Moselotte
The Moselotte (French pronunciation: [mozlɔt] ⓘ) is a river in Lorraine, in the French department of Vosges. It is a direct right tributary of the Moselle, and thus a sub-tributary of the Rhine.
| Moselotte | |
|---|---|
 The Moselotte flowing through Cornimont | |
  | |
| Location | |
| Country | France |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Mouth | Moselle |
• coordinates | 48.0137°N 6.6147°E |
| Length | 47.3 km (29.4 mi) |
| Basin size | 356 km2 (137 sq mi) |
| Discharge | |
| • average | 13.7 m3/s (480 cu ft/s) |
| Basin features | |
| Progression | Moselle→ Rhine→ North Sea |

Geography
The Moselotte rises in the massif des Vosges at the fontaine de la Duchesse, near the summit of Hohneck. It flows into the Moselle at Remiremont. Its length is 47.3 kilometres (29.4 mi),[1] while its watershed is 356 square kilometres (137 sq mi).
Communes traversed by the Moselotte
The Moselotte flows through, from upstream to downstream, the communes of La Bresse, Cornimont, Saulxures, Thiéfosse, Vagney, Saint-Amé, Le Syndicat, Dommartin-lès-Remiremont and Saint-Étienne-lès-Remiremont opposite the town of Remiremont.
Main tributaries
The Moselotte is fed by the following tributaries:
|
|
Lakes
The Moselotte watershed includes numerous natural lakes which are often enhanced by a small barrage, including lac de Blanchemer, lac de Lispach and lac des Corbeaux.
The presence of a high barrage at the foot of Kastelberg since 1983 has resulted in the appearance of the lac de la Lande. It collects water from several sources via conduits, and supplies the La Bresse commune with its energy.
At the entry downstream of Saulxures, a lake of 9.6 hectares (24 acres) was set up in 1998 under the name lac de la Moselotte which hosts a leisure center.
Hydrology – at Vagney station
Like the majority of Vosges rivers, the Moselotte is very substantial. Its flow rate has been observed during a period of 40 years Vagney at a place called Zainvilliers, which is upstream of the Moselotte's confluence with the Moselle.[2] The river's watershed at this point is 187 square kilometres (72 sq mi) or 53 percent of its entire watershed, corresponding to the upper half of its course.
The average interannual flow rate, or discharge at Vagney is 8.54 cubic metres per second (302 cu ft/s).
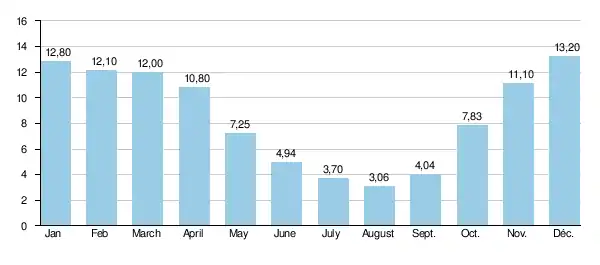
The Moselotte exhibits quite marked seasonal fluctuations, with a winter-spring period of high water whose monthly average flow rate is between 10.8 and 13.2 cubic metres per second (380 and 470 cu ft/s) from November to April inclusive, with a maximum in December. From the beginning of May, the flow rate falls off rapidly, reaching 3.06 cubic metres per second (108 cu ft/s) in August, which is not very severe for a body of water of this size. However year by year fluctuation can be more significant, as can those in the short term.
Average monthly flow rate of the Moselotte (m3/s) measured at Vagney hydrological station
Data taken over a 40-year period
At low water, the 3-year low instantaneous flow rate can drop to 0.37 cubic metres per second (13 cu ft/s) in the case of a dry five-year period, or about 370 litres per second (98 USgal/s), which is quite severe, but typical of rivers in the Moselle basin.
Floods can also be significant particularly bearing in mind the smallness of the watershed, only 187 square kilometres (72 sq mi). The maximum instantaneous flow rates over a 2-year and 5-year period (MIFR2 and MIFR5) measure 97 and 110 cubic metres per second (3,400 and 3,900 cu ft/s) respectively. The MIFR10 is 120 cubic metres per second (4,200 cu ft/s), the MIFR20 is 130 cubic metres per second (4,600 cu ft/s), while the MIFR50 rises to 150 cubic metres per second (5,300 cu ft/s).
The maximum instantaneous flow rate recorded at Vagney was 121 cubic metres per second (4,300 cu ft/s) on 15 February 1990, while the maximum daily average flow rate was 108 cubic metres per second (3,800 cu ft/s) on the same day. Comparing these values to the MIFR measurements for the river suggests that the flood on that day was approximately a 10-year event and thus likely to recur frequently.
Overall the Moselotte is an extremely abundant river in its upper course. The runoff curve number in this 53 percent of its watershed is 1,445 millimetres (56.9 in) annually, which is extremely high for the northern part of France, and more than four times higher than the French national average. It is also three times higher than the average over the French basin of the Moselle. The specific flow rate attaches to these facts the portentous figure of 45.7 litres per second per square kilometre of watershed.
Hydrology – at the confluence with the Moselle
The interannual flow rate/discharge of the Moselotte at its confluence with the Moselle is 13.7 cubic metres per second (480 cu ft/s), for a watershed of 356 square kilometres (137 sq mi).[3] The runoff curve number in its watershed is 1,214 millimetres (47.8 in), which is very high indeed, not merely much higher than the average for France (by more than a factor of three) with all basins included, but also much higher than the average for the French Moselle basin. In fact, the runoff curve number at Hauconcourt, located slightly downstream of the town of Metz, near where it leaves French territory, rises to 445 millimetres (17.5 in).[4] The specific flow rate of the Moselotte rises to 38.5 litres per second per square kilometre of watershed. This, along with the Breuchin (a tributary of the Lanterne and sub-tributary of the Saône which flows elsewhere in the same region) constitutes a record for the north third of France.
The Moselotte is clearly more abundant than the Moselle at their confluence, 13.7 cubic metres per second (480 cu ft/s) against 9.3 cubic metres per second (330 cu ft/s).[5]
Water quality
While in 2005, the water quality of the Moselotte was classified as category 1B, or "bonne" (good), the situation deteriorated somewhat in 2006, when the Rhine-Meuse water agency concluded that the river water analysed at the level of Autrive was now only "passable", or category 2.[6] The reason was a highly depressed rate of oxygen saturation (also classed as "passable"), which had gone from 76% in 2005 to 69% in 2006. The chemical oxygen demand, at 6.5 mg/L in 2006, was still classified "bonne". The ammonium ion level was measured at 0.09 mg/L, which was classed as "excellent".



Economy
Highly populated by trout, the river has given rise to a significant breakthrough in fish farming, namely the invention of artificial reproduction by Joseph Remy and Antoine Géhin in the 19th century. The Moselotte basin also has the highest density in the world in small hydroelectric barrages, which serve the watermills, sawmills, spinning and weaving houses along the river and its tributaries.
- The photograph opposite, taken upstream of La Bresse, shows a diversion powering a turbine. The main point has been equipped with a fish ladder.
A railway line once ran along the Moselotte valley between Remiremont and Cornimont. Today it has been transformed into a voie verte (green route) and replaced with bus service provided by TER Grand Est (line L09), extended to La Bresse.
See also
References
- Sandre. "Fiche cours d'eau - La Moselotte (A41-0200)".
- Banque Hydro – Station A4140202 – La Moselotte à Vagney (option Synthèse) (don't tick "Station en service")
- "Characteristic flow rates of the Moselotte" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2006-11-21. Retrieved 2011-09-24.
- Banque Hydro – Station A7930610 – La Moselle à Hauconcourt (Do not tick the box for "Station en service")
- "Characteristic flow rates of the Moselle upstream" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2006-11-21. Retrieved 2011-09-24.
- (in French)SIERM – Système d'Information sur l'Eau Rhin-Meuse: Qualité de l'eau superficielle (cours d'eau)
External links
- (in French) Description on the Pays de Remiremont website
- (in French) "Characteristic flow rates of the Moselotte" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2006-11-21. Retrieved 2011-09-24.