DeSoto, Texas
DeSoto is a city in Dallas County, Texas, United States. DeSoto is a suburb of Dallas and is part of the Best Southwest area, which includes DeSoto, Cedar Hill, Duncanville, and Lancaster.
DeSoto, Texas | |
|---|---|
| City of DeSoto | |
 Flag  | |
| Motto(s): "Live, Work, Play in DeSoto"[1] | |
 Location of DeSoto in Dallas County, Texas | |
| Coordinates: 32°35′57″N 96°51′32″W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| County | |
| Incorporated | 1949 |
| Government | |
| • Type | Council-manager |
| • City Council | Mayor Rachel Proctor Dinah Marks Kay Brown-Patrick Andre Byrd Nicole Raphiel Crystal Chism Letitia Hughes |
| • City manager | Brandon Wright |
| Area | |
| • Total | 21.67 sq mi (56.12 km2) |
| • Land | 21.63 sq mi (56.03 km2) |
| • Water | 0.03 sq mi (0.09 km2) |
| Elevation | 666 ft (203 m) |
| Population (2010) | |
| • Total | 49,047 |
| • Estimate (2019)[3] | 52,988 |
| • Density | 2,449.41/sq mi (945.70/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC-6 (Central) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-5 (Central) |
| ZIP codes | 75115, 75123 |
| Area code(s) | 214, 469, 945, 972 |
| FIPS code | 48-20092[4] |
| GNIS feature ID | 1373357[5] |
| Website | The City of DeSoto, Texas |
History
The area was first settled in 1847, making it one of the oldest communities in North Texas. A post office was established in 1881, and the settlement was named DeSoto in honor of Thomas Hernando DeSoto Stewart, a doctor dedicated to the community. By 1885, DeSoto was home to around 120 people, a cotton gin, and a general store. Soon after, the population declined to below 50. In 1930, 97 people were living in the community, with several businesses.

After World War II, DeSoto and surrounding areas began to grow. To improve the inadequate water distribution system, residents felt the need to incorporate the town. On February 17, 1949, a petition signed by 42 eligible voters was presented to the Dallas County judge requesting an election for incorporation. The vote took place on March 2. Of the 52 people who cast ballots, 50 voted in favor of incorporation and two were opposed. On March 3, 1949, the results were entered into the records of the Dallas County Commissioners Court, thereby creating the City of DeSoto. The new city was less than one square mile in size. On March 15, Wayne A. Chowning was elected mayor along with five aldermen. The first city council meeting was held two days later.
The first census conducted after DeSoto's incorporation occurred in 1950. eight businesses and 298 people were in the city. Following a series of annexations in 1953, the city covered around 15 sq mi (39 km2). By 1960, the population had grown to 1,969. In 1970, DeSoto was home to 6,617 people and 71 businesses.
During the 1970s, continued growth brought about improvements to the municipal infrastructure, including road construction, and a new water/sewage system. Industrial, commercial, and residential construction also increased. On October 26, 1974, an election was held to determine the status of Woodland Hills, a small, incorporated community located northwest of DeSoto. The result was 221 votes in favor of a merger with DeSoto and 219 opposed. Woodland Hills had a population of 366 at the time of annexation. The rapid growth that began in the early 1970s was sustained throughout the 1980s; 1980 census figures put the city's population at slightly over 15,000. By 1984, DeSoto had a total of 360 businesses, up from 168 in 1980.
The population surpassed 30,000 in 1990. City development progressed in the following years. A primary example of this was the creation of DeSoto's Town Center. Officials converted an abandoned strip center located at one of the city's main intersections into a unique central business district. Since its opening, the Town Center has become an anchor of the community, housing city hall, the public library, a civic center, recreation cente, and a 180-seat auditorium and outdoor amphitheater.
Throughout the 1990s, DeSoto experienced a significant change in the demographic composition of the city. In the 1990 census, Whites comprised 75.97% of the city's population, but that figure had declined to 48.83% in the 2000 census, and 17.4% non-Hispanic White by 2010. By contrast, the African American population grew rapidly. In 2000, African Americans were 45.53% of the population, up from 20.83% in 1990. Hispanics accounted for 4.98% of the population in 1990 and 7.30% in 2000. With roughly 45,500 residents as of 2005, DeSoto is the largest and most diverse city in southwest Dallas County.
On June 11, 2006, the National Civic League named DeSoto an "All-America City". The All-America City Award is the nation's oldest community-recognition program and recognizes communities whose citizens work together to identify and tackle community-wide challenges and achieve uncommon results.
A 2015 article related a growing trend of largely middle class and educated African Americans moving to DeSoto.[6]
Geography
DeSoto is located at 32°35′57″N 96°51′32″W (32.599286, −96.858828).[7]
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 21.6 sq mi (56 km2), all land.
Demographics
| Census | Pop. | Note | %± |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 298 | — | |
| 1960 | 1,969 | 560.7% | |
| 1970 | 6,617 | 236.1% | |
| 1980 | 15,538 | 134.8% | |
| 1990 | 30,544 | 96.6% | |
| 2000 | 37,646 | 23.3% | |
| 2010 | 49,047 | 30.3% | |
| 2019 (est.) | 52,988 | [3] | 8.0% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[8] | |||
2020 census
| Race / Ethnicity | Pop 2010[9] | Pop 2020[10] | % 2010 | % 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White alone (NH) | 8,542 | 5,640 | 17.42% | 10.05% |
| Black or African American alone (NH) | 33,337 | 38,971 | 67.97% | 69.41% |
| Native American or Alaska Native alone (NH) | 111 | 121 | 0.23% | 0.22% |
| Asian alone (NH) | 446 | 487 | 0.91% | 0.87% |
| Pacific Islander alone (NH) | 22 | 13 | 0.04% | 0.02% |
| Some Other Race alone (NH) | 57 | 229 | 0.12% | 0.41% |
| Mixed Race/Multi-Racial (NH) | 618 | 1,367 | 1.26% | 2.43% |
| Hispanic or Latino (any race) | 5,914 | 9,317 | 12.06% | 16.59% |
| Total | 49,047 | 56,145 | 100.00% | 100.00% |
As of the 2020 United States census, 56,145 people, 19,041 households, and 13,093 families resided in the city.
Politics
| Year | Democratic | Republican | Third Parties |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 85.76% 24,227 | 13.29% 3,754 | 0.95% 269 |
| 2016 | 83.59% 19,835 | 14.63% 3,472 | 1.78% 422 |
| 2012 | 82.39% 19,187 | 17.16% 3,997 | 0.45% 105 |
Government
DeSoto is a home-rule city with a council–manager form of government. Under this type of local government, the day-to-day management of the city is directed by a city manager, who is appointed by the city council and serves as chief administrative officer for the city. The city charter states this position will execute the laws and administer the government of the city.
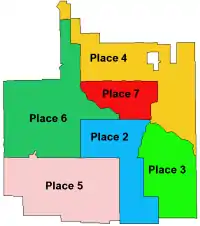
The city council consists of the mayor and six council members. The mayor represents the city as a whole and six council members represent particular districts (places) within the city. All are elected citywide for a term of three years with a limit of two terms.
| Current City Council Members[12] | |
| Place 1 | Rachel Proctor (mayor) |
| Place 2 | Kay Brown-Patrick |
| Place 3 | Nicole Raphiel |
| Place 4 | Andre' Byrd Sr. (mayor pro tem) |
| Place 5 | Dr. Dinah Marks |
| Place 6 | Crystal Chism |
| Place 7 | Letitia Hughes |

Mayors
| Term | Mayor |
|---|---|
| 1949–1953 | Wayne A. Chowning |
| 1953 | Willis Dawson |
| 1953–1955 | Floyd Huffstutler |
| 1955–1959 | J. B. Wadlington |
| 1959–1963 | E. G. Anderson |
| 1963–1965 | John Campbell |
| 1965–1967 | Les C. Zeiger |
| 1967–1969 | L. Carroll Moseley |
| 1969–1971 | H. H. Chandler |
| 1971–1972 | Roy Orr |
| 1972–1973 | Robert Nunneley |
| 1973–1977 | Charles Harwell |
| 1977–1979 | Durward Davis |
| 1979–1983 | Willis Russell |
| 1983–1987 | Ernest Roberts |
| 1987–1995 | David Doyle |
| 1995–2001 | Richard Rozier |
| 2001–2007 | Michael Hurtt |
| 2007–2010 | Bobby Waddle |
| 2010–2016 | Carl Sherman |
| 2016–2020 | Curtistene S. McCowan (died in office during her second term) |
| 2021–Present | Rachel L. Proctor |
City managers
| Term | City manager |
|---|---|
| 1964–1970 | Dewayne White |
| 1970–1973 | Jim Pratt |
| 1973–1977 | Joel Larkin |
| 1977–1981 | Dorothy Talley |
| 1981–1984 | Cliff Johnson |
| 1984–1985 | Jim McAlister |
| 1985–1987 | Kerry Sweatt |
| 1987–1992 | Mark Sowa |
| 1992–1993 | Ed Brady (interim) |
| 1993–1994 | Gary Whittle (interim) |
| 1994–1996 | Ron Holifield |
| 1996–1997 | Bill Lindley (interim) |
| 1997–2011 | Jim Baugh |
| 2011–2019 | Dr. Tarron J. Richardson |
| 2019–2020 | M. Renee Johnson (interim) |
| 2020–present | Brandon Wright |
Education
Most of DeSoto lies within the DeSoto Independent School District. The district has 12 schools (seven elementary schools, three middle schools, a high school, and a freshman campus) that serve about 8,000 students. The district's mascot is the eagle. A small portion of the city is located in the Duncanville Independent School District. Another small portion is in the Dallas Independent School District.[13]
Dallas County residents are zoned to Dallas College (formerly Dallas County Community College).[14]
Several private and parochial schools are in or near the city.
Media
The Focus Daily News is a daily newspaper published in DeSoto, covering Dallas County. It is owned by Publishers Newspapers.[15] It was founded in 1987, and has a daily circulation of 28,065 and a Sunday circulation of 36,297 as of 2012.[16]
Transportation
Major highways
Air
The city of DeSoto jointly owns the DeSoto Heliport with the Texas Department of Transportation and the DeSoto Economic Development Corporation.[17] The facility is operated by SKY Helicopters.[17][18]
Notes
References
- "The City of DeSoto, Texas". The City of DeSoto, Texas. Retrieved August 14, 2012.
- "2019 U.S. Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved August 7, 2020.
- "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". United States Census Bureau. May 24, 2020. Retrieved May 27, 2020.
- "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 31, 2008.
- "US Board on Geographic Names". United States Geological Survey. October 25, 2007. Retrieved January 31, 2008.
- "Affluent African-Americans Flock to DeSoto". nbcdfw.com. Retrieved June 22, 2021.
- "US Gazetteer files: 2010, 2000, and 1990". United States Census Bureau. February 12, 2011. Retrieved April 23, 2011.
- "Census of Population and Housing". Census.gov. Retrieved June 4, 2015.
- "P2 HISPANIC OR LATINO, AND NOT HISPANIC OR LATINO BY RACE – 2010: DEC Redistricting Data (PL 94-171) – DeSoto city, Texas". United States Census Bureau.
- "P2 HISPANIC OR LATINO, AND NOT HISPANIC OR LATINO BY RACE - 2020: DEC Redistricting Data (PL 94-171) - DeSoto city, Texas". United States Census Bureau.
- "Dallas County Election Results".
- City of Desoto – City Council. Retrieved 4 July 2006.
- "2020 CENSUS - SCHOOL DISTRICT REFERENCE MAP: Dallas County, TX" (PDF). U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved April 18, 2021.
- Texas Education Code, Sec. 130.176. DALLAS COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE DISTRICT SERVICE AREA.
- "Focus Daily News". Archived from the original on August 15, 2012. Retrieved August 14, 2012.
- "Focus Daily News". Nationwide Newspapers. Retrieved August 14, 2012.
- Epstein, Curt (October 8, 2014). "New Heliport Opens in Texas". Aviation International News. Retrieved May 11, 2018.
- "DeSoto Heliport". SKY Helicopters. Retrieved May 11, 2018.