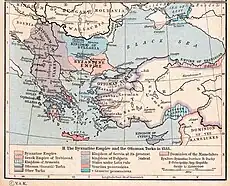
Fall of the Serbian Empire
The fall of the Serbian Empire was a decades-long process in the late 14th century. Following the death of childless Emperor Stefan Uroš V in 1371, the Empire was left without an heir and the magnates, velikaši, obtained the rule of its provinces and districts (in so called feudal fragmentation), continuing their offices as independent with titles such as gospodin, and despot, given to them during the Empire. This period is known as the dissolution or the beginning of the fall of the Serbian Empire.
| Fall of the Serbian Empire | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
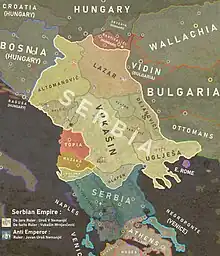 | |||||||
| |||||||
Between 1366 and 1371, King Vukašin was the co-ruler of Emperor Uroš, ruling the southern half, thus the Empire may be viewed as a de facto diarchy. Before 1371, the nobility were either directly subordinate to Emperor Uroš or to Vukašin. Vukašin died in the Battle of Maritsa (1371) against the invading Ottoman Empire, and southern Serbian provinces became nominal Ottoman vassals. Four months later, Uroš died. The lords could not agree on the rightful ruler; they dismissed Prince Marko, the son of Vukašin, and conflicts started between the nobles within a year. An assembly was held in 1374 without any success since the nobles were unable to agree on whether Marko or Prince Lazar would head the Serbian confederation as the Serbian king, and the state continued as before, fragmented and without central authority.
The period after the death of Uroš and Vukašin (1371–89) was marked with the rise and fall of Prince Lazar, and the power struggle of the minor provinces. Lazar ruled the most powerful Serbian principality, Moravian Serbia. The rule of Lazar ended with his death in the Battle of Kosovo in 1389, when Serbia stood up against invading Ottomans, an event that is deeply rooted in Serbdom. By 1395, most of the southern provinces had been conquered and annexed by the Ottomans, and the provinces of modern Central Serbia had accepted nominal Ottoman rule. Lazar was succeeded by his son, Stefan Lazarević, who ruled the rump Serbian Despotate, which finally fell to the Ottomans in 1459, thus marking the end of the medieval Serbian state.
Stefan Uroš V's rule
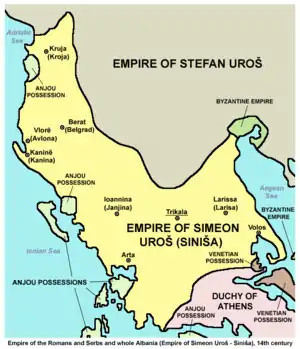
Emperor Dušan's son and heir Stefan Uroš V (1356–71), though by this time twenty years old, was weak, and unable to take forceful action against his nobles' separatist tendencies, hence his sobriquet "the Weak", as opposed to his father Dušan's, "the Mighty".
Dušan's half brother Simeon Uroš was expelled from Epirus and sought to obtain Serbia. He marched on Serbia in 1357 after he had himself proclaimed Tsar of the Greeks, Serbs, and Albanians at Kastoria in 1356. The forces of Stephen Uroš met the forces of Simeon near Scutari in Zeta and forced them to back down. Meanwhile, in the Serbian, Bulgarian and Byzantine borderlands of western Thrace, Matthew Kantakouzenos, the son of the Byzantine emperor John VI Kantakouzenos made war on the Serbs in 1356-57 but failed to capture Serres with his five-thousand Turks and was soon defeated in battle by Vojvoda Vojin and held for ransom. The ransom was paid by the Emperor John V Palaiologos and Matthew was allowed to retire to Morea. Now the lands that remained loyal to Uroš were most of Macedonia, including the land between the Struma and Mesta rivers and the Chalcidice peninsula. The lands that remained Serbian could be divided into three main parts: the western territories, including Zeta, the central Serbian lands of Uroš and the southern lands (including the eastern part of Macedonia with Serres its capital).
One of the strongest western nobles was Vojislav Vojinović and he quarreled with the Republic of Ragusa in the fall of 1358, when the Serbs and the Hungarians clashed along the Danube. The Hungarians penetrated deep into Serbian territory and the Serbian army retreated to avoid battle with the attackers. Vojislav waited until the Hungarians withdrew in 1359 then he attacked Ragusa. In 1363 the Hungarians and Wallachians were joined by Bosnian and Serbian forces committed to expel the Ottoman Turks from Europe. Caught by surprise near Adrianople, these forces were defeated by the Turks in 1364 on the banks of the Maritsa river. In 1365 Vukašin was proclaimed King of Serbia and co-ruler with Uroš, and Jovan Uglješa was made Despot in the Serbian principality of Serres.
History
Battle of Maritsa
There was a far more serious problem for Serbia — and the whole Balkans — than the internal squabbling of the Serbian nobles, and that was the advance of the Ottoman Turks in Europe. Followed by their penetration into Thrace, in 1354 they acquired Gallipoli on the European side of the Dardanelles. From there, they expanded into Thrace taking Demotika from the Byzantines in 1361 and Philippopolis from the Bulgarians in 1363 and finally in 1369 the major city of Adrianople. By 1370 Turks had occupied most of Thrace to the Rhodopes and to the Balkan Mountains. As they reached the Rhodopes they collided with Jovan Uglješa who had extended his realm beyond the Mesta into this territory and the threat from them became increasingly serious.
On September 26, 1371, King Vukašin with his brother Despot Jovan Uglješa led the Serb Army against the advancing Ottoman Empire led by the beylerbey of Rumeli Lala Şâhin Paşa at the Battle of Maritsa.[1] The offensive against the Turks was originally scheduled for early 1371, but was delayed perhaps because Uglješa had hoped that Bulgaria might also join the coalition. King Vukašin and his son Marko were in Scutari preparing for action against Nicholas Altomanovich when they were summoned east to join up with Uglješa and his army and then together they easily penetrated into what was supposedly Turkish territory and reached Cernomen on the Maritsa River, where the Serbs did not bother to post sentries or have scouts as did the Turks. Furthermore, they did not keep their horses or their weapons in readiness and they allowed themselves to be surprised. The Ottomans won the battle, as they attacked the Serbian army while they rested. The bodies of the commanders were not found.
Prince Marko inherited the royal title of his father, and became the co-ruler of Emperor Uroš.
Death of the Emperor
Stefan Uroš V died childless in December 2/4 1371, after much of the Serbian nobility had been destroyed by the Turks in the Battle of Maritsa earlier that year. Vukašin's son Marko inherited his father's royal title, and thus became the disputed successor of the Serbian throne, the nobles pursued their own interests, quarreling with each other.
Real power in northern Serbia was held by Prince Lazar. The latter did not assume the imperial or royal titles (associated with the House of Nemanjic), and in 1377 accepted king Tvrtko I of Bosnia (a maternal grandson of Serbian king Stefan Dragutin) as titular King of Serbia. Serbia proper became a vassal of the Ottomans in 1390 but remained effectively ruled by the Lazarevićs and then by their Brankovićs successors until the fall of Smederevo in 1459.
Đurađ II Balšić's edict
In 1372 Đurađ had succeeded his father Stracimir as the lord of Upper Zeta. Đurađ, in the standards of collective family reign, issued together with his uncles Balša II and presiding Đurađ I an edict in the Republic of Ragusa on 30 November 1373. The edict confirmed the laws of Emperor Stefan Uroš from the Serbian Nemanjić and gave privileges to Ragusian traders, including imposed taxes to the Adriatic City. It also included a unique clause, recognizing the sovereignty and territorial integrity of the Serbian Empire even though for years without an Emperor and any form of centralized strong authority, a note that if anyone became the new sovereign Emperor of the Serbs and the Serbian nobility and lands, all the points shall be transferred from the Balšićs to him. Đurađ I's logotet Vitko was the witness, as well as Dragaš Kosačić.[2] The collectivity of the family of the Balšićs marked this unique feudal system applied to their domain.
Plots against Marko
When his father died, "young king" Marko legally became a king and the co-ruler of Tsar Uroš. Soon afterwards came the end of the Nemanjić dynasty, when Uroš died on 2 or 4 December 1371, which formally made Marko the sovereign of the Serbian state. Serbian lords, however, did not even consider to recognize him as their supreme ruler,[3] and the separatism within the state increased even more.[4] After the demise of the two brothers and the destruction of their armies, the House of Mrnjavčević was left without any real power.[3] Lords surrounding Marko took the opportunity and seized significant parts of his patrimony. By 1372, Đurađ I Balšić grabbed Prizren and Peć, and Prince Lazar Hrebeljanović took Priština. By 1377 Vuk Branković acquired Skopje, and Albanian magnate Andrea Gropa became practically independent in Ohrid. The latter possibly remained a vassal to Marko as he had been to Vukašin.[4][5] Gropa's son-in-law was Marko's relative Ostoja Rajaković of the clan of Ugarčić from Travunia. He was one of the Serbian nobles from Zachlumia and Travunia (adjacent principalities in present-day Herzegovina) who had received lands in the newly conquered parts of Macedonia during Tsar Dušan's reign.[6]
After the Battle of Maritsa, Marko, the son of Vukašin Mrnjavčević, was crowned king and gained his father's lands. However, his friendship with the Balšićs soon crumbled. This was a result of Đurađ, in 1371, expelling his first wife Olivera, Marko's sister, and took Prizren from Marko. Lazar Hrebeljanović, prince of Moravian Serbia, conquered Priština in the same year. Đurađ took Peć a year later, stripping most of Marko's lands north of Šar mountain.[7]
Plot against Nikola
In the spring of 1371, Marko participated in the preparations for a campaign against Nikola Altomanović, the major lord in the west of the Empire. The campaign was planned jointly by King Vukašin and Đurađ I Balšić, the lord of Zeta, who was married to Olivera, the king's daughter. In July that year, Vukašin and Marko camped with their army outside Scutari, on Balšić's territory, ready to make an incursion towards Onogošt in Altomanović's land. The attack never happened, as the Ottomans threatened the land of Despot Jovan Uglješa, the lord of Serres, Vukašin's younger brother who ruled in eastern Macedonia. The forces of the Mrnjavčevićs were quickly directed eastward.[8][9] Having in vain looked for allies, the two brothers finally entered with their own troops into the territory controlled by the Ottomans. At the Battle of Maritsa on 26 September 1371, the Turks annihilated the Serbian army; not even the bodies of Vukašin and Jovan Uglješa were ever found. The place where it was fought, near the village of Ormenio in the east of present-day Greece, has ever since been called Sırp Sındığı "Serbian Rout" in Turkish. The outcome of this battle had serious consequences—it actually opened up the Balkans to the Turks.[10][11]
In 1371, Đurađ announced to Ragusan Republic that Vukašin Mrnjavčević and his son, Marko, along with their armies, were in Scutari with Đurađ, preparing an attack on Altomanović. Dubrovnik assisted their campaign by providing ships to transport men and supplies, since their campaign was in Dubrovnik's interests. However, the campaign never took place as Vukašin and Marko went to aid Vukašin's brother, Jovan Uglješa, in a campaign against the Turks, which ended up in total disaster that was the Battle of Maritsa. Altomanović though was now in even more trouble. Prince Lazar Hrebeljanović of Serbia and Ban Tvrtko I of Bosnia allied themselves to defeat Nikola Altomanović. Desperate for a strong ally, Altomanović began negotiations with Đurađ. Most historians agree that in concluding negotiations, Đurađ gained the towns of Trebinje, Konavle and Dračevica from Altomanović, possibly a bribe to remain neutral within the war. Other historians, however, follow Mauro Orbini's account and argue that Đurađ never concluded such an agreement, rather conquered the towns he gained from the agreement himself after Altomanović was defeated in 1373.[9]
Assembly of 1374
The Assembly (Sabor) took place on September 26, 1374, symbolically three years since the Battle at Maritsa. The Assembly was held to stop the discord between Serbian nobles. Marko and Lazar both claimed the titles of King, with Vuk Branković supporting Lazar.[12]
Crowning of Tvrtko
On 26 October 1377, Tvrtko had himself crowned as Stephen Tvrtko I, by the Grace of God, King of the Serbs, Bosnia and the Seaside and the Western Lands. Today, some historians consider that he was crowned in the Monastery of Mileševa, even though there is no evidence of that.[13] Another possibility, supported by archaeological evidences, is that he was crowned in Mile near Visoko in the church which was built in time of Stephen II Kotromanić's reign, where he was also buried alongside his uncle Stjepan II.[14][15] Stephen (Stefan) was the standard title of the rulers of the Nemanjić dynasty. In 1375–1377 Tvrtko created a unique genealogy that explicitly stated his descent from the Nemanjići.
Death of Balšić
Đurađ I died on 13 January 1378 in Scutari. However, recent studies now conclude that Đurađ died in 1379 rather than in 1378. The rule of Zeta was passed down to his younger brother, Balša II. Đurađ's death caused quite a stir between Zeta's neighbours. Bosnian Ban Tvrtko I annexed Đurađ's territories bordering Dubrovnik in 1377, along with the remainder of Đurađ's coastal lands between the Bay of Kotor and the land previously annexed in 1377 at the time of his death. Tvrtko secured these possessions through Đurađ's death, free of worry of any counter-attack.
Vuk Branković also took this opportunity to gain Đurađ's land. Branković sent his forces into Metohija and seized Prizren, along with the rest of Đurađ's holdings in the region.[16]
Rise of Lazar
"v leto 6889. godine ubi Crep i Vitomir Turke na Dubravci"
"In the summer of 1380, Crep and Vitomir killed the Turks on Dubravnica"
-Lazar's chronicles on his commanders[17]
By 1379, Prince Lazar Hrebeljanović, the governor of Pomoravlje, emerged as most powerful among the Serbian nobles. In his signatures, he titled himself as the "Autocrat of all the Serbs" (самодрьжць вьсѣмь Србьлѥмь); nevertheless, he was not powerful enough to unite all Serbian lands under his authority. The families of Balšić and Mrnjavčević, Konstantin Dragaš (maternally a Nemanjić), Vuk Branković, Tvrtko and Radoslav Hlapen, ruled in their respective domains without consulting with Lazar.[18] Another king besides Marko advanced on the political scene: in 1377, the Metropolitan of Mileševa crowned Tvrtko I, maternally related to the Nemanjići, "King of the Serbs, Bosnia and the Seaside and the Western Lands". He had previously taken some western parts of the former Serbian Empire.[19] After taking Nikola Altomanovic's lands in 1379, he subordinated Radič Branković.[20]
Battle of Kosovo

On 28 June 1389, Serbian forces led by Prince Lazar, Vuk Branković, and Tvrtko's nobleman Vlatko Vuković of Zachlumia, confronted the Ottoman army led by Sultan Murad I and his two sons Bayezid and Yakub. This was the Battle of Kosovo—the most famous battle in Serbia’s medieval history. If the earlier Battle of Maritsa was the beginning of the end of the Serbian Empire, then the Battle of Kosovo less than 20 years later was the death knell. The majority of the Serbian army was obliterated in battle, although it started out well for the Serbs; Vuk Brankovic, who led the Serbian right wing, routed the left wing of the Ottomans being led by another son of Murad, Yakub, after the Serbian heavy cavalry began the battle by hitting the Ottoman left hard and damaging their center, pushing them back and gaining the initial advantage. Murad's other son, Bayezid, commanded the Ottoman right, which was made up of four Turkish, two Serbian, and one Bulgarian division. He held off the forces of Vlatko Vukovic and the Serbian/Bosnian component of the Serbian left. Bayezid, with his reserves fresh and ready for battle, counterattacked Lazar's Serbs, who had been pushing hard against the Ottoman center. His troops broke through to the wounded Lazar himself, captured him and other Serbian nobles, and took them before the face of Murad, who by this point was dying after being stabbed by a Serbian false deserter, Milos Obilic. Before Murad's death, he watched the beheading of Lazar and the other nobles. While the Serbs then retreated, the Ottoman army also withdrew, due to their heavy casualties, and Bayezid returned to Adrianople to consolidate his hold on his new throne. The battle was clearly a loss for the Serbian prince and his vassals;[21] although they had destroyed most of the opposing force, few Serbian troops remained, while the Turks had many more troops in the east. Consequently, the Serbian principalities that were not already Ottoman vassals soon began to submit in the following years.[22]
The majority of the Serbian army was obliterated in battle;[22] but both Lazar and Murad lost their lives in it, and the remnants of their armies eventually retreated from the battlefield. Furthermore, in response to Turkish pressure,[23] some Serbian noblemen wed their daughters, including the daughter of Prince Lazar, to Bayezid.[24][25] In the wake of these marriages, Stefan Lazarević became a loyal ally of Bayezid, going on to contribute significant forces to many of Bayezid's future military engagements, including the Battle of Nicopolis. Eventually, the Serbian Despotate would, on numerous occasions, attempt to defeat the Ottomans in conjunction with the Hungarians until its final defeat in 1459 and again in 1540.
Administration

| Provinces | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Map | Name (Territory) | Ruler(s) | Notes | |
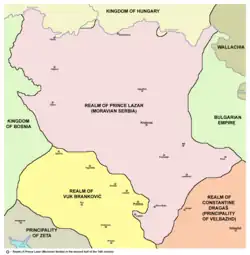 | Moravian Serbia (Central Serbia) | Lazar Hrebeljanović Stefan Lazarević | Ottoman vassal 1390- | |
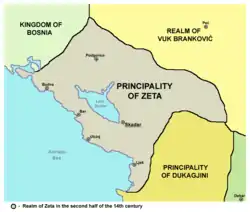 | Zeta Lordship (South Montenegro and northernmost Albania) | Balšić noble family | . | |
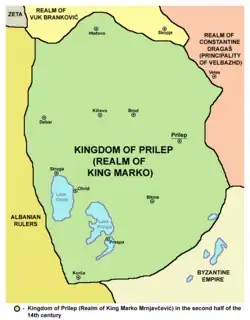 | Prilep Lordship (Western North Macedonia) | Marko Mrnjavčević | Becomes Ottoman vassal after Maritsa. | |
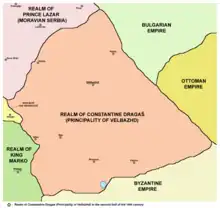 | Domain of the Dejanović family (Eastern North Macedonia) | Jovan Dragaš Konstantin Dejanović | Becomes Ottoman vassal after Maritsa. | |
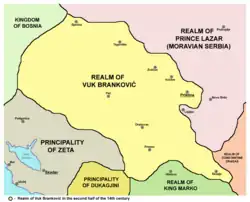 | Branković District (Lower Raška, Kosovo and Upper Vardar) | Vuk Branković Đurađ Branković | Ottoman vassal 1392-1396 | |
| Minor / Brief / : | ||||
 | Altomanović District (Herzegovina, Raška, North Kosovo and Zlatibor) | Nikola Altomanović | District conquered by neighbouring nobles by 1373. | |
Legacy
Serbian epic poems speak of the fall of the Serbian Empire.[26][27]
References
- Ostrogorsky 1956, pp. 481.
- Šuica 2000.
- Mihaljčić 1975, p. 168.
- Fine 1994, p. 379.
- Šuica 2000, pp. 35–36.
- Šuica 2000, p. 42.
- Fine 1994, p. 380.
- Mihaljčić 1975, p. 137.
- Fine 1994, p. 377.
- Fine 1994, p. 379-382.
- Ćorović 2001, Маричка погибија.
- Popović 1988, p. 18.
- Dr. Željko Fajfric: Kotromanići Archived 2013-10-23 at the Wayback Machine.
- Mile declared as national monument Archived 2008-02-03 at the Wayback Machine. 2003.
- Anđelić Pavao, Krunidbena i grobna crkva bosanskih vladara u Milima (Arnautovićima) kod Visokog. Glasnik Zemaljskog muzeja XXXIV/1979., Zemaljski muzej Bosne i Hercegovine, Sarajevo, 1980,183-247
- Fine 1994, p. 389.
- Stevanović, Miladin. "VUK BRANKOVIĆ: JUNAK ILI IZDAJNIK". Scribd. Archived from the original on 2010-06-09.
- Mihaljčić 1975, pp. 164–165, 220.
- Fine 1994, p. 393.
- Ćirković 2004, p. 81.
- Fine 1994, p. 408-411.
- Fine 1994, p. 408.
- Bloodlines: From Ethnic Pride to Ethnic Terrorism By Vamik D. Volkan, p. 61
- The Ottoman Empire, 1700-1922 By Donald Quataert, p. 26
- History of the Ottoman Empire and Modern Turkey By Stanford Jay Shaw, Ezel Kural Shaw, p. 24
- Stojan Novaković (1872). Kosovo Srpske narodne pjesme o boju na Kosovu: Pokusaj da se sastave u cjelinu kao spjev. Lavoslav Hartmán. pp. 10–.
- Propast carstva srpskog na kosovu: u narodnim pesmama. S.F. Ognjanović. 1910.
Sources
- Bataković, Dušan T., ed. (2005). Histoire du peuple serbe [History of the Serbian People] (in French). Lausanne: L’Age d’Homme. ISBN 9782825119587.
- Ćirković, Sima (2004). The Serbs. Malden: Blackwell Publishing. ISBN 9781405142915.
- Ćorović, Vladimir (2001). Istorija srpskog naroda (in Serbian) (Internet ed.). Belgrade: Ars Libri.
- "The Rise and Fall of the Serbian Empire and the Extinction of Serbian Independence". The Balkans: A History of Bulgaria, Serbia, Greece, Rumania, Turkey. Clarendon Press. 1915. pp. 89-102.
- Dvornik, Francis (1962). The Slavs in European History and Civilization. New Brunswick, New Jersey: Rutgers University Press.
- Fine, John Van Antwerp Jr. (1994) [1987]. The Late Medieval Balkans: A Critical Survey from the Late Twelfth Century to the Ottoman Conquest. Ann Arbor, Michigan: University of Michigan Press. ISBN 0472082604.
- Gavrilović, Zaga (2001). Studies in Byzantine and Serbian Medieval Art. London: The Pindar Press. ISBN 9781899828340.
- Mihaljčić, Rade (1975). Крај Српског царства [End of the Serbian Empire]. Belgrade: Srpska književna zadruga.
- Nicol, Donald M. (1993) [1972]. The Last Centuries of Byzantium, 1261-1453. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521439916.
- Nicol, Donald M. (1996). The Reluctant Emperor: A Biography of John Cantacuzene, Byzantine Emperor and Monk, c. 1295-1383. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521522014.
- Orbini, Mauro (1601). Il Regno de gli Slavi hoggi corrottamente detti Schiavoni. Pesaro: Apresso Girolamo Concordia.
- Орбин, Мавро (1968). Краљевство Словена. Београд: Српска књижевна задруга.
- Ostrogorsky, George (1956). History of the Byzantine State. Oxford: Basil Blackwell.
- Popović, Tatyana (1988). Prince Marko: The Hero of South Slavic Epics. New York: Syracuse University Press. ISBN 9780815624448.
- Sedlar, Jean W. (1994). East Central Europe in the Middle Ages, 1000-1500. Seattle: University of Washington Press. ISBN 9780295800646.
- Soulis, George Christos (1984). The Serbs and Byzantium during the reign of Tsar Stephen Dušan (1331-1355) and his successors. Washington: Dumbarton Oaks Library and Collection. ISBN 9780884021377.
- Šuica, Marko (2000). Немирно доба српског средњег века. Властела српских обласних господара. Službeni list SRJ. ISBN 978-86-355-0452-0.
- Раде Михаљчић (1975). Крај Српског царства. Српска књижевна задруга.
- Rade Mihaljčić (1989). Kraj srpskog carstva. Beogradski izdavačko-grafički zavod. ISBN 9788613003465.
Further reading
- Ferjančić, B. (1975) Vladarska ideologija u srpskoj diplomatici posle propasti Carstva, 1371. in: Božić I., Đurić B. [ed.] O knezu Lazaru, naučni skup, Kruševac, 1971, Beograd: Filozofski fakultet, 139-150
- Nikola B. Popović; Nikola Kusovac; Desanka Milošević; Velimir Vesović (1991). Ilustrovana istorija Srba: Propast srpskog carstva 1371-1389. Litera. ISBN 9788674670125.