List of distinct cell types in the adult human body
There are about 30 trillion (3×1013) human cells in the adult human body, varying from about 20 to 40 trillion depending on the sex, age and weight, and a roughly equal number of bacterial cells.[1][2][3][4][5][6] The human cells have been categorized into over 400 cell types[2] based on location and function within the body, of which about 230 types are listed here.

 |
Cell type | % cell count |
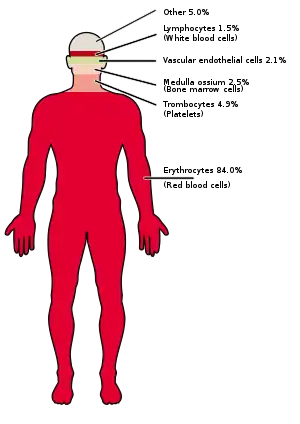
| Erythrocytes (red blood cells) | 84.0 | |
| Platelets | 4.9 | |
| Bone marrow cells | 2.5 | |
| Vascular endothelial cells | 2.1 | |
| Lymphocytes | 1.5 | |
| Hepatocytes | 0.8 | |
| Neurons and glia | 0.6 | |
| Bronchial endothelial cells | 0.5 | |
| Epidermal cells | 0.5 | |
| Respiratory interstitial cells | 0.5 | |
| Adipocytes (fat cells) | 0.2 | |
| Dermal fibroblasts | 0.1 | |
| Muscle cells | 0.001 | |
| Other cells | 2.0 |
.png.webp)
 |
| Part of a series of lists about |
| Human anatomy |
|---|
There are many different types of cells in the human body.
Major efforts to map all human cells
Several efforts have been made to make a list or a map of all human cells.[8][9][10] One of the largest and most recent is the HuBMAP (Human BioMolecular Atlas Program).[11] They managed to organize 1551 samples across 17 collections. However, this project still only mapped about 31 of the human bodies' 70 organs. Their datasets and visualisations place great emphasis on biomarkers and location in the body, but less on cell development and how cells can change over time. Usually specific surface proteins are used to identify cells, and based on this they are put into different categories. Another major effort to make an overview of these proteins that allows us to observe cell types is the Swedish Protein Atlas.[12]
The EU have attempted to map everything in the human brain,[13][14] however a lot of the areas in the model which is currently available does not have cellular resolution available.
Complete lists of human cells known so far
Cells derived primarily from endoderm
The endodermal cells primarily generate the lining and glands of the digestive tube[15]
| name | Progenitor
(precursor cell) |
Predecessor Cells | Area it is found | Function | Cell type | Cell subtype | Originally derived from | Known biomarkers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brunner's gland cell | in duodenum | enzyme and alkaline mucus secretion | Exocrine secretory epithelial cells | Endoderm | ||||
| Insulated goblet cell | Respiratory and digestive tracts | mucus secretion | ||||||
| Foveolar cell | Stomach | |||||||
| Chief cell | pepsinogen secretion | |||||||
| Parietal cell | hydrochloric acid secretion | |||||||
| Pancreatic acinar cell | Pancreas (confirmation needed) | bicarbonate and digestive enzyme secretion | ||||||
| Paneth cell | small intestine | lysozyme secretion | ||||||
| Type II pneumocyte | Lungs | surfactant secretion | ||||||
| Club cell | ||||||||
| Type I pneumocyte | formation of the Blood-Gas Barrier | Barrier cell | ||||||
| Gall bladder epithelial cell | Gall bladder | |||||||
| Centroacinar cell | Pancreas | |||||||
| Intercalated duct cell | ||||||||
| Intestinal brush border cell (with microvilli) | ||||||||
| K cell | gastric inhibitory peptide secretion | Hormone-secreting cells | Enteroendocrine cell | |||||
| L cell | glucagon-like peptide-1, peptide YY3-36, oxyntomodulin, and glucagon-like peptide-2) secretion | |||||||
| I cell | cholecystokinin (CCK) secretion | |||||||
| G cell | gastrin secretion | |||||||
| Enterochromaffin cell | serotonin secretion | |||||||
| Enterochromaffin-like cell | histamine secretion | |||||||
| N cell | neurotensin secretion | |||||||
| S cell | secretin secretion | |||||||
| D cell | somatostatin secretion | |||||||
| Mo cell (or M cell) | motilin secretion | |||||||
| other hormones secreted: vasoactive intestinal peptide, substance P, alpha and gamma-endorphin, bombesin | ||||||||
| Thyroid epithelial cell | Thyroid gland cells | |||||||
| Parafollicular cell | ||||||||
| Parathyroid chief cell | Parathyroid gland cells | |||||||
| Oxyphil cell | ||||||||
| Alpha cell | glucagon secretion | Pancreatic islets (islets of Langerhans) | ||||||
| Beta cell | insulin and amylin secretion | |||||||
| Delta cell | somatostatin secretion | |||||||
| Epsilon cell | ghrelin secretion | |||||||
| PP cell (gamma cell) | pancreatic polypeptide secretion |
Nervous system
There are nerve cells, also known as neurons, present in our human body. They are branched out. These cells make up nervous tissue. A neuron consists of a cell body with a nucleus and cytoplasm, from which long thin hair-like parts arise.
Central nervous system neurons and glial cells
(large variety of types, still poorly classified)
| Name | Progenitor (precursor cell) | Predecessor Cells | Area it is found | Function in the body | Cell type | Cell Subtype | Originally derived from | Known Biomarkers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salivary gland mucous cell | Exocrine secretory epithelial cells | Ectoderm | ||||||
| Salivary gland serous cell | ||||||||
| Von Ebner's gland cell | in tongue | (washes taste buds) | ||||||
| Mammary gland cell | (milk secretion) | |||||||
| Lacrimal gland cell | (tear secretion) | |||||||
| Ceruminous gland cell | in ear | (earwax secretion) | ||||||
| Eccrine sweat gland dark cell | (glycoprotein secretion) | |||||||
| Eccrine sweat gland clear cell | (small molecule secretion) | |||||||
| Apocrine sweat gland cell | (odoriferous secretion, sex-hormone sensitive) | |||||||
| Gland of Moll cell in eyelid | (specialized sweat gland) | |||||||
| Sebaceous gland cell | (lipid-rich sebum secretion) | |||||||
| Bowman's gland cell | in nose | (washes olfactory epithelium) | ||||||
| Corticotropes | Hormone-secreting cells | Anterior/Intermediate pituitary cells | ||||||
| Gonadotropes | Anterior/Intermediate pituitary cells | |||||||
| Lactotropes | Anterior/Intermediate pituitary cells | |||||||
| Melanotropes | Anterior/Intermediate pituitary cells | |||||||
| Somatotropes | Anterior/Intermediate pituitary cells | |||||||
| Thyrotropes | Anterior/Intermediate pituitary cells | |||||||
| Magnocellular neurosecretory cells, | secrete oxytocin and vasopressin | |||||||
| Parvocellular neurosecretory cells | secrete thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH), vasopressin, oxytocin, neurotensin, and prolactin | |||||||
| Chromaffin cells (adrenal gland) | ||||||||
| Keratinocyte | (differentiating epidermal cell) | Epithelial cells | ||||||
| Epidermal basal cell (stem cell) | ||||||||
| Melanocyte | ||||||||
| Trichocyte | (gives rise to hair and nail cells) | |||||||
| Medullary hair shaft cell | Trichocyte | |||||||
| Cortical hair shaft cell | Trichocyte | |||||||
| Cuticular hair shaft cell | Trichocyte | |||||||
| Huxley's layer hair root sheath cell | Trichocyte | |||||||
| Henle's layer hair root sheath cell | Trichocyte | |||||||
| Outer root sheath hair cell | Trichocyte | |||||||
| Surface epithelial cell | cornea, tongue, mouth, nasal cavity, distal anal canal, distal urethra, and distal vagina | |||||||
| basal cell (stem cell) | cornea, tongue, mouth, nasal cavity, distal anal canal, distal urethra, and distal vagina | |||||||
| Intercalated duct cell | (salivary glands) | |||||||
| Striated duct cell | ||||||||
| Lactiferous duct cell | (mammary glands) | |||||||
| Ameloblast | (deposit tooth enamel) | |||||||
| Odontoblast | (tooth dentin formation) | Oral cells | ||||||
| Cementoblast | (tooth cementum formation) | |||||||
| Auditory inner hair cells of organ of Corti | Sensory transducer cells | |||||||
| Auditory outer hair cells of organ of Corti | ||||||||
| Basal cells of olfactory epithelium | (stem cell for olfactory neurons) | |||||||
| Cold-sensitive primary sensory neurons | ||||||||
| Heat-sensitive primary sensory neurons | ||||||||
| Merkel cells of epidermis | ||||||||
| Olfactory receptor neurons | ||||||||
| Pain-sensitive primary sensory neurons | ||||||||
| Photoreceptor rod cells | Photoreceptor cells of retina in eye | |||||||
| Photoreceptor blue-sensitive cone cells of eye | Photoreceptor cells of retina in eye | |||||||
| Photoreceptor green-sensitive cone cells of eye | Photoreceptor cells of retina in eye | |||||||
| Photoreceptor red-sensitive cone cells of eye | Photoreceptor cells of retina in eye | |||||||
| Proprioceptive primary sensory neurons | ||||||||
| Touch-sensitive primary sensory neurons | ||||||||
| Chemoreceptor glomus cells of carotid body cell | (blood pH sensor) | |||||||
| Outer hair cells of vestibular system of ear | (acceleration and gravity) | |||||||
| Inner hair cells of vestibular system of ear | ||||||||
| Taste receptor cells of taste bud | ||||||||
| Cholinergic neurons (various types) | Autonomic neuron cells | |||||||
| Adrenergic neural cells (various types) | ||||||||
| Peptidergic neural cells (various types) | ||||||||
| Inner pillar cells of organ of Corti | Sense organ and peripheral neuron supporting cells | |||||||
| Outer pillar cells of the organ of Corti | ||||||||
| Inner phalangeal cells of organ of Corti | ||||||||
| Outer phalangeal cells of organ of Corti | ||||||||
| Border cells of organ of Corti | ||||||||
| Hensen's cells of organ of Corti | ||||||||
| Vestibular apparatus supporting cells | ||||||||
| Taste bud supporting cells | ||||||||
| Olfactory epithelium supporting cells | ||||||||
| Olfactory ensheathing cells | ||||||||
| Schwann cells | ||||||||
| Satellite glial cells | ||||||||
| Enteric glial cells | ||||||||
| Basket cells | Central nervous system neurons and glial cells | Neuron | Interneurons | |||||
| Cartwheel cells | Interneurons | |||||||
| Stellate cells | Interneurons | |||||||
| Golgi cells | Interneurons | |||||||
| Granule cells | Interneurons | |||||||
| Lugaro cells | Interneurons | |||||||
| Interneurons | ||||||||
| Martinotti cells | Interneurons | |||||||
| Chandelier cells | Interneurons | |||||||
| Cajal–Retzius cells | Interneurons | |||||||
| Double-bouquet cells | Interneurons | |||||||
| Neurogliaform cells | Interneurons | |||||||
| Retina horizontal cells | Interneurons | |||||||
| Starburst amacrine cells | Interneurons - > Amacrine cells | |||||||
| Renshaw cells | Interneurons - >Spinal interneurons | |||||||
| Spindle neurons | Principal cells | |||||||
| Fork neurons | Principal cells | |||||||
| Place cells | Principal cells-> Pyramidal cells | |||||||
| Grid cells | Principal cells-> Pyramidal cells | |||||||
| Speed cells | Principal cells-> Pyramidal cells | |||||||
| Head direction cells | Principal cells-> Pyramidal cells | |||||||
| Betz cells | Principal cells-> Pyramidal cells | |||||||
| Boundary cells | Principal cells->Stellate cells | |||||||
| Bushy cells | Principal cells | |||||||
| Purkinje cells | Principal cells | |||||||
| Medium spiny neurons | Principal cells | |||||||
| Astrocytes | ||||||||
| Oligodendrocytes | ||||||||
| Tanycytes | Ependymal cells | |||||||
| Pituicytes | ||||||||
| Anterior lens epithelial cell | Lens cells | |||||||
| Crystallin-containing lens fiber cell |
Cells derived primarily from mesoderm
Note: Cephalic connective tissue and bones are derived from the Cranial neural crest which comes from the ectoderm germ layer
List of databases relevant to this list
| Name | Provider | Sources of revenue/sponsers |
|---|---|---|
| HubMap[17] | A series of US based universities | Unknown |
References
- Hatton IA, Galbraith ED, Merleau NS, Miettinen TP, Smith BM, Shander JA (September 2023). "The human cell count and size distribution". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 120 (39): e2303077120. doi:10.1073/pnas.2303077120. PMC 10523466. PMID 37722043.
- "Mapping the human body one cell at a time: New study reveals the intricate relationship between cell size and count". News-Medical.net. 2023-09-19. Retrieved 2023-10-18.
- Society, Max Planck. "Cellular cartography: Charting the sizes and abundance of our body's cells reveals mathematical order underlying life". medicalxpress.com. Retrieved 2023-10-18.
- Sender R, Fuchs S, Milo R (August 2016). "Revised Estimates for the Number of Human and Bacteria Cells in the Body". PLOS Biology. 14 (8): e1002533. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1002533. PMC 4991899. PMID 27541692.
- Hewings-Martin Y (12 July 2017). "How many cells are in the human body?". Medical News Today. Retrieved 28 June 2023.
- Zimmer C (23 October 2013). "How Many Cells Are In Your Body?". National Geographic. Retrieved 29 June 2023.
- Hatton, Ian A.; Galbraith, Eric D.; Merleau, Nono S. C.; Miettinen, Teemu P.; Smith, Benjamin McDonald; Shander, Jeffery A. (2023-09-26). "The human cell count and size distribution". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 120 (39). doi:10.1073/pnas.2303077120. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 10523466. PMID 37722043.
- "Home". humancellatlas.org. Retrieved 5 May 2023.
- "NIH to build a detailed map of cells within the human body". National Institutes of Health (NIH). 26 September 2018. Retrieved 5 May 2023.
- Davis D. "The ambitious quest to map every cell in our body". BBC. Retrieved 5 May 2023.
- "The HuBMAP Human BioMolecular Atlas Program". HuBMAP Consortium. Retrieved 5 May 2023.
- "The Human Protein Atlas". www.proteinatlas.org. Retrieved 19 July 2023.
- "Siibra Explorer". atlases.ebrains.eu. Retrieved 2023-07-02.
- "Medical Data Analytics". The Human Brain Project. Retrieved 2 July 2023.
- Gilbert SF (2000). "Endoderm". Developmental Biology (6th ed.). Sunderland (MA): Sinauer Associates. Retrieved 2023-07-02.
- "CCF ASCT+B Reporter". Hubmap Consortium.
- "The Human BioMolecular Atlas Program (HuBMAP)". commonfund.nih.gov. 5 January 2017. Retrieved 2023-07-12.