Konobelodon
Konobelodon is an extinct genus of amebelodont from southern Europe, China, and North America.
| Konobelodon Temporal range: Miocene, | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Mandible of Konobelodon britti on display at the State Museum of Pennsylvania | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Proboscidea |
| Family: | †Amebelodontidae |
| Genus: | †Konobelodon Lambert, 1990 |
| Species | |
Taxonomy
Konobelodon was originally coined as a subgenus of Amebelodon,[2] and was subsequently elevated to full generic rank in a 2014 re-appraisal of "Mastodon" atticus.[3] Within Amebelodontinae, Konobelodon is closely related to Platybelodon and Torynobelodon.[1] The genus Konobelodon likely originated in eastern Eurasia, with K. robustus being known from the Liushu Formation in the Gansu Province of China.[4] Under this hypothesis, it diverged via separate migrations westward into Europe and western Asia, represented by K. atticus, and eastward into North America, where the genus arrived c. 7 Ma and survived until the very end of the Miocene.[3]
Description
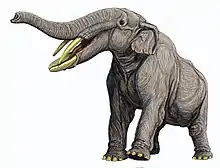
As shovel-tusked amebelodonts, Konobelodon has two pairs of tusks, one growing from the upper jaw and a second from the lower. K. robustus is estimated to have had a body mass between 2802 and 7367 kg, making it generally larger than gomphotheres on account of its thicker limb bones. Its standing posture, however, was not likely as column-like as that of extant elephants and American brevirostrine gomphotheres.[4]
References
- Wang, S.; SHI, Q.; HE, W.; Chen, S.; Yang, X. (2016). "— A new species of the tetralophodont amebelodontine Konobelodon Lambert, 1990 (Proboscidea, Mammalia) from the Late Miocene of China". Geodiversitas. 38 (1): 65–97. doi:10.5252/g2016n1a4. S2CID 87203029.
- Lambert, W. D. (1990). "Rediagnosis of the genus Amebelodon (Mammalia, Proboscidea, Gomphotheriidae) with a new subgenus and species, Amebelodon (Konobelodon) britti". Journal of Paleontology. 64 (6): 1032–1041. Bibcode:1990JPal...64.1032L. doi:10.1017/S0022336000019855. S2CID 131312289.
- Konidaris, G. E.; Roussiakis, S. J.; Theodorou, G. E.; Koufos, G. D. (2014). "The Eurasian occurrence of the shovel-tusker Konobelodon (Mammalia, Proboscidea) as illuminated by its presence in the late Miocene of Pikermi (Greece)". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 34 (6): 1437–53. Bibcode:2014JVPal..34.1437K. doi:10.1080/02724634.2014.873622. S2CID 84396676.
- Wang, ShiQi; Shi, QinQin; He, Wen; Chen, ShanQin; Yang, XiangWen (2016-03-25). "A new species of the tetralophodont amebelodontine Konobelodon Lambert, 1990 (Proboscidea, Mammalia) from the Late Miocene of China". Geodiversitas. 38 (1): 65–97. doi:10.5252/g2016n1a4. ISSN 1280-9659. S2CID 87203029.


