Elephantidae
Elephantidae is a family of large, herbivorous proboscidean mammals collectively called elephants and mammoths. These are large terrestrial mammals with a snout modified into a trunk and teeth modified into tusks. Most genera and species in the family are extinct. Only two genera, Loxodonta (African elephants) and Elephas (Asian elephants), are living.
| Elephantidae Temporal range: | |
|---|---|
.jpg.webp) | |
| A male Asian elephant (Elephas maximus) in the wild at Bandipur National Park in India | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Proboscidea |
| Superfamily: | Elephantoidea |
| Family: | Elephantidae Gray, 1821 |
| Type genus | |
| Elephas | |
| Genera[1] | |
| |
| Synonyms[4] | |
| |
The family was first described by John Edward Gray in 1821,[5] and later assigned to taxonomic ranks within the order Proboscidea. Elephantidae has been revised by various authors to include or exclude other extinct proboscidean genera.
Description
Elephantids are distinguished from more primitive proboscideans like gomphotheres by their teeth, which have parallel lophs (homologous to the cusp pairs of more primitive proboscideans) bound by cement, allowing them to become more hypsodont (high-crowned) and more efficient in consuming grass.[6]
 Tooth of Mammut americanum (Mammutidae)
Tooth of Mammut americanum (Mammutidae) Molar of Gomphotherium angustidens, a "trilophodont gomphothere"
Molar of Gomphotherium angustidens, a "trilophodont gomphothere" Molar of Anancus, a "tetralophodont gomphothere"
Molar of Anancus, a "tetralophodont gomphothere" Molar of a modern African bush elephant (Loxodonta africana)
Molar of a modern African bush elephant (Loxodonta africana) Tooth of Mammuthus sp.
Tooth of Mammuthus sp.
Classification
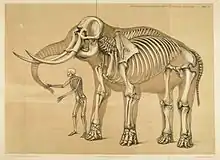

Scientific classification of Elephantidae taxa embraces an extensive record of fossil specimens, over millions of years, some of which existed until the end of the last ice age. Some species were extirpated more recently. The discovery of new specimens and proposed cladistics have resulted in systematic revisions of the family and related proboscideans.
Elephantids are classified informally as the elephant family, or in a paleobiological context as elephants and mammoths. The common name elephant primarily refers to the living taxa, the modern elephants, but may also refer to a variety of extinct species, both within this family and in others. Other members of the Elephantidae, especially members of the genus Mammuthus, are commonly called mammoths.
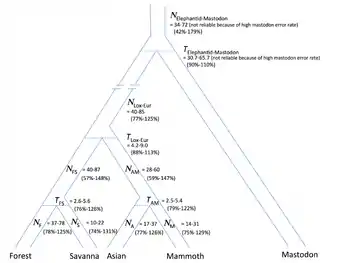
Taxonomy of elephantids based on nuclear genomes (ignoring hybridisation), according to Palkopoulou et al. 2018:[7]
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
- Elephantidae
- Loxodonta (African)
- L. africana African bush elephant
- L. cyclotis African forest elephant
- Elephas (Asiatic)
- E. maximus Asian elephant
- E. m. maximus Sri Lankan elephant
- E. m. indicus Indian elephant
- E. m. sumatranus Sumatran elephant
- E. m. borneensis Borneo elephant
- E. maximus Asian elephant
- Loxodonta (African)
Extinct species
- Elephantidae
- †Stegotetrabelodon
- S. syrticus
- S. orbus
- S. lybicus
- S. emiratus
- Subfamily Elephantinae
- †Primelephas
- P. gomphotheroides
- P. korotorensis
- Elephas
- Loxodonta
- †Palaeoloxodon
- P. recki
- P. antiquus
- P. namadicus
- P. naumanni
- P. creutzburgi
- P. xylophagou
- P. iolensis
- P. cypriotes
- P. lomolinoi
- P. tiliensis
- P. mnaidriensis
- P. falconeri
- †Mammuthus
- M. africanavus
- M. columbi
- M. creticus
- M. exilis
- M. lamarmorai
- M. meridionalis
- M. primigenius
- M. rumanus
- M. subplanifrons
- M. trogontherii
- Possibly †Stegodibelodon
- St. schneideri
- †Primelephas
- †Stegotetrabelodon
Evolutionary history
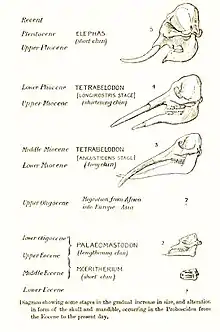
Elephantids are thought to have evolved from gomphotheres, with some authors proposing the most likely ancestors to be African species of the "tetralophodont gomphothere" Tetralophodon.[8] The earliest members of the family, are known from the Late Miocene, around 9–10 million years ago.[9] While early members of Elephantidae had lower tusks, these were lost in later members.[10] The modern genera of elephants and mammoths had diverged from each other by the end of the Miocene. Elephantids began to migrate out of Africa during the Pliocene, with mammoths and Elephas arriving in Eurasia around 3–3.8 million years ago.[11] Around 1.5 million years ago, mammoths migrated into North America.[12] At the end of the Early Pleistocene, around 0.8 million years ago, Palaeoloxodon migrated out of Africa, becoming widespread across Eurasia.[13] Palaeoloxodon and Mammuthus became extinct during the Late Pleistocene-Holocene, with the last population of mammoths persisting on Wrangel Island until around 4,000 years ago.[14]
References
- Shoshani, J.; Ferretti, M.P.; Lister, A.M.; Agenbroad, L.D.; Saegusa, H.; Mol, D.; Takahashi, K. (2007). "Relationships within the Elephantinae using hyoid characters". Quaternary International. 169–170: 174–185. Bibcode:2007QuInt.169..174S. doi:10.1016/j.quaint.2007.02.003.
- H. T. Mackaye, M. Brunet, and P. Tassy. 2005. Selenetherium kolleensis nov. gen. nov. sp.: un nouveau Proboscidea (Mammalia) dans le Pliocène tchadien. Geobios 38(6):765-777
- Kalb, J. E.; & Froehlich, D. J. (1995). "Interrelationships of Late Neogene Elephantoids: New evidence from the Middle Awash Valley, Afar, Ethiopia". Geobios. 28 (6): 727–736. doi:10.1016/s0016-6995(95)80068-9.
- Maglio, Vincent J. (1973). "Origin and Evolution of the Elephantidae". Transactions of the American Philosophical Society. 63 (3): 16. doi:10.2307/1006229. JSTOR 1006229.
- Gray, John Edward (1821). "On the natural arrangement of vertebrose animals". London Medical Repository. 15: 297–310.
- Lister, Adrian M. (2013-06-26). "The role of behaviour in adaptive morphological evolution of African proboscideans". Nature. 500 (7462): 331–334. Bibcode:2013Natur.500..331L. doi:10.1038/nature12275. ISSN 0028-0836. PMID 23803767. S2CID 883007.
- Eleftheria Palkopoulou; Mark Lipson; Swapan Mallick; Svend Nielsen; Nadin Rohland; Sina Baleka; Emil Karpinski; Atma M. Ivancevic; Thu-Hien To; R. Daniel Kortschak; Joy M. Raison; Zhipeng Qu; Tat-Jun Chin; Kurt W. Alt; Stefan Claesson; Love Dalén; Ross D. E. MacPhee; Harald Meller; Alfred L. Roca; Oliver A. Ryder; David Heiman; Sarah Young; Matthew Breen; Christina Williams; Bronwen L. Aken; Magali Ruffier; Elinor Karlsson; Jeremy Johnson; Federica Di Palma; Jessica Alfoldi; David L. Adelson; Thomas Mailund; Kasper Munch; Kerstin Lindblad-Toh; Michael Hofreiter; Hendrik Poinar; David Reich (2018). "A comprehensive genomic history of extinct and living elephants". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 115 (11): E2566–E2574. Bibcode:2018PNAS..115E2566P. doi:10.1073/pnas.1720554115. PMC 5856550. PMID 29483247.
- Geraads, Denis; Zouhri, Samir; Markov, Georgi N. (2019-05-04). "The first Tetralophodon (Mammalia, Proboscidea) cranium from Africa". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 39 (3): e1632321. Bibcode:2019JVPal..39E2321G. doi:10.1080/02724634.2019.1632321. ISSN 0272-4634. S2CID 202024016.
- H. Saegusa, H. Nakaya, Y. Kunimatsu, M. Nakatsukasa, H. Tsujikawa, Y. Sawada, M. Saneyoshi, T. Sakai Earliest elephantid remains from the late Miocene locality, Nakali, Kenya Scientific Annals, School of Geology, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Greece VIth International Conference on Mammoths and Their Relatives, vol. 102, Grevena -Siatista, special volume (2014), p. 175
- Mothé, Dimila; Ferretti, Marco P.; Avilla, Leonardo S. (2016-01-12). Beatty, Brian Lee (ed.). "The Dance of Tusks: Rediscovery of Lower Incisors in the Pan-American Proboscidean Cuvieronius hyodon Revises Incisor Evolution in Elephantimorpha". PLOS ONE. 11 (1): e0147009. Bibcode:2016PLoSO..1147009M. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0147009. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 4710528. PMID 26756209.
- Iannucci, Alessio; Sardella, Raffaele (March 2023). "What Does the "Elephant-Equus" Event Mean Today? Reflections on Mammal Dispersal Events around the Pliocene-Pleistocene Boundary and the Flexible Ambiguity of Biochronology". Quaternary. 6 (1): 16. doi:10.3390/quat6010016. ISSN 2571-550X.
- Lister, A. M.; Sher, A. V. (November 13, 2015). "Evolution and dispersal of mammoths across the Northern Hemisphere". Science. 350 (6262): 805–809. Bibcode:2015Sci...350..805L. doi:10.1126/science.aac5660. PMID 26564853. S2CID 206639522.
- Lister, Adrian M. (2004), "Ecological Interactions of Elephantids in Pleistocene Eurasia", Human Paleoecology in the Levantine Corridor, Oxbow Books, pp. 53–60, ISBN 978-1-78570-965-4, retrieved 2020-04-14
- Arppe, Laura; Karhu, Juha A.; Vartanyan, Sergey; Drucker, Dorothée G.; Etu-Sihvola, Heli; Bocherens, Hervé (October 2019). "Thriving or surviving? The isotopic record of the Wrangel Island woolly mammoth population". Quaternary Science Reviews. 222: 105884. Bibcode:2019QSRv..22205884A. doi:10.1016/j.quascirev.2019.105884. hdl:10138/309133. S2CID 203103403.
External links
 Media related to Elephantidae at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Elephantidae at Wikimedia Commons Data related to Elephantidae at Wikispecies
Data related to Elephantidae at Wikispecies


