Greenville, Indiana
Greenville is an incorporated town in Floyd County, Indiana. The population was 595 at the 2010 census. Greenville is located in the greater Louisville metropolitan area.
Greenville, Indiana | |
|---|---|
| Town of Greenville | |
 | |
 Location of Greenville in Floyd County, Indiana. | |
| Coordinates: 38°22′22″N 85°59′19″W | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Indiana |
| County | Floyd |
| Township | Greenville |
| Area | |
| • Total | 0.90 sq mi (2.34 km2) |
| • Land | 0.90 sq mi (2.34 km2) |
| • Water | 0.00 sq mi (0.00 km2) |
| Elevation | 827 ft (252 m) |
| Population (2020) | |
| • Total | 1,365 |
| • Density | 1,509.96/sq mi (582.88/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC-5 (EST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-4 (EDT) |
| ZIP code | 47124 |
| Area code(s) | 812 & 930 |
| FIPS code | 18-29844[3] |
| GNIS feature ID | 0435458[2] |
| U.S. Highway | |
| Major State Roads | |
| Website | http://www.visitgreenvillein.com |
History
Founding
Greenville was platted in 1816 by Andrew Mundell and Benjamin Haines some three years before Floyd County was established. During the first three years of Greenville's development, the village was a part of Clark County.[4]
John Baptiste Ford
Captain John Baptiste Ford found his way to Greenville as a 14-year-old runaway from Danville, Kentucky. Ford began as an apprentice with his future father-in-law in the local saddle shop which led him into his first business venture. Ford purchased the Old Mill and saddle shop from its owner, added a grocery and began making tin pie safes which he sold throughout the country. Later, Ford moved to New Albany and established several businesses, and became the first man to succeed in making plate glass in the United States. That success was the precursor to several glass companies, most notably the Pittsburgh Plate Glass Company now known as PPG. Ford became the father of American plate glass.[5]
That original building that housed the mill, saddle shop and grocery still stands today. Historically referred to as the Old Mill and Ford's Flour Mill, the Greenville Station is believed to be the oldest commercial building in Greenville. Construction on the original wooden structure began in 1810 and finished in 1812. In 1840, Ford helped to erect the present brick structure.[6] Besides housing Ford's grocery and the saddle shop, the Old Mill was the Greenville Post Office from 1823 until the early 1940s when it was relocated to H. Miller's house at the corner of East First Street and Hwy 150. The Station was a stop for the 104-mile stagecoach route that ran from Falls Cities to the Wabash River. The building also served as a stop along the Pony Express route from 1861 to 1867. The Greenville Station served as lodge hall for two civil organizations: the fraternal order of the Free and Accepted Masons and the International Order of Oddfellows. Through a majority of the early 20th century, the Greenville Station was referred to by the townspeople as the "lodge building" or the "lodge."[7]
Ford was on the board for the Floyd County Seminary from 1850 - 1852. Ford was a philanthropist and always gave back to the community even after he left Greenville. He paid for the construction of the Simpson Memorial United Methodist Church in 1899.[8] In 2017, the Greenville Town Council named a road "John Baptiste Ford Drive" to honor Ford's history and significant contributions to both the community and industrialism.[9] The Greenville Historic Preservation Commission had a historic marker approved by the Indiana Historic Bureau in 2019. The historic marker is the only John B. Ford specific historic marker in the country and the first IHB approved marker in Floyd County outside of New Albany.[10]
Civil War
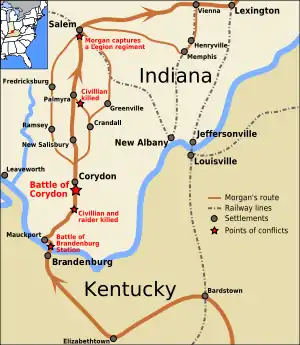
Morgan's Raid came through Greenville on July 10, 1863, led by Confederate General John Hunt Morgan. After the Battle of Corydon, Morgan sent a column of troops through Greenville. Confederate troops were reported east of Greenville, at eight o'clock, and some of the scouts burned the railroad bridge at Farrabee Station, fifteen miles further north, at ten o'clock.[11]
Greenville resident Ephraim L. Girdner enlisted with the Union Army in 1861. He was captured by the Confederates during the Battle of Richmond in 1862, he was promoted to Captain of his regiment in 1864, and was also part of Sherman's March to the Sea engaging is several battles along the way. Much of Girdner's communications and military documents during the Civil War were preserved by his family and donated as the "Girdner Papers" to the library at Emory University in Atlanta.[12]
County Seat
Early in Floyd County's history, Greenville was initially to be the county seat. It was proposed that either New Albany or Greenville would become the county seat. The contest was left up to who could make the largest donation. The contest was animated but New Albany added the donation of a bell for the court house. The offer of the bell was irresistible and vanquished Greenville from the contest.[13]
Incorporation
Greenville was surveyed by George Smith, county surveyor, and incorporated October 28, 1879.[14]
Fire of 1908
On March 26, 1908, a fire destroyed most of the town's original buildings. Today, the Station stands just two doors from one of the city's oldest home (rebuilt in 1908), which still boasts some of John B. Ford's original plate glass works.[15]
The Town Flag
The Greenville Town Flag was designed by Glenn Burkhart in 1969, then just a 5th grader at Greenville Elementary School. The design was part of a contest held by the Greenville Town Council and the Greenville Park Board. Glenn received a $25 bond as a prize for winning the contest. His original drawing and the original flag from 1969 have been preserved. The Greenville Historic Preservation Commission held a flag re-dedication ceremony in January 2019 for the Flag's 50 year anniversary.[16][17]
Churches
The Simpson Memorial United Methodist Church was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2004.[18]
Notable residents
- John Baptiste Ford lived in Greenville from 1825 to 1854 and pursued several business ventures while living in Greenville. After leaving Greenville, Ford went on to become an influential industrialist, eventually establishing Pittsburgh Plate Glass Company (now PPG Porter) and Michigan Alkali Company (went on to become BSAF).
- Norman Jay Colman In 1850, Colman became the first principal in Greenville when the Floyd County Seminary opened in town at the same location as the present day school. He went on to a successful political career including becoming the 1st Secretary of Agriculture appointed by President Grover Cleveland in 1889. In 2018, the Greenville Town Council named a road after Colman to honor his contributions to the community and to the agriculture industry.
- Roscoe Miller was a pitcher in MLB who played four seasons in 1901 - 1904 with the Detroit Tigers, New York Giants, and Pittsburgh Pirates. His rookie season was his best finishing 23–13 with 35 complete games which is still an American League rookie record.
Historic buildings
- Simpson Memorial United Methodist Church It was designed by church plan catalog architect Benjamin D. Price and built by Capt. John Nafius in 1899. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places on September 29, 2004.[8]
- Jersey Park Farm is a historic home and farm located just on the outskirts of Greenville. The farmhouse was built about 1875, and consists of a two-story, Federal style rectangular section with a two-story round section and one-story round section. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1984.
- The Station was built in 1840 by John Baptiste Ford and is the oldest commercial building in town.
Geography
Greenville is located at 38°22′22″N 85°59′19″W (38.372768, -85.988685).[19]

According to the 2010 census, Greenville has a total area of 0.78 square miles (2.02 km2), all land.[20]
The township is situated such that, clockwise, it borders the township of Jackson Township, Washington County to the northwest, Wood Township, Clark County to the northeast, Laffayette Township in Floyd County to the east, Georgetown Township to the south, Jackson Township, Harrison County to the southwest, and Morgan Township, Harrison County to the west.
Big and Little Indian Creeks meander through the township, which are tributaries in the Ohio River watershed.
Demographics
| Census | Pop. | Note | %± |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1880 | 394 | — | |
| 1890 | 313 | −20.6% | |
| 1900 | 309 | −1.3% | |
| 1910 | 227 | −26.5% | |
| 1920 | 225 | −0.9% | |
| 1930 | 257 | 14.2% | |
| 1940 | 285 | 10.9% | |
| 1950 | 298 | 4.6% | |
| 1960 | 453 | 52.0% | |
| 1970 | 611 | 34.9% | |
| 1980 | 537 | −12.1% | |
| 1990 | 508 | −5.4% | |
| 2000 | 591 | 16.3% | |
| 2010 | 595 | 0.7% | |
| 2020 | 1,365 | 129.4% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census[21] | |||
2010 census
As of the census[22] of 2010, there were 595 people, 219 households, and 162 families residing in the town. The population density was 762.8 inhabitants per square mile (294.5/km2). There were 241 housing units at an average density of 309.0 per square mile (119.3/km2). The racial makeup of the town was 95.5% White, 1.5% African American, 0.8% Native American, 0.8% Asian, 0.5% from other races, and 0.8% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 2.0% of the population.
There were 219 households, of which 40.6% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 56.6% were married couples living together, 11.9% had a female householder with no husband present, 5.5% had a male householder with no wife present, and 26.0% were non-families. 18.3% of all households were made up of individuals, and 8.3% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.72 and the average family size was 3.12.
The median age in the town was 40.3 years. 77% of residents were over the age of 18; 6.4% were between the ages of 20 and 24; 26.5% were from 25 to 44; 25.7% were from 45 to 64; and 14.7% were 65 years of age or older. The gender makeup of the town was 46.8% male and 53.2% female.[23]
2000 census
As of the census[3] of 2000, there were 591 people, 224 households, and 174 families residing in the town. The population density was 954.9 inhabitants per square mile (368.7/km2). There were 238 housing units at an average density of 384.6 per square mile (148.5/km2). The racial makeup of the town was 97.12% White, 0.34% African American, 1.02% Asian, 0.51% from other races, and 1.02% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 0.51% of the population.
There were 224 households, out of which 39.3% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 65.2% were married couples living together, 8.0% had a female householder with no husband present, and 22.3% were non-families. 19.6% of all households were made up of individuals, and 11.6% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.64 and the average family size was 3.03.
In the town, the population was spread out, with 28.4% under the age of 18, 4.4% from 18 to 24, 31.3% from 25 to 44, 23.5% from 45 to 64, and 12.4% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 37 years. For every 100 females, there were 101.0 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 96.7 males.
The median income for a household in the town was $49,271, and the median income for a family was $50,972. Males had a median income of $44,464 versus $26,484 for females. The per capita income for the town was $24,343. About 5.0% of families and 4.0% of the population were below the poverty line, including 2.1% of those under age 18 and 15.7% of those age 65 or over.
Education
The community is within the New Albany-Floyd County Consolidated School Corporation. Greenville is within the attendance boundaries of Greenville Elementary School,[24] Highland Hills Middle School,[25] and Floyd Central High School.[26]
Greenville Elementary School is located within the town limits.[27]
References
- "2020 U.S. Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved March 16, 2022.
- U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Greenville, Indiana
- "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 31, 2008.
- Floyd County Historical Society. This is Our Community. p. 222.|year=2009|Page=30
- William Earl Aiken. The Roots Grow Deep. Libbey Owens Ford Glass Company. p. 222.|year=1957|Page=2-4
- "Chapter XVI Greenville Township". LA Williams & Co, 1882. September 28, 2016. Retrieved September 28, 2016.
- Roberts Family (1993). "The History of the Station Building" (PDF).
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - "National Register of Historic Places Submission Form for the Simpson Memorial United Methodist Church" (PDF). August 11, 2004. Retrieved February 12, 2019.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - "John Baptiste Ford Drive". Town of Greenville. Greenville, Indiana. December 13, 2017. Retrieved February 12, 2019.
- "Greenville Approved for Historic Marker". News and Tribune. New Albany, Indiana. August 13, 2018. Retrieved February 12, 2019.
- Ewbank, Louis (September 11, 2015). Morgan's Raid in Indiana. Indianapolis: C. E. PAULEY & COMPANY. ISBN 978-1517286699.
- Ephraim Girdner Papers, United States census, 1861-1866; Emory University, Atlanta, Georgia; roll 468,.
- History of the Ohio Falls Cities and Their Counties. p. 222.|year=1882|publisher=L.A. Williams & Co.|page=293
- History of the Ohio Falls Cities and Their Counties. p. 222.|year=1882|publisher=L.A. Williams & Co.|page=298
- "Appeal for Aid: The Suffers from the Greenville Fire Appeal to the People in General for Assistance". August 31, 1908. Retrieved February 12, 2019.
- "Commission Rededicates Greenville Flag". News and Tribune. New Albany, Indiana. January 16, 2019. Retrieved February 12, 2019.
- "Historical Commission to Rededicate Greenville Flag". The Clarion. Corydon, Indiana. January 9, 2019. Retrieved February 12, 2019.
- "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places. National Park Service. July 9, 2010.
- "US Gazetteer files: 2010, 2000, and 1990". United States Census Bureau. February 12, 2011. Retrieved April 23, 2011.
- "G001 - Geographic Identifiers - 2010 Census Summary File 1". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved July 16, 2015.
- "Census of Population and Housing". Census.gov. Retrieved June 4, 2015.
- "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved December 11, 2012.
- "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved December 9, 2019.
- "Greenville Redistrict" (Archive). New Albany-Floyd County Consolidated School Corporation. Retrieved on April 9, 2015.
- <Highland Hills Middle School District Map> (Archive). New Albany-Floyd County Consolidated School Corporation. Retrieved on April 9, 2015.
- Floyd Central High School District Map (Archive). New Albany-Floyd County Consolidated School Corporation. Retrieved on April 9, 2015.
- Home page. Greenville Elementary School. Retrieved on April 9, 2015.