Downwelling
Downwelling is the process of accumulation and sinking of higher density material beneath lower density material, such as cold or saline water beneath warmer or fresher water or cold air beneath warm air. It is the sinking limb of a convection cell. Upwelling is the opposite process, and together, these two forces are responsible in the oceans for the thermohaline circulation. The sinking of the cold lithosphere at subduction zones is another example of downwelling in plate tectonics.

Oceanic downwelling

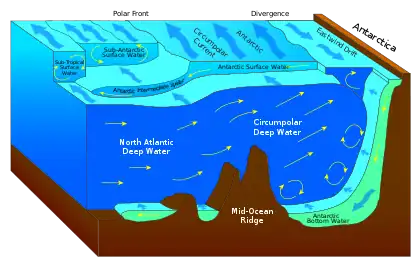
Downwelling occurs in anti-cyclonic regions of the ocean where warm rings spin clockwise, causing surface convergence. When these surface waters converge, the surface water is pushed downwards. Downwelling can also occur as a result of the wind driving the sea towards the coastline. Downwelling regions have low productivity because the nutrients in the water column are used but are not continuously replenished by cold, nutrient-rich water from below the surface.[1]
Oxygenation
Downwelling also allows for deep ocean oxygenation to occur because these waters are able to bring dissolved oxygen down from the surface to help facilitate aerobic respiration in organisms throughout the water column. Without this renewal, the dissolved oxygen in the sediment and within the water column would be quickly used up by biological processes and anaerobic bacteria would take over decomposition, leading to a build-up of hydrogen sulfide. In these toxic conditions, there are very few benthic animals that would survive. In the most extreme cases, a lack of downwelling could possibly lead to mass extinction. Paleontologists have suggested that 250 million years ago, deep ocean ventilation slowed nearly to a halt, and the ocean became stagnant. Sulfide and methane-rich waters low on oxygen filled the deep ocean and progressed onto the continental shelves, wiping out 95% of all marine species in the greatest extinction event in Earth's history, the Permian extinction.[2]
Locations
Downwelling occurs in polar regions where ice formation causes the remaining water to become saltier and therefore denser, in the subpolar gyre of the North Atlantic where several surface currents meet, and where cold waters meet warmer waters, such as along the outermost boundary of the Southern Ocean where cold Antarctic water sinks below warmer South Pacific and South Atlantic waters.[3] There is also downwelling on a few coastlines where the wind blows in such a direction that it causes Ekman transport to move water towards the coast, which then causes the water to pile up and be pushed down.[4]
Mantle downwelling
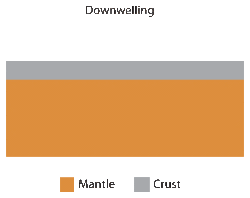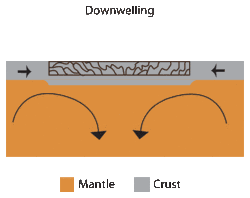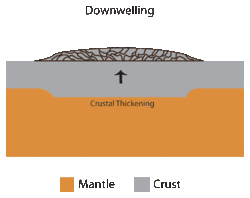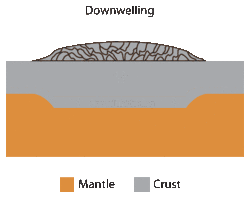
Downwelling can also be observed on the Earth's mantle[5][6] and is one of the models used to explain the formation of tessera on Venus.
See also
- Convection – Fluid flow that occurs due to heterogeneous fluid properties and body forces.
- Denmark Strait cataract – Underwater waterfall in the Atlantic
- Upwelling – Replacement by deep water moving upwards of surface water driven offshore by wind
References
- "Ocean Motion : Definition : Wind Driven Surface Currents - Upwelling and Downwelling". Retrieved 12 March 2016.
- "NOAA Ocean Explorer: Education - Multimedia Discovery Missions - Lesson 8 - Ocean Currents - Activities: Currents and Marine Life". Retrieved 12 March 2016.
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (USA). "Thermohaline Circulation - Currents: NOAA's National Ocean Service Education". oceanservice.noaa.gov. Retrieved 2022-06-07.
- "G115 - Introduction to Oceanography". Retrieved 12 March 2016.
- "Dynamics of continents & basins: Sedimentary basins". geosci.usyd.edu.au. Retrieved 28 February 2021.
- Pysklywec, Russell N.; Shahnas, M. Hosein (2003). "Time-dependent surface topography in a coupled crust–mantle convection model" (PDF). Retrieved 28 February 2021.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help)