Windows-1252
Windows-1252 or CP-1252 (code page 1252) is a single-byte character encoding of the Latin alphabet that was used by default in Microsoft Windows for English and many Romance and Germanic languages including Spanish, Portuguese, French, and German (though missing uppercase ẞ). This character-encoding scheme is used throughout the Americas, Western Europe, Oceania, and much of Africa.
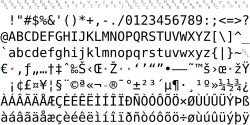 | |
| MIME / IANA | windows-1252[1] |
|---|---|
| Alias(es) | cp1252 (code page 1252) |
| Language(s) | All supported by ISO/IEC 8859-1 plus full support for French and Finnish and ligature forms for English; e.g. Danish (except for a rare exceptional letter), Irish, Italian, Norwegian, Portuguese, Spanish, Swedish, German (missing uppercase ẞ), Icelandic, Faroese, Luxembourgish, Albanian, Estonian, Swahili, Tswana, Catalan, Basque, Occitan, Rotokas, Romansh, Dutch (except the IJ/ij character, substituted by IJ/ÿ), and Slovene (except the č character, substituted by ç). |
| Created by | Microsoft |
| Standard | WHATWG Encoding Standard |
| Classification | extended ASCII, Windows-125x |
| Extends | ISO 8859-1 (excluding C1 controls) |
| Transforms / Encodes | ISO 8859-15 |
It is the most-used single-byte character encoding in the world. As of January 2023, 1.4%[2] of all web sites declare ISO 8859-1 which is treated as Windows-1252 by all modern browsers (as demanded by the HTML5 standard[3]), plus 0.3% of all websites declared use of Windows-1252,[2][4] for a total of 1.7% (and only 16 of the top 1000 websites[5]). Pages declared as ASCII, or a missing or invalid charset, are also assumed to be Windows-1252 by browsers.
Depending on the country or language, use can be much higher than the global average, e.g., for Brazil website use is at 9.2%,[6] and in Germany at 3.9%[7][8] (these are the sums of ISO-8859-1 and CP1252 declarations).
Windows-1252 is often assumed to be the encoding of text in operating systems, in particular on Microsoft Windows;[9] this is only gradually being changed to UTF-8.
All modern operating systems, including Windows, now use Unicode code points and text encodings by default, which are portable across all of the world's major languages.
Details
This character encoding is a superset of ISO 8859-1 in terms of printable characters, but differs from the IANA's ISO-8859-1 by adding additional characters in the 80 to 9F (hex) range (the ISO standards reserve this range for control characters). Notable additional characters include curly quotation marks and all printable characters from ISO 8859-15. It is known to Windows by the code page number 1252, and by the IANA-approved name "windows-1252".
At one stage many Microsoft internet products produced text in Windows-1252 but marked as ISO-8859-1. A result was that all the quotes and apostrophes (produced by "smart quotes") were replaced with question marks or boxes when viewed on non-Windows operating systems. Most modern web browsers and e-mail clients treat the media type charset ISO-8859-1 as Windows-1252 to accommodate such mislabeling. This behavior is now required by the HTML5 specification.[3] Browsers appear to treat the charset "ASCII" and missing charsets the same.
Historically, the phrase "ANSI Code Page" was used in Windows to refer to non-DOS encodings; the intention was that most of these would be ANSI standards such as ISO-8859-1. Even though Windows-1252 was the first and by far most popular code page named so in Microsoft Windows parlance, the code page has never been an ANSI standard. Microsoft explains, "The term ANSI as used to signify Windows code pages is a historical reference, but is nowadays a misnomer that continues to persist in the Windows community."[10]
In LaTeX packages, CP-1252 is referred to as "ansinew".
IBM uses code page 1252 (CCSID 1252 and euro sign extended CCSID 5348) for Windows-1252.[11][12][13]
Codepage layout
The following table shows Windows-1252. Differences from ISO-8859-1 have the Unicode code point number below the character, based on the Unicode.org mapping of Windows-1252 with "best fit". A tooltip, generally available only when one points to the immediate left of the character, shows the Unicode code point name and the decimal Alt code.
| Windows-1252 (CP1252)[15][16][17][18][19] | ||||||||||||||||
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | A | B | C | D | E | F | |
| 0_ | NUL | SOH | STX | ETX | EOT | ENQ | ACK | BEL | BS | HT | LF | VT | FF | CR | SO | SI |
| 1_ | DLE | DC1 | DC2 | DC3 | DC4 | NAK | SYN | ETB | CAN | EM | SUB | ESC | FS | GS | RS | US |
| 2_ | SP | ! | " | # | $ | % | & | ' | ( | ) | * | + | , | - | . | / |
| 3_ | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | : | ; | < | = | > | ? |
| 4_ | @ | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O |
| 5_ | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | [ | \ | ] | ^ | _ |
| 6_ | ` | a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | i | j | k | l | m | n | o |
| 7_ | p | q | r | s | t | u | v | w | x | y | z | { | | | } | ~ | DEL |
| 8_ | € 20AC |
‚ 201A |
ƒ 0192 |
„ 201E |
… 2026 |
† 2020 |
‡ 2021 |
ˆ 02C6 |
‰ 2030 |
Š 0160 |
‹ 2039 |
Π0152 |
Ž 017D |
|||
| 9_ | ‘ 2018 |
’ 2019 |
“ 201C |
” 201D |
• 2022 |
– 2013 |
— 2014 |
˜ 02DC |
™ 2122 |
š 0161 |
› 203A |
œ 0153 |
ž 017E |
Ÿ 0178 | ||
| A_ | NBSP | ¡ | ¢ | £ | ¤ | ¥ | ¦ | § | ¨ | © | ª | « | ¬ | SHY | ® | ¯ |
| B_ | ° | ± | ² | ³ | ´ | µ | ¶ | · | ¸ | ¹ | º | » | ¼ | ½ | ¾ | ¿ |
| C_ | À | Á | Â | Ã | Ä | Å | Æ | Ç | È | É | Ê | Ë | Ì | Í | Î | Ï |
| D_ | Ð | Ñ | Ò | Ó | Ô | Õ | Ö | × | Ø | Ù | Ú | Û | Ü | Ý | Þ | ß |
| E_ | à | á | â | ã | ä | å | æ | ç | è | é | ê | ë | ì | í | î | ï |
| F_ | ð | ñ | ò | ó | ô | õ | ö | ÷ | ø | ù | ú | û | ü | ý | þ | ÿ |
According to the information on Microsoft's and the Unicode Consortium's websites, positions 81, 8D, 8F, 90, and 9D are unused; however, the Windows API MultiByteToWideChar maps these to the corresponding C1 control codes. The "best fit" mapping documents this behavior, too.[15]
History
- The first version of the codepage 1252 used in Microsoft Windows 1.0 did not have positions D7 and F7 defined. All the characters in the ranges 80–9F were undefined too.
- The second version, used in Microsoft Windows 2.0, positions D7, F7, 91, and 92 had been defined.
- The third version, used since Microsoft Windows 3.1, had all the present-day positions defined, except euro sign and Z with caron character pair.
- The final version listed above debuted in Microsoft Windows 98 and was ported to older versions of Windows with the euro symbol update.
OS/2 extensions
The OS/2 operating system supports an encoding by the name of Code page 1004 (CCSID 1004) or "Windows Extended".[20][21] This mostly matches code page 1252, with the exception of certain C0 control characters being replaced by diacritic characters.
| Code page 1004 (differing rows only)[22][23][24][25] | ||||||||||||||||
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | A | B | C | D | E | F | |
| 0_ | NUL | SOH | STX | ETX | ˉ 02C9 |
˘ 02D8 |
˙ 02D9 |
BEL | ˚ 02DA |
HT | ˝ 02DD |
˛ 02DB |
ˇ 02C7 |
CR | SO | SI |
MSDOS extensions [rare]
There is a rarely used, but useful, graphics extended code page 1252 where codes 0x00 to 0x1f allow for box drawing as used in applications such as MSDOS Edit and Codeview. One of the applications to use this code page was an Intel Corporation Install/Recovery disk image utility from mid/late 1995. These programs were written for its P6 User Test Program machines (US example[26]). It was used exclusively in its then EMEA region (Europe, Middle East & Africa). In time the programs were changed to use code page 850.
| Graphics Extended Code Page 1252 | ||||||||||||||||
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | A | B | C | D | E | F | |
| 0_ | ○ | ■ | ↑ | ↓ | → | ← | ║ | ═ | ╔ | ╗ | ╚ | ╝ | ░ | ▒ | ► | ◄ |
| 1_ | │ | ─ | ┌ | ┐ | └ | ┘ | ├ | ┤ | ┴ | ┬ | ♦ | ┼ | █ | ▄ | ▀ | ▬ |
Palm OS variant
Each Palm OS device supports a single language and a single character encoding, depending on its locale.[27]
For languages such as English and French, Palm OS uses a custom character encoding based on Windows-1252. For Japanese, it instead uses a multibyte character encoding based on code page 932. Regardless of the system locale, all characters in the range 0x00 to 0x7F are guaranteed to be the same, except 0x5D which is the Yen sign in Japanese and a backslash on all others.[27]
Palm OS 3.1 introduced several changes to the character encoding to better align with Windows-1252:[28]
- The special Palm OS glyphs "shortcut stroke" (0x9D) and "command stroke" (0x9E) were copied to 0x16 and 0x17, to ensure they were in the range guaranteed to be consistent between locales.[28] Starting in Palm OS 3.3, 0x16 and 0x17 are the only code points for those characters,[29] leaving 0x9D and 0x9E undefined.[30]
- The numeric space (0x80) and horizontal ellipsis (0x85) were copied to 0x19 and 0x18 (respectively), to ensure they were in the range guaranteed to be consistent between locales.[28][29]
- The Euro sign was added at 0x80, replacing what was previously the numeric space.[29]
- The playing card suits were copied to the font Symbol 9,[28] although their original code points remain valid.[29][30]
The following is the variant of Windows-1252 used by Palm OS 3.3 onward for English and several other locales.[29] Python gives it the palmos label, describing it as the encoding for Palm OS 3.5.[31] Differences from Windows-1252 have their Unicode code point.
| Palm OS 3.3 character encoding[30][32] | ||||||||||||||||
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | A | B | C | D | E | F | |
| 8_ | €[lower-alpha 1] | ‚ | ƒ | „ | …[lower-alpha 2] | † | ‡ | ˆ | ‰ | Š | ‹ | Œ | ♦ 2666 |
♣ 2663 |
♥ 2665 | |
| 9_ | ♠ 2660 |
‘ | ’ | “ | ” | • | – | — | ˜ | ™ | š | › | œ | [lower-alpha 3] | [lower-alpha 4] | Ÿ |
- Prior to Palm OS 3.1, the character at code point 0x80 was U+2007 NUMERIC SPACE; starting in Palm OS 3.1, 0x80 is the Euro sign and 0x19 is U+2007 NUMERIC SPACE instead.[29]
- Starting in Palm OS 3.1, this character is also duplicated at 0x18.[lower-alpha 5][lower-alpha 6]
- Prior to Palm OS 3.3, this code point was the Palm OS-exclusive character "shortcut stroke"; starting in Palm OS 3.3, this code point is undefined.[28][29]
- Prior to Palm OS 3.3, this code point was the Palm OS-exclusive character "command stroke"; starting in Palm OS 3.3, this code point is undefined.[28][29]
See also
References
- Character Sets, Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA), 2018-12-12
- "Historical trends in the usage statistics of character encodings for websites, January 2023". w3techs.com. Retrieved 2023-01-16.
- "Encoding". WHATWG. 27 January 2015. sec. 5.2 Names and labels. Archived from the original on 4 February 2015. Retrieved 4 February 2015.
- "Frequenty Asked Questions". w3techs.com.
- "Usage Survey of Character Encodings broken down by Ranking". w3techs.com. Retrieved 2023-02-16.
- "Distribution of Character Encodings among websites that use Brazil". w3techs.com. Retrieved 2023-02-16.
- "Distribution of Character Encodings among websites that use .de". w3techs.com. Retrieved 2023-02-16.
- "Distribution of Character Encodings among websites that use German". w3techs.com. Retrieved 2023-01-16.
- "c++ - What is the native narrow string encoding on Windows?". Stack Overflow. Retrieved 2023-02-16.
- Wissink, Cathy (5 April 2002). "Unicode and Windows XP" (PDF). Microsoft. p. 1. Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 February 2015. Retrieved 4 February 2015.
- "Code page 1252 information document". Archived from the original on 2016-03-03.
- "CCSID 1252 information document". Archived from the original on 2016-03-26.
- "CCSID 5348 information document". Archived from the original on 2014-11-29.
- "Database Client Installation Guide". Oracle. Retrieved 2021-02-14.
- "Unicode mappings of Windows-1252 with 'Best Fit'". Unicode. Archived from the original on 4 February 2015. Retrieved 4 February 2015.
- Code Page 01252 (pdf), IBM, 1998, archived (PDF) from the original on 27 October 2023
- Code Page (CPGID) 01252 (txt), IBM, 1998, archived from the original on 8 April 2023
- International Components for Unicode (ICU), ibm-1252_P100-2000.ucm, 2002-12-03
- International Components for Unicode (ICU), ibm-5348_P100-1997.ucm, 2002-12-03
- "Code page 1004 information document". Archived from the original on 2015-06-25.
- "CCSID 1004 information document". Archived from the original on 2016-03-26.
- "Code Page 01004" (PDF). IBM. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-07-08. (version based on Windows 3.1 version of Windows-1252)
- Code Page CPGID 01004 (pdf) (PDF), IBM
- Code Page CPGID 01004 (txt), IBM
- Borgendale, Ken (2001). "Codepage 1004 - Windows Extended". OS/2 codepages by number. Archived from the original on 2018-05-13. Retrieved 2018-05-13. (version based on current version of Windows-1252)
- Storaasli, Olaf (1996). "Performance of the NASA equation solvers on computational mechanics applications" (PDF). Performance of NASA Equation Solvers on Computational Mechanics Applications. NASA. doi:10.2514/6.1996-1505. S2CID 15711051. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2019-05-03.
- "Chapter 13: Localized Applications". Palm OS Programmer's Companion (PDF). Palm Computing Platform. March 16, 2000. p. 321.
- "Appendix B: Compatibility Guide". Palm OS SDK Reference (PDF). Palm Computing Platform. March 16, 2000. pp. 1181–1182.
- Walleij, Linus. "Palm Pilot Character Sets And Unicode Mappings". GNU Recode. Datorföreningen vid Lunds Universitet och Lunds Tekniska Högskola. Retrieved 10 October 2023.
- Parker, Greg. "Palm OS Built-in Fonts". Sealie Software. Retrieved 10 October 2023.
- "codecs — Codec registry and base classes (§ Text Encodings)". The Python Standard Library—Python 3.9.4 Documentation. Python Software Foundation.
- Mullender, Sjoerd (13 July 2002). "Python Character Mapping Codec for Palm OS 3.5". CPython source tree. Python Software Foundation. Retrieved 9 December 2021.
External links
- Microsoft's code charts for Windows-1252 ("Code Page 1252 Windows Latin 1 (ANSI)")
- Unicode mapping table and code page definition with best fit mappings for Windows-1252