Henyey track
The Henyey track is a path taken by pre-main-sequence stars with masses greater than 0.5 solar masses in the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram after the end of the Hayashi track. The astronomer Louis G. Henyey and his colleagues in the 1950s showed that the pre-main-sequence star can remain in radiative equilibrium throughout some period of its contraction to the main sequence.
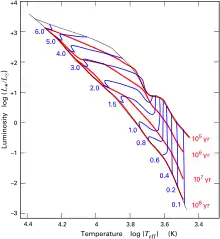
Stellar evolution tracks (blue lines) for the pre-main-sequence. The nearly-horizontal curves are called Henyey tracks.
High-mass stars have nearly horizontal evolution tracks from their birth until they arrive on the main sequence. Lighter stars, first follow the nearly-vertical Hayashi track before bending left into the Henyey track.
The end (leftmost point) of every track is labeled with the star's mass in solar masses, and represents its position on the main sequence. The red curves labeled in years are isochrones at the given ages. In other words, stars years old lie along the curve labeled , and similarly for the other 3 isochrones.
High-mass stars have nearly horizontal evolution tracks from their birth until they arrive on the main sequence. Lighter stars, first follow the nearly-vertical Hayashi track before bending left into the Henyey track.
The end (leftmost point) of every track is labeled with the star's mass in solar masses, and represents its position on the main sequence. The red curves labeled in years are isochrones at the given ages. In other words, stars years old lie along the curve labeled , and similarly for the other 3 isochrones.
The Henyey track is characterized by a slow collapse in near hydrostatic equilibrium, approaching the main sequence almost horizontally in the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram (i.e. the luminosity remains almost constant).[1]
See also
References
- Fang, Herczeg, Rizzuto (2017). "Age Spreads and the Temperature Dependence of Age Estimates in Upper Sco". The Astrophysical Journal. 842 (2): 123. arXiv:1705.08612. Bibcode:2017ApJ...842..123F. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aa74ca. S2CID 119087788.
- Henyey, L. G.; Lelevier, R.; Levée, R. D. (1955). "The Early Phases of Stellar Evolution". Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific. 67 (396): 154–160. Bibcode:1955PASP...67..154H. doi:10.1086/126791.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.