Double-barreled cannon
The double-barreled cannon is an American Civil War-era experimental weapon and is now a modern landmark located in Athens, Georgia. While originally built for warfare, the cannon never saw battle. It is part of the Downtown Athens Historic District, in the National Register of Historic Places.

History
Concept
This concept dates from 1642 and Florentine gun maker Antonio Petrini. He cast the first cannon with the intention of simultaneously firing two balls linked by a chain from side-by-side barrels, which were meant to scythe down enemy soldiers like standing wheat when it reached them. For the cannon to work, the powder behind each round shot had to ignite at the same instant, which rarely happened.
In 1862, Georgia dentist, builder, and mechanic John Gilleland raised money from a coterie of Confederate citizens in Athens, Georgia to build the chain-shot gun for a cost of $350. Cast in one piece, the gun featured side-by-side bores, each a little over 3 inches in diameter and splayed slightly outward so the shots would diverge and stretch the chain taut. The two barrels have a divergence of 3 degrees, and the cannon was designed to shoot simultaneously two cannonballs connected with a chain to "mow down the enemy somewhat as a scythe cuts wheat". During tests, the Gilleland cannon effectively mowed down trees, tore up a cornfield, knocked down a chimney, and killed a cow. None of the previously mentioned items were anywhere near the gun's intended target.
A treatise that describes Antonio Petrini's cannon survives in the Royal Armories of the Tower of London, while Gilleland's gun sits on the lawn of the Athens, Georgia, city hall.
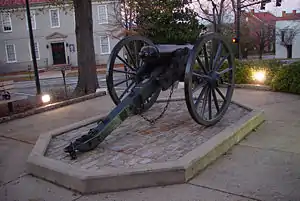
Execution
Gilleland's invention was a failure. When it was first tested on April 22, 1862, it was aimed at a target of two upright poles. Uneven combustion of the powder and casting imperfections in the barrels gave the connected balls a spinning movement in an off-center direction, with witnesses reporting that on its first firing it "plowed up about an acre of ground, tore up a cornfield, mowed down saplings, and then the chain broke, the two balls going in different directions".[1]
On its second firing, the chain shot across the horizon and into a thicket of pine. "[The] thicket of young pines at which it was aimed looked as if a narrow cyclone or a giant mowing machine had passed through," reported another witness.[1]
On its third firing, the chain snapped immediately and one ball tore into a nearby cabin, knocking down its chimney; the other spun off erratically and struck a nearby cow, killing it instantly. Gilleland considered the test-firings a success.[1]
Civil War use

Gilleland tried to promote his invention to the Confederate States Army's arsenal in Augusta, Georgia, where it was found unfit for its purpose. He continued to try to promote his invention to other military leaders around Augusta, but failed to interest anyone. Finally his contraption was used as a signal gun in Athens to warn the citizens about an invasion by the Union Army.
On 27 July 1864, the cannon was fired after a report was heard of several thousand Union soldiers approaching nearby Monroe, Georgia. However, this report turned out to be false. The cannon disappeared in 1891 and was found again twelve years later.
Modern use
Currently, the cannon is on display on the front lawn of the City Hall of Athens, Georgia, where it is a contributing property of the Downtown Athens Historic District. A local landmark and public curiosity, the cannon is one of the most popular and well-known attractions in the city. It is still pointing northward in a symbolic gesture of defiance against the North it was built to fight.
Other multi-barreled cannons
.JPG.webp)
While the cannon preserved at Athens is the most famous double-barreled cannon, it is not the only one. Another notable example was called Elizabeth-Henry, named after Charles I's youngest children.[2] It was used by the Cavaliers during the English Civil War, and fired 2-ounce charges. It could also fire grapeshot. The barrels were wrapped in leather to prevent rusting.
Multi-barreled cannons have also been built in India, and an example with six barrels, similar to the ribauldequins of the Middle Ages, has been preserved in the Nehru Scientific Center.[3]
In Poland, cannons with as many as seven barrels were in use in the 16th century. These were similar to the volley guns and organ battery of the 19th century, but in a larger caliber.
However, these other cannons did not attempt the Athens gun's idea of firing a connected round simultaneously from multiple barrels.
In 2012 a slightly modernized version was built, at customer request, by the Gunsmoke gun shop on the reality television series American Guns (Season 2, Ep 8).[4] By using a more modern ignition system than Civil War-era the Gunsmoke crew were able to achieve some success in firing the barrels properly. The gun used in the episode was actually built by Sprik's Cannon Works and sold to Gunsmoke for their TV show. The barrel was to be welded together by Sprik's Cannon Works, who also did the ignition system for a more accurate discharge of both barrels at the same time.
See also
References
- Scott Gutzke. "Battery B, 4th U.S. Light Artillery - The Athens Double-Barreled Cannon". Batteryb.com. Archived from the original on 29 July 2010. Retrieved 9 February 2010.
- "Earl of Northampton's Artillery page". Northamptons.org.uk. Archived from the original on 6 September 2009. Retrieved 9 February 2010.
- "Episode guide-American Guns Season 2 Episode 8". Discovery Channel website. Retrieved 27 June 2012.
External links
 Media related to Athens double-barrelled cannon at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Athens double-barrelled cannon at Wikimedia Commons- Athens Double-Barreled Cannon by Richard Irby
- The Athens Clarke County Virtual Tour Page about the double-barreled cannon.
- An extensive article about the history of the double-barreled cannon.
- A replica of an earlier double-barreled cannon
- Panoramic view at cannon site.
- The Athens Double-Barrelled Cannon historical marker