Guro District, Seoul
Guro District (Guro-gu) is a district of Seoul, South Korea, which was separated from Yeongdeungpo District on April 1, 1980. Located in the southwestern part of the city, where besides Yangcheon District and Geumcheon District Guro District has an important position as a transport link which contains railroads, land routes from the rest of Seoul to the south of the country. The Gyeongbu and Gyeongin railway lines connect Seoul to Busan and Incheon. In addition, Seoul Metropolitan Subway lines 1, 2, and 7, and major highways intersect in Guro District.
Guro
구로구 | |
|---|---|
| 구로구 · 九老區 | |
| Korean transcription(s) | |
| • Hangul | 구로구 |
| • Hanja | 九老區 |
| • Revised Romanization | Guro-gu |
| • McCune–Reischauer | Kuro-gu |
 Guro Digital Industrial Complex | |
 Flag | |
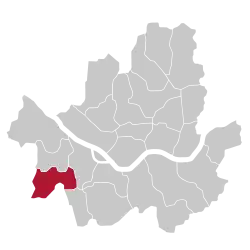 Location of Guro District in Seoul | |
| Coordinates: 37.495°N 126.887°E | |
| Country | South Korea |
| Region | Sudogwon |
| Special City | Seoul |
| Administrative dong | 15 |
| Area | |
| • Total | 20.11 km2 (7.76 sq mi) |
| Population (2010)[1] | |
| • Total | 417,339 |
| • Density | 21,000/km2 (54,000/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+9 (Korea Standard Time) |
| Postal code.. | 08200 ~ 08499 |
| Area code(s) | +82-2-2600,800~ |
| Website | Guro-gu official website |
The name Guro originates from the legend that nine (Korean: gu) old men (Korean: ro) enjoyed longevity in the district.
A digital industrial complex is located in Guro District. The Guro Digital Industrial Complex, which played a leading industrial role mainly with textile manufacturing, dressmaking and other labour-intensive industries in 1967, has been rapidly changed into an IT industrial complex. This complex played a pivotal role in the economic growth of the South Korea's development era, referred to as the "Miracle on the Han River", and also contributed 10 percent of national export in the 1970s.
Twenty-one percent of the total area of Guro District is a restricted zone to be used as a greenbelt with the only arboretum in Seoul. The zone is changing into a lively district as large labour-intensive factories are moving from the area and the council is developing what it terms its four zones.
An "e-government" system based on this hosted the international e-participation forum[2] on February 7–9, 2007, with the participation of more than thirty-seven countries. The forum was launched with the theme "Promoting Democracy and Regional Development" and twenty-five mayors including André Santini (Issy-les-Moulineaux, France), Kevin Foy (Chapel Hill, US), Apirak Kosayothin (Bangkok, Thailand), Uvais Mohamed Emthiyas (Colombo, Sri Lanka), and world experts such as Dr William H. Dutton (Director of Oxford Internet Institute at the University of Oxford, UK) and Dr Ari-Veiko Anttiroiko (professor at the University of Tampere, Finland) participated in the forum. The Guro Declaration,[3] adopted during the forum, aims to set up a portal site for e-government development and to establish a concrete project in order to bridge the digital divide among the world's cities. This practice has been recognised for providing a new important step in the development of e-democracy.
The e-participation forum was a key factor for Guro to play the leading role in bridging the digital divide among cities, to provide I.T. enterprises located in Guro Digital Industrial Complex the opportunity to launch into the international market, to improve its image and become a global leader to concrete e-democracy.
History

Early history
History of Guro can be divided into two origins: old Bupyeong and old Siheung areas.
The eastern part was known as Ingbeollo-hyeon (仍伐奴縣 – meaning ‘land spreading’) during the Goguryeo Dynasty (37 BC - AD 668) but it changed into Gogyang-hyeon (穀壤縣) in the period of the Unified Silla Dynasty (668 - 935), and again changed into Geumju (衿州) and Siheung (始興) during the Goryeo Dynasty (918 - 1392). Following a complete reorganisation of the district in 1413, it changed to Geumcheon-hyeon (衿川縣), later into Siheung-hyeon (始興縣) in 1795, and became part of Siheung-gun(始興郡), Gyeonggi Province, until 1949.
The western part was known as Jubuto-gun (主夫土郡) during the Goguryeo Dynasty (37 BC - AD 668) but it changed into Jangje-gun (長堤郡) in the period of the Unified Silla Dynasty (668 - 935), and again changed into Annam(安南), Gyeyang(桂陽), Gilju(吉州) and Bupyeong(富平) during the Goryeo Dynasty (918 - 1392). In Joseon era, this area was mainly part of Sutan Township of Bupyeong Dohobu or Bupyeong Metropolitan Prefecture. In 1895, Bupyeong Dohobu was downgraded to Bupyeong County, and it was merged with outer part of old Incheon City to form Bucheon County.
20th century
On August 13, 1949, the eastern part was incorporated in the enlarged administrative district of Seoul and eastern part of Sosa Town of Bucheon County was incorporated to Seoul in 1963. This area remained in the jurisdiction of Yeongdeungpo until April 1, 1980 when Guro became a new district.
Neighbourhoods of Cheolsan and Gwangmyeong were once considered for annexation to Guro, but the plan foundered as government officials were afraid of further boundary expansion of Seoul and consequently Gwangmyeong City was established in place of the annexation plan.
21st century
Textile manufacturing, dressmaking, and other labour-intensive industries declined after the 1990s and this affected regional development and became the cause of many problems.[4] Because of this, Guro District council has divided the district into four zones and has started developing each zone according to its characteristics in order to revitalise the economy of the area.[5] The four zones are: the Garibong Redevelopment Zone, Sindorim & Guro Stations area, the Gaebong Residential Area and the New Town Development on the Southwestern Outskirts.[6] After the reorganisation of the industrial structure in the late 1990s, more than 80% of I.T. companies settled in the area, creating the Guro Digital Industrial Complex. Meanwhile, many apartments were built replacing the old textile manufacturing factories to become a new, attractive residential area for south-west Seoul. The Development of Guro District's Four Zones is intended to be the centre for environmentally friendly residences, cutting-edge digital industry and logistics.
Geography
.jpg.webp)
There are nineteen dong in Guro District, which has an area of 20.11 km², covering 3.3% of the total area of Seoul. Among the nineteen dong, Oryu 2-dong is the largest (4.6 km²), while Garibong 2-dong is the smallest (0.14 km²). The district is composed of 7.08 km² (35.2%) which is residential, 0.42 km² (2.1%) commercial, 6.89 km² (34.3%) industrial and 5,72 km² (28.4%) as a green belt. The geography is mostly flat, but there are some hills in the western area of the district 100 m above sea level.
Two waterways run through the district - Anyangcheon (south to north, flowing into the Han River) and Dorimcheon (east to west, flowing into Anyangcheon).
Since 2005, Anyangcheon has been a protected wildlife zone with considerable efforts being undertaken by the Seoul city government to improve environmental conditions and increase the presence of wildlife and the associated habitats.[7]
Dorimcheon, on the other hand, has been extensively redeveloped and built over. For most of its course with Seoul and in Guro district in particular it runs through artificially created channels beneath or alongside Seoul Metro Line 2. Towards Sindorim station the stream reverts to a natural state and the surrounding area has been restored to provide habitats for wildlife and recreational facilities for the public.
Administrative divisions
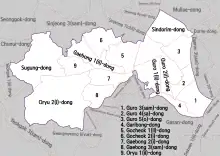
Guro District is composed of the 15 haengjeong-dong (dongs designated by administrative purpose)
- Garibong-dong (가리봉동 加里峰洞)
- Gaebong-dong (개봉동 開峰洞), further divided into Gaebong Dongs 1, 2, 3
- Gocheok-dong (고척동 高尺洞), further divided into Gocheok Dongs 1, 2
- Guro-dong (구로동 九老洞), further divided into Guro dongs 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
- Oryu-dong (오류동 梧柳洞), further divided into Oryu Dongs 1, 2
- Cheonwang-dong (천왕동 天旺洞), beopjeong-dong belonged to the hangjeong-dong, Oryu2-dong
- Hang-dong (항동 航洞), beopjeong-dong belonged to the hangjeong-dong, Oryu2-dong
- Sugung-dong (수궁동 水宮洞)
- Sindorim-dong (신도림동 新道林洞)
Economy


Guro Digital Complex
Guro Industrial Complex (later renamed Guro Digital Complex), the first industrial complex of the country, was created in Guro 3-dong in 1967. The World Industrial Exhibition held in Guro District in 1968 contributed to remarkable development of Guro Industrial Complex and the textile manufacturing, dressmaking, and other labour-intensive industries dubbed the "Miracle on the Han River" during the 1960s and 1970s. Guro Industrial Complex contributed 10% of national export. The Guro Industrial Complex has rapidly changed from a manufacturing industrial zone into a futuristic industrial hub, centering on research and development activities, advanced information and knowledge industries since 2000, and has developed into the largest digital industrial complex in Korea. As of 2008, there are about 8,000 venture companies with more than 100,000 staff in an area of two million m². Moreover, it is the hub for the nation's high-tech industry which continuously focuses on R&D, high-tech knowledge and information industry. More than 80% of the companies are I.T. companies with a total production of about 5.5 trillion won and an export of about 1.5 trillion won. Especially importantly, the Korea Venture Business Association is located in Guro Industrial Complex.
D-Cube City
D-Cube City is a large, integrated leisure complex immediately adjacent to Sindorim Station and modeled on the Roppongi Hills development in Tokyo.[8] It contains a Hyundai department store, a Sheraton hotel, a Lotte Cinema and arts center, a park and apartment buildings. Construction began in 2007 and the complex was opened in 2011. The project cost 1.3 billion KRW and has served as a catalyst for development in the area.
Techno Mart
Guro district hosts one of the, large Techno Marts in Seoul, the other being in Gangbyeon on the north east side of the city.[9] The Guro Techno Mart is next to Sindorim Station and is home to large number of electronics stores, as well as other facilities including a wedding venue and an Emart.
Seoul Industrial Tools Commercial Complex
Owing to its industrial past, Guro district hosts the large Seoul Industrial Tools Commercial Complex which is located close to Guro Station on Line 1.[10] The large complex is primarily wholesale in nature but caters to a diverse range of customers from factories to individuals.[11] The complex was established in 1981 as a cooperative effort by local businesses. As of 2008 the complex was home to 1,900 stores.[12]
Government and infrastructure



Local government
The administration of Guro District is mainly composed of digital, sanitary and welfare administration.
Digital administration
The digital administration is the embodiment of e-government standards. Guro District combines high tech information technology and administration to provide a digital administrative service to the citizens and a good business environment to companies.
- E-Services refers to e-procurement, health check-up appointments at the district public health centre, civil affairs, tailored bidding information services available via the Internet, a cyber culture centre and cyber shopping mall for business.
- E-Administration refers to e-approvals, knowledge management, and performance-based personnel management systems that allow quick and efficient administration with no use of paper.
- E-Information is the OPEN (Online Procedures Enhancement for Civil Applications) system, newsletters, Internet broadcasting and integrated administrative information system in order to provide citizens with real-time results on topics of civil affairs as well as a wide range of useful information.
- E-Participation is the email to the Mayor, environment-related reporting via the Internet, a Cyber Policy Forum, Cyber Citizen Panels, Citizen Opinion Polling with short message services via the Internet and mobile tools, contests for citizens' best ideas, submission of citizens' comments regarding regulations, and citizens participating in the budget process.
Sanitary administration
Sanitary Administration is concentrating its efforts to reduce environmental pollution and expand the green zone in the area of Guro Industrial Complex that was once seriously polluted. Many citizens are actively participating in environmental organisations such as Ansamo and Hwansamo. Especially, the Ggalggeumi Volunteers revived the practice of citizens cleaning up their neighborhood streets and roads on a daily basis with the participation of about 12,000 citizens, which became the first citizens’ voluntary organisation in the area of environment. Years of restoration efforts have resulted in upgrading the water quality of the Anyang Stream, and also the Dorim and Mokgam streams, which are tributaries of the Anyang stream, will be restored to be more ecologically sound rivers. The degree of air pollution in Guro District is about 0.004ppm of sulphuric acid gas and 0.4ppm of nitrogen monoxide, much lower than the average level of Seoul Metropolitan area and the WHO standard.
Welfare administration
Among many welfare administrative services, Guro District especially has the u-healthcare and supporting disabled people policy.
The u-healthcare system is the service provided by Guro Public Health Centre's doctors through mobile phones or PDA to patients with diabetes, blood pressure, obesity, respiratory disease and other conditions. Physicians retrieve data for diagnosis and treatment as needed. This service is provided either at home or at the dong office. This is the first time in the country that this kind of service has been executed using a high-tech healthcare system policy. Guro District runs the Welfare and Computer Education Centres for the disabled, lends equipment for low-income disabled, supports in-house repairing and provides many other facilities that made the district the top disabled supporter for the last 4 consecutive years among the 25 districts of Seoul.
National government
The Korea Transportation Safety Authority operates the Aviation Safety Center in Guro District.[13]
Healthcare
Guro district is home to numerous small hospitals and clinics. In addition, Korea University operates Korea University Guro Hospital within the district, the largest hospital in southwestern Seoul.[14]
Education

Guro District has a total of 83 education facilities: four universities, 11 high schools, 13 junior high schools, 23 elementary schools and 33 kindergartens. Furthermore, there are 33 public and private libraries with more than 420,000 books.
Dongyang Technical College provides education with a specialised curriculum focused mainly on high-tech practical training courses and supplies manpower to the companies located at the Guro Digital Industrial Complex.
Sungkonghoe University trains students who will work for public welfare, social services, human rights and peace of the world. It is also training students to work in industrial fields.
Dongyang Mirae University opened in 1965 (under the former name of Dongyang Advanced Industrial Technical School). The university focuses on STEM courses including chemistry, telecommunications engineering and system automation. The programs offered at the university are 3 to 4 years in length.
Seoul Hanyoung University is a postgraduate education provider with an academic focus on theology, divinity and counseling & psychology.[15]
Culture and sports
_05.jpg.webp)
The Jump Guro Festival is held for 3 days in mid-September every year. Some typical events of Jump Guro Festival are the Venturers' Necktie Marathon, e-sports tournament, performing entertainments and many other activities. A building for Art and Culture with two storeys below and six above ground, located in Guro-dong, has facilities for art performances such as orchestra, stage musicals, theatre and exhibitions.
Furthermore, Guro District has a wrestling team and has won a silver medal at the Olympics and a gold at the Asian Games.
Guro Cultural Foundation
Guro Cultural Foundation is the district level umbrella organization for all cultural activities in the district.[16] It manages numerous facilities within the distinct which host a range of musical, theatrical and other cultural groups. The most recently opened facility is the Sindorim Opera House which is located next to and above Sindorim Station.[17]
Chinatown
Guro district is home to one of two the town chinatowns in Seoul, the other being in Gwangjin district. The Guro chinatown straddles the border between Guro district and Yeongdeungpo district and strectches from Dearim-dong to the north to Namguro in the south.[18] The area is known for containing a significant number of Chinese restaurants and shops which primarily cater to the Chinese expatriate community in the area. This is particularly concentrated at Uma 2-gil, known as Yeonbyeon Street.[19] Namguro Market serves as the focal point for shopping in the area and is adjacent to Namguro station on Seoul Metro Line 7.
Gocheok Sky Dome
Guro district is home to Gocheok Sky Dome, a baseball venue which opened in 2015. It the home of KBO club Kiwoom Heroes. Since opening the stadium has been used extensively for national and international baseball events. The stadium has also hosted numerous international music concerts with performers such as Sam Smith, Queen and U2 all playing at the venue.[20]
Transportation

.jpg.webp)

Railroad
While the Gyeongbu line runs through Guro district, Korail does not serve or operate any stations in the district. The closest station is Yeongdeungpo station, approximately 1.5 km north east of Sindorim station.
Metro
There are two major metro interchanges within Guro district - Sindorim Station (Lines 1 and 2) and Daerim (Lines 2 and 7). Sindorim station is one of the busiest transfer points in Seoul with over 320,000 people using the station daily.[21]
- Seoul Subway Line 1 (Gyeongbu Line)
- (Yeongdeungpo-gu) ← Sindorim — Guro → (Geumcheon-gu)
- Seoul Subway Line 1 (Gyeongin Line)
- Seoul Subway Line 2 Circle Line
- (Dongjak-gu) ← Guro Digital Complex — Daerim — Sindorim → (Yeongdeungpo-gu)
- Seoul Subway Line 2 Sinjeong Branch
- Sindorim — Dorimcheon → (Yangcheon-gu)
- (Yeongdeungpo-gu) ← Namguro → (Geumcheon-gu) — (Gwangmyeong) ← Cheonwang — Onsu → (Bucheon)
Bus
City buses run on major streets and the town buses reach every corner of the district where city buses do not. The Gyeong-in (Seoul-Incheon) motorway runs through Guro District and has a median bus lane system which allows buses to avoid heavy traffic, and the buses that provides services to Incheon International Airport take about one hour from the district.
Airport Limousine Bus
Guro district is served by two airport limousine bus services. Service 6003 stops at Guro Station, Guro district office and Daerim Station.[22] Service 6018 stops at the Sheraton hotel at Sindorim.[23] Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, both services are suspended.
GTX
Construction of the new high speed commuter rail service, GTX, commenced in 2017. Three separate lines - A, B & C are under construction or in the planning stage. GTX B will, once completed, connect Sondgo, Incheon, in the Southwest and Maseok in Namyangju, in the Northeast. Sindorim will be one of the GTX B stations located within Seoul, along with Yeouido, Yongsan and Seoul Station. Construction of GTX B will commence in 2022.
International relations

Acting as Vice-Chair City of Global Cities Dialogue (GCD) for the Asian Region, Guro District has also participated at the World e-Gov Forum as the guest of honour and Mayor Yang gave a speech during the Opening Ceremony. Also, a close sister relationship with Issy-les-Moulineaux created the Guro Esplanade in Issy and hoisted the flag of South Korea in front of the City Hall of Issy-les-Moulineaux. Guro District hosted the e-Participation Forum from February 7 to February 9, 2007 with the participation of 700 people from more than 37 countries.
Sister cities
 Issy-les-Moulineaux, France
Issy-les-Moulineaux, France Pingdu, China
Pingdu, China Tongzhou, China
Tongzhou, China
Friendship cities
 Chapel Hill, United States
Chapel Hill, United States Dadong, China
Dadong, China Xiangfang, China
Xiangfang, China Kuching, Malaysia[24]
Kuching, Malaysia[24]
Tourist attractions
- Nine Scenic Views of Guro
- Pureun Arboretum and Hang-dong Railroad Track
- Anyangcheon Stream Walkway
- Myeongpum (Outstanding) Guro Olle Trail
- D-Cube City (D-Cube Department Store and Sheraton Hotel)
- Gocheok Sky Dome (Domed Baseball Park in Gocheok-dong)
- Guro Arts Valley Theater and Issy-les-Moulineaux Park
- Seoul Digital Industrial Complex (Former Korea Export Industrial Corporation)
- Namguro Market
- Tomb of Princess Jeongseon and Gung-dong Eco Park
Gallery
 Gungdong Ecological Park
Gungdong Ecological Park A Concert by the Seoul Philharmonic Orchestra conducted by Myung-Whun Chung in Guro District
A Concert by the Seoul Philharmonic Orchestra conducted by Myung-Whun Chung in Guro District Handprinting Ceremony Honoring Mayors from around the World
Handprinting Ceremony Honoring Mayors from around the World The Anyang Stream at night
The Anyang Stream at night Guro-gu Public Medical Centre
Guro-gu Public Medical Centre
References
- Korean Statistical Information Service (Korean) > Population and Household > Census Result (2010) > Population by Administrative district, Sex and Age / Alien by Administrative district and Sex, Retrieved 2010-06-02.
- "狭小土地活用で立派な住宅を建てる為に知っておきたいこと". www.eforum-guro.com.
- "Welcome to Guro District Office!!". Archived from the original on 2007-10-09.
- "Welcome to Guro District Office!!". english.guro.go.kr. Archived from the original on 9 October 2007. Retrieved 11 January 2022.
- "Welcome to Guro District Office!!". english.guro.go.kr. Archived from the original on 9 October 2007. Retrieved 11 January 2022.
- "Welcome to Guro District Office!!". english.guro.go.kr. Archived from the original on 9 October 2007. Retrieved 11 January 2022.
- "Archived copy". english.seoul.go.kr. Archived from the original on 20 June 2007. Retrieved 2 February 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - "D-Cube City becomes key Seoul landmark". 29 January 2012.
- "Techno Mart".
- "Tool complex in Guro is a Mr. Fix It paradise". 18 August 2008.
- "Tool complex in Guro is a Mr. Fix It paradise". 18 August 2008.
- "Tool complex in Guro is a Mr. Fix It paradise". 18 August 2008.
- "Aviation Safety Center." Korea Transportation Safety Authority. Retrieved on August 30, 2010.
- "Korea University Guro Hospital".
- "Seoul Hanyoung University :: International Graduate School".
- "메인 | 구로문화재단".
- "신도림 오페라하우스/지하소극장 | 구로문화재단".
- "Where to Find Real Chinese Food in Seoul | 10 Magazine". 14 November 2016.
- 김, 용필. "서울의 옌벤조선족마을, 중국동포타운 - 디지털구로문화대전". www.grandculture.net. Retrieved 2023-10-19.
- "Looking back at 14 years of Super Concert". 10 January 2020.
- "하루 환승 32만명 '역시 신도림'".
- "Line Route 6003 - 공항 - Bus Schedules".
- "6018 Route: Schedules, Stops & Maps - 쉐라톤서울디큐브시티호텔".
- "MBKS establishes relationship with Korean city". Borneo Post Online. 2012-08-30. Retrieved 2020-12-17.
External links
- Guro District website Archived 2015-05-15 at the Wayback Machine (in English)
