gets less frozen in the coming winters and it becomes thus "Atlantified" additional evaporation will increase future snowfalls in Finland and much of continental Europe.[27]
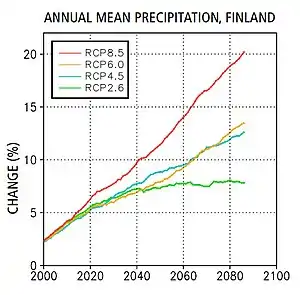
Climate change
References
- "Climate elements". Finnish Meteorological Institute. Retrieved November 16, 2017.
- "Map of climate classifications of Europe and Middle East" (JPG). People.eng.unimelbb.edu.au. Retrieved December 31, 2018.
- Köppen Climate Classification System Encyclopedia of Earth
- Karttunen, Hannu & Koistinen, Jarmo & Saltikoff, Elena & Manner, Olli: Ilmakehä, sää ja ilmasto. Ursan julkaisuja 107. Helsingissä: Ursa, 2008. ISBN 978-952-5329-61-2. page 357-358
- Solantie, Reijo (2001). "Suomen ilmaston erityispiirteitä". Tieteessä tapahtuu (in Finnish). Retrieved November 15, 2017.
- "Mercury Hits All Time Record of 37.2 Degrees". YLE Uutiset. Helsinki: Yleisradio Oy. July 29, 2010. Retrieved July 29, 2010.
- "Lämpötilan ennätykset" (in Finnish). Helsinki: Ilmatieteen laitos. November 14, 2007. Retrieved July 29, 2010.
- Sairanen, Sara (August 16, 2022). "Heinolassa mitattiin hurja hellelukema! Suomessa eletään nyt poikkeuksellisen lämmintä viikkoa" [‘Unusually high temperature recorded in Heinola! This week is exceptionally warm in Finland’]. Ilta-Sanomat (in Finnish). Sanoma. Retrieved August 16, 2022.
- "Elokuun lämpöennätys tarkentui: 33,8 astetta". YLE Uutiset (in Finnish). Helsinki: Yleisradio Oy. August 8, 2010. Retrieved August 8, 2010.
- Konttinen, Matti (November 6, 2020). "Marraskuun lämpöennätys meni taas rikki: Ahvenanmaalla 16,6 astetta" [‘Again record high in November: 16.6 degrees in the Åland Islands’]. yle.fi (in Finnish). Yle. Retrieved November 7, 2020.
- "Säähavaintoarkisto 20.12.2015 - Päivätilastot - FMI Avoin data". kilotavu.com. Retrieved May 31, 2023.
- Sairanen, Sara (June 2, 2023). "Kesäkuun kylmyysennätys rikkoutui jälleen" [‘Record low for June again’]. Iltasanomat (in Finnish). Sanoma. Retrieved June 2, 2023.
- Ylen aamu 2 June 2023.
- "FMI normals 1991-2020". fmi.fi. Retrieved October 7, 2021.
- "FMI data". FMI. Retrieved September 25, 2020.
- "weatheronline.uk". weatheronline.co.uk. Retrieved July 25, 2022.
- "FMI open data". Finnish Meteorological Institute. Retrieved July 25, 2022.
- "Normal period 1991–2020". Archived from the original on September 30, 2021. Retrieved October 7, 2021.
- "FMI normals 1991-2020". FMI. Retrieved October 14, 2021.
- "FMI open data". FMI. Retrieved September 7, 2019.
- Juha Kersalo and Pentti Pirinen. (2009). Suomen Maakuntien Ilmasto Helsinki: Finnish Meteorological Institute. (in Finnish)
- "Oulu climate guide". Weather 2 Travel. Retrieved May 13, 2022.
- "Tuulitilastot". fmi (in Finnish). Finnish Meteorological Institute. Retrieved November 18, 2017.
- "Snow statistics". Finnish Meteorological Institute. Retrieved November 16, 2017.
- "Snow damage". Luke. Natural Resources Institute Finland. Retrieved November 18, 2017.
- Kuusisto, Esko. "Snow accumulation and snowmelt in Finland" (PDF). National board of waters. Retrieved November 16, 2017.
- Bailey, Hannah; Hubbard, Alun; Klen, Eric S.; Mustonen, Kaisa-Riikka; Akers, Pete D.; Marttila, Hannu; Welker, Jeffrey M. (April 1, 2021). "Arctic sea-ice loss fuels extreme European snowfall". Nature Geoscience. 14 (5): 283–288. doi:10.1038/s41561-021-00719-y. hdl:10037/20941.
- Which nations are most responsible for climate change? Guardian 21 April 2011
- Pipatti, Riitta. "Statistics Finland - Greenhouse gases". www.stat.fi. Retrieved April 12, 2018.
- Finland far behind climate goals, think tank says YLE 22.1.2020
- Europe's Great Coal Collapse of 2019 Sandbag UK 18.9.2019
- Darby, Megan (June 3, 2019). "Finland to be carbon neutral by 2035. One of the fastest targets ever set". Climate Home News. Retrieved May 11, 2020.
- "Finland will achieve carbon neutrality by 2035". Sustainable Development Goals. United Nations. Retrieved May 11, 2020.