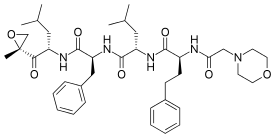
Carfilzomib
Carfilzomib, sold under the brand name Kyprolis, is an anti-cancer medication acting as a selective proteasome inhibitor. Chemically, it is a tetrapeptide epoxyketone and an analog of epoxomicin.[3] It was developed by Onyx Pharmaceuticals.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Kyprolis |
| Other names | PX-171-007 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a612031 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 97%[2] |
| Metabolism | Extensive; CYP plays a minor role |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.219.957 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C40H57N5O7 |
| Molar mass | 719.924 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved it in July 2012.[4][5]
Medical uses
The FDA approved carfilzomib in July 2012, for use in people with multiple myeloma who have received at least two prior therapies, including treatment with bortezomib and an immunomodulatory therapy (such as lenalidomide) and have demonstrated disease progression on or within 60 days of completion of the last therapy.[4]
Mechanism
Carfilzomib covalently [6] irreversibly binds to and inhibits the chymotrypsin-like activity of the 20S proteasome, an enzyme that degrades unwanted cellular proteins. Carfilzomib displays minimal interactions with non-proteasomal targets, thereby improving safety profiles over bortezomib.[6] Inhibition of proteasome-mediated proteolysis results in a build-up of polyubiquitinated proteins, which may cause cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, and inhibition of tumor growth.[3]
History
Carfilzomib is derived from epoxomicin, a natural product that was shown by the laboratory of Craig Crews at Yale University to inhibit the proteasome.[7] The Crews laboratory subsequently invented a more specific derivative of epoxomicin named YU101,[8] which was licensed to Proteolix, Inc. Scientists at Proteolix invented a new, distinct compound that had potential use as a drug in humans, known as carfilzomib. Proteolix advanced carfilzomib to multiple phase I and II clinical trials, including a pivotal phase 2 clinical trial designed to seek accelerated approval.[9] Clinical trials for carfilzomib continue under Onyx Pharmaceuticals, which acquired Proteolix in 2009.[9]
In January 2011, the FDA granted carfilzomib fast-track status, allowing Onyx to initiate a rolling submission of its new drug application for carfilzomib.[10] In December 2011, the FDA granted Onyx standard review designation,[11][12] for its new drug application submission based on the 003-A1 study, an open-label, single-arm phase IIb trial. The trial evaluated 266 heavily-pretreated patients with relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma who had received at least two prior therapies, including bortezomib and either thalidomide or lenalidomide.[13]
Initial approval was based on response rate.[4] Data demonstrating an overall survival benefit was demonstrated in the ENDEAVOR trial and approved by the FDA.[14]
Clinical trials & side effects
Completed
A single-arm, phase II trial (003-A1) of carfilzomib in patients with relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma showed that single-agent carfilzomib demonstrated a clinical benefit rate of 36% in the 266 patients evaluated and had an overall response rate of 22.9% and median duration of response of 7.8 months. The FDA approval of carfilzomib was based on results of the 003-A1 trial.[2]
In a phase II trial (004), carfilzomib had a 53% overall response rate among patients with relapsed and/or refractory multiple myeloma who had not previously received bortezomib. This study also included a bortezomib-treated cohort. Results were reported separately.[15] This study also found prolonged carfilzomib treatment was tolerable, with approximately 22% of patients continuing treatment beyond one year. The 004 trial was a smaller study originally designed to investigate the impact of carfilzomib treatment in relationship to bortezomib treatment in less heavily pretreated (1–3 prior regimens) patients.[16]
A phase II trial (005), which assessed the safety, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and efficacy of carfilzomib, in patients with multiple myeloma and varying degrees of renal impairment, where nearly 50% of patients were refractory to both bortezomib and lenalidomide, demonstrated that pharmacokinetics and safety were not influenced by the degree of baseline renal impairment. Carfilzomib was tolerable and demonstrated efficacy.[17]
In another phase II trial (006) of patients with relapsed and/or refractory multiple myeloma, carfilzomib in combination with lenalidomide and dexamethasone demonstrated an overall response rate of 69%.[18]
A phase II trial (007) for multiple myeloma and solid tumors showed promising results.[19][20]
In phase II trials of carfilzomib, the most common grade 3 or higher treatment-emergent adverse events were hematologic toxicity [21] with thrombocytopenia, anemia, lymphopenia, neutropenia, pneumonia, fatigue and hyponatremia.[22]
In a frontline phase I/II study, the combination of carfilzomib, lenalidomide, and low-dose dexamethasone was highly active and well tolerated, permitting the use of full doses for an extended time in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients, with limited need for dose modification. Responses were rapid and improved over time, reaching 100% very good partial response.[23]
Furthermore, gastrointestinal disturbances, including diarrhea and nausea are non hematologic group of side effects commonly reported with proteasome inhibitors.[21] Additionally, cardiovascular toxicity may be an outcome of carfilzomib treatment due to the effects on proteasomes in the myocardium.[21] Thus, patient evaluation and risk assessment prior to initiation of therapy with carfilzomib is crucial.[24]
ASPIRE trial
A phase III confirmatory clinical trial, known as the ASPIRE trial, compared carfilzomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (KRd) versus lenalidomide and dexamethasone (Rd) in patients with relapsed multiple myeloma and found improved progression-free survival and overall survival. Treatment discontinuation because of adverse effects occurred less frequently in the KRd arm, and events included thrombocytopenia, hypertension, and heart failure.[25][26]
Society and culture
Economics
Carfilzomib costs approximately US$10,000 per 28-day cycle.[27]
References
- "Prescription medicines: registration of new chemical entities in Australia, 2016". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). 21 June 2022. Retrieved 10 April 2023.
- "Kyprolis- carfilzomib injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution". DailyMed. 26 August 2020. Retrieved 13 November 2020.
- "NCI Drug Dictionary". National Cancer Institute. Retrieved 13 November 2020.
- "FDA Approves Kyprolis for Some Patients with Multiple Myeloma". FDA. 2012-07-20. Archived from the original on 2013-01-28. Retrieved 2013-07-23.
- "Drug Approval Package: Kyprolis (carfilzomib) for Injection NDA #202714". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 20 August 2012. Retrieved 10 April 2023.
- Park JE, Park J, Jun Y, Oh Y, Ryoo G, Jeong YS, et al. (May 2019). "Expanding therapeutic utility of carfilzomib for breast cancer therapy by novel albumin-coated nanocrystal formulation". Journal of Controlled Release. 302: 148–159. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.04.006. PMC 6638563. PMID 30954620.
- Meng L, Mohan R, Kwok BH, Elofsson M, Sin N, Crews CM (August 1999). "Epoxomicin, a potent and selective proteasome inhibitor, exhibits in vivo antiinflammatory activity". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 96 (18): 10403–8. Bibcode:1999PNAS...9610403M. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.18.10403. PMC 17900. PMID 10468620.
- Myung J, Kim KB, Lindsten K, Dantuma NP, Crews CM (February 2001). "Lack of proteasome active site allostery as revealed by subunit-specific inhibitors". Molecular Cell. 7 (2): 411–20. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(01)00188-5. PMID 11239469.
- "Carfilzomib: From Discovery To Drug". Chemical & Engineering News. 2012-08-27. Retrieved 2013-07-30.
- "Onyx multiple myeloma drug wins FDA fast-track status". San Francisco Business Times. 2011-01-31. Retrieved 2011-09-01.
- "Beacon Breaking News – Carfilzomib to Get Standard, Not Priority, FDA Review". The Myeloma Beacon. Retrieved 2012-02-27.
- "Fast Track, Accelerated Approval and Priority Review; Accelerating Availability of New Drugs for Patients with Serious Diseases". FDA. Archived from the original on 2012-02-17. Retrieved 2012-02-27.
- "PX-171-003-A1, an open-label, single-arm, phase (Ph) II study of carfilzomib (CFZ) in patients (pts) with relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma (R/R MM): Long-term follow-up and subgroup analysis". ASCO 2011; Abstract 8027. 2011. Archived from the original on 2012-03-23. Retrieved 2011-09-01.
- Broderick JM (18 January 2018). "FDA Approves Carfilzomib Label Update in Myeloma". OncLive. Retrieved 10 April 2023.
- Vij R, Siegel DS, Jagannath S, Jakubowiak AJ, Stewart AK, McDonagh K, et al. (September 2012). "An open-label, single-arm, phase 2 study of single-agent carfilzomib in patients with relapsed and/or refractory multiple myeloma who have been previously treated with bortezomib". British Journal of Haematology. 158 (6): 739–48. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2012.09232.x. PMC 5818209. PMID 22845873.
- Vij R, Wang M, Kaufman JL, Lonial S, Jakubowiak AJ, Stewart AK, et al. (June 2012). "An open-label, single-arm, phase 2 (PX-171-004) study of single-agent carfilzomib in bortezomib-naive patients with relapsed and/or refractory multiple myeloma". Blood. 119 (24): 5661–70. doi:10.1182/blood-2012-03-414359. PMC 4123327. PMID 22555973.
- Badros AZ, Vij R, Martin T, Zonder JA, Kunkel L, Wang Z, et al. (August 2013). "Carfilzomib in multiple myeloma patients with renal impairment: pharmacokinetics and safety". Leukemia. 27 (8): 1707–14. doi:10.1038/leu.2013.29. PMC 3740399. PMID 23364621.
- "European Hematology Association (EHA) 18th Congress. June 13-16, 2013". The Myeloma Beacon. 2013. Retrieved 2013-07-13.
- "Nikoletta Lendval, MD PhD et al. Phase II Study of Infusional Carfilzomib in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma". Presented at: 54th ASH Annual Meeting and Exposition: December 2012. Retrieved 2013-07-23.
- "Phase II results of Study PX-171-007: A phase Ib/II study of carfilzomib (CFZ), a selective proteasome inhibitor, in patients with selected advanced metastatic solid tumors" - ASCO 2009; Abstract 3515.
- Guerrero-Garcia TA, Gandolfi S, Laubach JP, Hideshima T, Chauhan D, Mitsiades C, et al. (December 2018). "The power of proteasome inhibition in multiple myeloma". Expert Review of Proteomics. 15 (12): 1033–1052. doi:10.1080/14789450.2018.1543595. PMID 30427223. S2CID 53303519.
- Siegel DS, Martin T, Wang M, et al. (2011-03-09). "Results of PX-171- 003-A1, an open-label, single-arm, phase 2 study of carfilzomib in patients with relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma. Presented at: 52nd ASH Annual Meeting and Exposition; December 4-7, 2010; Orlando, Florida". December 2010. OncLive.com. Retrieved 2011-09-01.
- "Final Results of a Frontline Phase 1/2 Study of Carfilzomib Lenalidomide, and Low-Dose Dexamethasone (CRd) in Multiple Myeloma (MM)". ASH 20111; Abstract 631. Retrieved 2012-02-27.
- Efentakis P, Kremastiotis G, Varela A, Nikolaou PE, Papanagnou ED, Davos CH, et al. (February 2019). "Molecular mechanisms of carfilzomib-induced cardiotoxicity in mice and the emerging cardioprotective role of metformin". Blood. 133 (7): 710–723. doi:10.1182/blood-2018-06-858415. PMID 30482794.
- "Phase 3 Study Comparing Carfilzomib, Lenalidomide, and Dexamethasone (CRd) Versus Lenalidomide and Dexamethasone (Rd) in Subjects With Relapsed Multiple Myeloma". ClinicalTrials.gov. 2011-08-04. Retrieved 2011-09-01.
- Stenger, Matthew (January 31, 2018). "ASPIRE Trial: Final Overall Survival Results in Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma". The ASCO Post. Retrieved March 28, 2021.
- "FDA Approves Kyprolis (Carfilzomib) For Relapsed And Refractory Multiple Myeloma". The Myeloma Beacon. Retrieved 2012-07-20.