Murrumbidgee River
The Murrumbidgee River (/mʌrəmˈbɪdʒi/[6]) is a major tributary of the Murray River within the Murray–Darling basin and the second longest river in Australia. It flows through the Australian state of New South Wales and the Australian Capital Territory, descending 1,500 metres (4,900 ft) over 1,485 kilometres (923 mi),[2] generally in a west-northwesterly direction from the foot of Peppercorn Hill in the Fiery Range of the Snowy Mountains towards its confluence with the Murray River near Boundary Bend.
| Murrumbidgee River | |
|---|---|
 Murrumbidgee River at Wagga Wagga | |
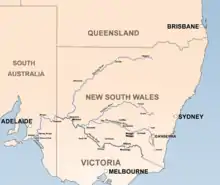 The Murrumbidgee is a major tributary of the Murray River | |
| Etymology | Aboriginal Wiradjuri language: "big water"[1] |
| Nickname(s) | 'bidgee |
| Location | |
| Country | Australia |
| State/Territory | |
| IBRA | |
| Districts | |
| Municipalities | |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Peppercorn Hill |
| • location | Snowy Mountains, NSW |
| • coordinates | 35°35′7″S 148°36′5″E |
| • elevation | 1,560 m (5,120 ft) |
| Mouth | confluence with Murray River |
• location | near Boundary Bend, NSW/Vic |
• coordinates | 34°43′43″S 143°13′8″E |
• elevation | 55 m (180 ft) |
| Length | 1,485 km (923 mi)[2] |
| Basin size | 84,917 km2 (32,787 sq mi) |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Wagga Wagga[3] |
| • average | 120 m3/s (4,200 cu ft/s)[3] |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Narrandera |
| • average | 105 m3/s (3,700 cu ft/s) |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Balranald |
| • average | 27 m3/s (950 cu ft/s) |
| Basin features | |
| River system | Murray River, Murray-Darling basin |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | Gudgenby River, Cotter River, Goodradigbee River, Tumut River |
| • right | Bredbo River, Molonglo River, Yass River, Lachlan River |
| Reservoirs | Tantangara Reservoir, Lake Burrinjuck |
| [4][5] | |
The word Murrumbidgee or Marrambidya means "big water" in the Wiradjuri language, one of the local Australian Aboriginal languages.[7][8][1][9] The river itself flows through several traditional Aboriginal Australian lands, home to various Aboriginal peoples. In the Australian Capital Territory, the river is bordered by a narrow strip of land on each side; these are managed as the Murrumbidgee River Corridor (MRC).[10] This land includes many nature reserves, eight recreation reserves, a European heritage conservation zone and rural leases.
Flow
The mainstream of the river system flows for 900 kilometres (560 mi).[11] The river's headwaters arise from the wet heath and bog at the foot of Peppercorn Hill situated along Long Plain which is within the Fiery Range of the Snowy Mountains; and about 50 kilometres (31 mi) north of Kiandra. From its headwaters it flows to its confluence with the Murray River. The river flows for 66 kilometres (41 mi) through the Australian Capital Territory near Canberra,[12] picking up the important tributaries of the Gudgenby, Queanbeyan, Molonglo and Cotter Rivers. The Murrumbidgee drains much of southern New South Wales and all of the Australian Capital Territory, and is an important source of irrigation water for the Riverina farming area.
The reaches of the Murrumbidgee in the Australian Capital Territory (ACT) are affected by the complete elimination of large spring snow melt flows and a reduction of average annual flows of almost 50%, due to Tantangara Dam.[13] Tantangara Dam was completed in 1960 on the headwaters of Murrumbidgee River and diverts approximately 99% of the river's flow at that point into Lake Eucumbene.[14][15] This has extremely serious effects on native fish populations and other native aquatic life and has led to serious siltation, stream contraction, fish habitat loss and other problems. The Murrumbidgee where it enters the ACT is effectively half the river it used to be.[15][16]
A study suggests a section of the upper river's channels are relatively new in geological terms, dating from the early Miocene (the Miocene era being from 23 to 5 million years ago). It is suggested that the Upper Murrumbidgee is an anabranch of the Tumut River (that once continued north along Mutta Mutta Creek) when geological uplift near Adaminaby diverted its flow. From Gundagai onwards the rivers flow within its ancestral channel.[17]
In June 2008 the Murray-Darling Basin Commission released a report on the condition of the Murray-Darling basin, with the Goulburn and Murrumbidgee Rivers rated in a very poor condition in the Murray-Darling basin with fish stocks in both rivers were also rated as extremely poor, with only 13 of the original 22 native fish species still found in the Murrumbidgee River.[18]
History
The Murrumbidgee River runs through the traditional lands of the Ngarigo, Ngunnawal, Wiradjuri, Nari Nari and Muthi Muthi Aboriginal peoples.
Exploration
The Murrumbidgee River was known to Europeans before it was first recorded by them. In 1820 the explorer Charles Throsby informed the Governor of New South Wales that he anticipated finding "a considerable river of salt water (except at very wet seasons), called by the natives Mur-rum-big-gee". In the expedition journal, Throsby wrote as a marginal note: "This river or stream is called by the natives Yeal-am-bid-gie ...".[19] The river he had stumbled upon was in fact the Molonglo River, Throsby reached the actual river in April 1821.[20]
In 1823, Brigade-Major John Ovens and Captain Mark Currie reached the upper Murrumbidgee when exploring south of Lake George.[21] In 1829, Charles Sturt and his party rowed down the lower half of the Murrumbidgee River in a stoutly built, large row-boat, from Narrandera to the Murray River, and then down the Murray River to the sea. They then rowed back upstream, against the current, to their starting point.[22] Sturt's description of their passage through the junction of the Murrumbidgee and Murray Rivers is dramatic. His description of wild strong currents in the Murrumbidgee—in the middle of summer (14 January 1830), when flows are declining and close to the seasonal summer/autumn minimum, are in contrast to the reduced flow seen at the junction today in mid-summer:
The men looked anxiously out ahead; for the singular change in the river had impressed on them an idea, that we were approaching its termination ... We were carried at a fearful rate down its gloomy and contracted banks ... At 3 p.m., Hopkinson called out that we were approaching a junction, and in less than a minute afterwards, we were hurried into a broad and noble river ... such was the force with which we had been shot out of the Morumbidgee, that we were carried nearly to the bank opposite its embouchure, whilst we continued to gaze in silent astonishment on the capacious channel [of the Murray River] we had entered ...
The Murrumbidgee basin was opened to settlement in the 1830s and soon became an important farming area.

Ernest Favenc, when writing on Australian exploration, commented on the relatively tardy European discovery of the river and that the river retained a name used by Indigenous Australians:
Here we may remark on the tenacity with which the Murrumbidgee River long eluded the eye of the white man. It is scarcely probable that Meehan and Hume, who on this occasion were within comparatively easy reach of the head waters, could have seen a new inland river at that time without mentioning the fact, but there is no record traceable anywhere as to the date of its discovery, or the name of its finder. When in 1823 Captain Currie and Major Ovens were led along its bank on to the beautiful Maneroo country by Joseph Wild, the stream was then familiar to the early settlers and called the Morumbidgee. Even in 1821, when Hume found the Yass Plains, almost on its bank, he makes no special mention of the river. From all this we may deduce the extremely probable fact that the position of the river was shown to some stockrider by a native, who also confided the aboriginal name, and so it gradually worked the knowledge of its identity into general belief. This theory is the more feasible as the river has retained its native name. If a white man of any known position had made the discovery, it would at once have received the name of some person holding official sway.[23]
Navigation
The river was once used as a transport route, with paddle steamers navigating the river as far as Gundagai. The river trade declined with the coming of the railways. Paddle steamers last used the Murrumbidgee in the 1930s. To allow the steamers and towed barges to pass, there were opening bridges at Hay , Balranald, and Carathool[24][25]
Floods

The river has risen above 7 metres (23 ft) at Gundagai nine times between 1852 and 2010, an average of just under once every eleven years. Since 1925, flooding has been minor with the exception of floods in 1974 and in December 2010, when the river rose to 10.2 metres (33 ft) at Gundagai.[26] In the 1852 disaster, the river rose to just over 12.2 m (40 ft). The following year the river again rose to just over 12.5 m (41 ft). The construction of Burrinjuck Dam from 1907 has significantly reduced flooding but, despite the dam, there were major floods in 1925, 1950, 1974 and 2012.[27][28]
The most notable flood was in 1852 when the town of Gundagai was swept away and 89 people, a third of the town's population, were killed. The town was rebuilt on higher ground.[29]
In 1925, four people died and the flooding lasted for eight days.[30][31][32]
The reduction in floods has consequences for wildlife, particularly birds and trees. There has been a decline in bird populations and black box flood plain eucalypt forest trees are starting to lose their crowns.[33]
Major flooding occurred during March 2012 along the Murrumbidgee River including Wagga Wagga, where the river peaked at 10.56 metres (34.6 ft) on 6 March 2012.[34] This peak was 0.18 metres (0.59 ft) below the 1974 flood level of 10.74 metres (35.2 ft).[28]
Wetlands
Major wetlands along the Murrumbidgee or associated with the Murrumbidgee catchment include:[35]
- Lowbidgee Floodplain, 2,000 square kilometres (772 sq mi) between Maude and Balranald
- Mid-Murrumbidgee Wetlands along the river from Narrandera to Carathool
- Fivebough and Tuckerbil Swamps
- Tomneys Plain
- Micalong Swamp
- Lake George
- Yaouk Swamp
- Black Swamp & Coopers Swamp
- Big Badja Swamp
Tributaries



The Murrumbidgee River has about 90 named tributaries in total; 24 rivers, and numerous creeks and gullies. The ordering of the basin, from source to mouth, of the major tributaries is:
| Rivers of the Murrumbidgee River basin | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Catchment river | Elevation at confluence[36] | River mouth | Coordinates[37][38] | River length[36] | ||||||
| Tributary | ||||||||||
| Tributary | ||||||||||
| Tributary | ||||||||||
| Murrumbidgee River | 55 m (180 ft) | Murray | 34°43′43″S 143°13′8″E | ~900 km (559 mi) | ||||||
| Numeralla River | 706 m (2,316 ft) | Murrumbidgee | 36°3′56″S 149°9′1″E | 94 km (58 mi) | ||||||
| Kybeyan River | 745 m (2,444 ft) | Numeralla | 36°13′13″S 149°21′25″E | 36 km (22 mi) | ||||||
| Big Badja River | 735 m (2,411 ft) | Numeralla | 36°10′27″S 149°20′52″E | 94 km (58 mi) | ||||||
| Bredbo River | Murrumbidgee | |||||||||
| Strike-a-Light River | Bredbo | |||||||||
| Gudgenby River | Murrumbidgee | |||||||||
| Naas River | Gudgenby | |||||||||
| Orroral River | Gudgenby | |||||||||
| Cotter River | Murrumbidgee | |||||||||
| Paddys River | Cotter | |||||||||
| Tidbinbilla River | Paddys | |||||||||
| Gibraltar Creek | Paddys | |||||||||
| Molonglo River | Murrumbidgee | |||||||||
| Jerrabomberra Creek | Molonglo | |||||||||
| Sullivans Creek | Molonglo | |||||||||
| Queanbeyan River | Molonglo | |||||||||
| Goodradigbee River | 345 m (1,132 ft) | Murrumbidgee | 35°00′S 148°38′E | 105 km (65 mi) | ||||||
| Yass River | 345 m (1,132 ft) | Murrumbidgee | 34°52′36″S 148°46′55″E | 139 km (86 mi) | ||||||
| Tumut River | 220 m (722 ft) | Murrumbidgee | 35°1′18″S 148°10′51″E | 182 km (113 mi) | ||||||
| Goobarragandra River | 272 m (892 ft) | Tumut | 35°20′S 148°15′E | 56 km (35 mi) | ||||||
| Doubtful Creek | 1,290 m (4,232 ft) | Tumut | 36°06′S 148°26′E | 15 km (9 mi) | ||||||
| Lachlan River | 68 m (223 ft) | Murrumbidgee | 34°22′S 143°47′E | ~1,440 km (895 mi) | ||||||
| Crookwell River | 430 m (1,411 ft) | Lachlan | 34°16′39″S 149°7′53″E | 78 km (48 mi) | ||||||
| Abercrombie River | 378 m (1,240 ft) | Lachlan | 34°01′S 149°28′E | 130 km (81 mi) | ||||||
| Bolong River | 569 m (1,867 ft) | Abercrombie | 34°08′S 149°37′E | 60 km (37 mi) | ||||||
| Isabella River | 479 m (1,572 ft) | Abercrombie | 34°00′S 149°39′E | 51 km (32 mi) | ||||||
| Boorowa River | 303 m (994 ft) | Lachlan | 33°57′S 148°50′E | 134 km (83 mi) | ||||||
| Belubula River | 263 m (863 ft) | Lachlan | 33°33′S 148°28′E | 165 km (103 mi) | ||||||
Population centres
River crossings
The list below notes past and present bridges that cross over the Murrumbidgee River. There were numerous other crossings before the bridges were constructed and many of these still exist today.
Downstream from Wagga Wagga
| Crossing | Image | Coordinates | Built | Location | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Balranald Bridge |  | 34°38′47.2″S 143°33′56.6″E | 1973 | Balranald | Sturt Highway | |
| Matthews Bridge |  | 34°28′40″S 144°18′03.4″E | 1957 | Maude | Work started on
a replacement for this bridge in 2020.[39] | |
| Hay Bridge |  | 34°30′58.4″S 144°50′32.4″E | 1973 | Hay | Cobb Highway | |
| Carrathool Bridge |  | 34°26′57.4″S 145°25′02.3″E | 1924 | Carrathool | ||
| Darlington Point Bridge |  | 34°34′01.2″S 146°00′09.5″E | 1979 | Darlington Point | Kidman Way | |
| Euroley Bridge | 34°38′19.6″S 146°22′25.8″E | 2003 | Yanco | |||
| Narrandera Rail Bridge |  | 34°45′30.7″S 146°32′08.5″E | 1885 | Narrandera | Tocumwal railway line | Not in use[40] |
| Narrandera Bridge |  | 34°45′20.8″S 146°32′53.7″E | Newell Highway | |||
| Collingullie Bridge |  | 35°01′59.3″S 147°06′29.6″E | Collingullie |
Wagga Wagga to Burrinjuck
| Crossing | Image | Coordinates | Built | Location | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gobbagombalin Bridge | .jpg.webp) | 1997 | Wagga Wagga | Olympic Highway | [41] | |
| Wiradjuri Bridge |  | 1995 | Hampden Avenue, replaced the Hampden Bridge | |||
| Hampden Bridge |  | 1895 | Demolished in 2014 | [42] | ||
| Murrumbidgee River Rail Bridge |  | 2006 | Main Southern railway line. Replaced the previous bridge built in 1881 | |||
| Eunony Bridge | .jpg.webp) | 1975
and 2020 |
Eunony Bridge Road, top bridge decking replaced in 2020 with the original pylons | |||
| Low Bridge |  | 35°04′42.3″S 147°49′17.7″E | Mundarlo | |||
| Sheahan Bridge |  | 35°04′05.9″S 148°05′42.8″E | 1977
and 2009 |
Gundagai | The bridge was duplicated in 2009.[43] Photograph shows Hume Highway; looking south from Gundagai, bridge in mid distance. | |
| Gundagai Rail Bridge |  | 35°04′23.7″S 148°06′16.2″E | 1902 | Tumut railway line, now disused | ||
| Prince Alfred Bridge |  | 35°04′27.8″S 148°06′24.8″E | 1867 | Prince Alfred Road, former Hume Highway. Main iron spans at southern end still in use for local traffic. Northern wooden spans now disused and in dilapidated condition. | ||
| Gobarralong Bridge |  | 34°59′34.2″S 148°14′13.2″E | Gobarralong | |||
| Jugiong Bridge | .JPG.webp) | 34°49′30.3″S 148°19′55.6″E | Jugiong | |||
Upstream from Burrinjuck
| Crossing | Image | Coordinates | Location | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taemas Bridge |  | 35°00′12.7″S 148°50′53.2″E | Wee Jasper | 1930 | |
| Uriarra Crossing |  | 35°14′38.0″S 148°57′07.1″E | Uriarra | ||
| Cotter Road bridge |  | 35°19′22.2″S 148°57′01.4″E | Australian Capital Territory | Cotter Road, near the confluence with the Cotter River | |
| Point Hut crossing |  | 35°27′07.1″S 149°04′25.4″E | Gordon | ||
| Tharwa Bridge |  | 35°30′30.9″S 149°04′13.9″E | Tharwa | 1895 | |
| Angle Crossing |  | 35°34′59.0″S 149°06′32.6″E | Williamsdale | Angle Crossing Road, a ford | |
| Bumbalong Bridge | .jpg.webp) |
35°51′31.266″S 149°08′4.780″E | Colinton | Little known and little used, low-level bridge that links the otherwise isolated locality of Bumbalong to the locality of Colinton. Bumbalong Road connects the local road from the bridge to the Monaro Highway at Colinton. | |
| Billilingra Bridge |  | 36°00′04.2″S 149°07′59.6″E | Billilingra | ||
| Binjura Bridge |  | 36°10′13.4″S 149°05′28.1″E | Binjura | ||
| Bolaro Bridge |  | 35°58′50.0″S 148°50′24.5″E | Bolaro | ||
| Yaouk Bridge |  | 35°49′34.1″S 148°48′10.9″E | Yaouk | ||
| Tantangara Bridge |  | 35°47′58.2″S 00°40′34.0″E | Tantangara | Tantangara Road, immediately downstream from the Tantangara Reservoir wall | |
| Tantangara Dam |  | 35°47′43.7″S 148°39′47.5″E | Tantangara | Tantangara Reservoir was constructed between 1958 and 1960. No public access to the dam to cross the river. | |
| Long Plain Bridge |  | Long Plain |
Images
.JPG.webp) Second photo of source and area of Murrumbidgee
Second photo of source and area of Murrumbidgee.JPG.webp) Water oozing from heath at source area of Murrumbidgee
Water oozing from heath at source area of Murrumbidgee Tantangara Dam
Tantangara Dam Yaouk Bridge
Yaouk Bridge Murrumbidgee at Bolaro
Murrumbidgee at Bolaro Tharwa Bridge looking south; Tharwa is to the right
Tharwa Bridge looking south; Tharwa is to the right Point Hut Crossing, ACT, looking south
Point Hut Crossing, ACT, looking south Junction with Cotter, in moderate flood
Junction with Cotter, in moderate flood Uriarra Crossing, ACT, in moderate flood
Uriarra Crossing, ACT, in moderate flood Approach to Taemas Bridge
Approach to Taemas Bridge Taemas Bridge, from north
Taemas Bridge, from north.JPG.webp) Jugiong Bridge
Jugiong Bridge The Prince Alfred bridge crosses the Murrumbidgee River at Gundagai, photographed c. 1885
The Prince Alfred bridge crosses the Murrumbidgee River at Gundagai, photographed c. 1885 The Murrumbidgee at Gundagai
The Murrumbidgee at Gundagai Murrumbidgee River Crossing at Mundarlo
Murrumbidgee River Crossing at Mundarlo Eunony Bridge viewed from Eunanoreenya looking towards Gumly Gumly
Eunony Bridge viewed from Eunanoreenya looking towards Gumly Gumly Former Wagga Wagga railway bridge
Former Wagga Wagga railway bridge New concrete railway bridge at Wagga Wagga
New concrete railway bridge at Wagga Wagga Hampden Bridge at Wagga Wagga
Hampden Bridge at Wagga Wagga Wiradjuri Bridge
Wiradjuri Bridge Gobbagombalin (Gobba) Bridge
Gobbagombalin (Gobba) Bridge
Distances along the river
- Gundagai to Wagga Wagga – 138 km (86 mi)
- Wagga Wagga to Yarragundy – 37 km (23 mi)
- Yarragundy to Yiorkibitto – 77 km (48 mi)
- Yiorkibitto to Grong Grong – 58 km (36 mi)
- Grong Grong to Narrandera – 21 km (13 mi)
- Narrandera to Yanco or Bedithera – 18 km (11 mi)
- Yanco to Yanco Station – 29 km (18 mi)
- Yanco to Gogeldrie – 21 km (13 mi)
- Gogeldrie to Tubbo – 24 km (15 mi)
- Tubbo to Cararburry – 55 km (34 mi)
- Cararbury to Carrathool – 66 km (41 mi)
- Carrathool to Burrabogie – 56 km (35 mi)
- Burrabogie to Illilliwa – 42 km (26 mi)
- Illilliwa to Hay – 22 km (14 mi)
- Hay to Toogambie – 63 km (39 mi)
- Toogambie to Maude – 40 km (25 mi)
- Maude to Lachlan Junction – 71 km (44 mi)
- Lachlan Junction to Balranald – 137 km (85 mi)
- Balranald to Canally – 42 km (26 mi)
- Canally to Weimby, Murray Junction – 61 km (38 mi)
- Total distance from Gundagai to Murrumbidgee Junction – 1,078 km (670 mi)[44]
See also
References
- "Murrumbidgee River". Geographical Names Register (GNR) of NSW. Geographical Names Board of New South Wales. Retrieved 8 June 2008.
- "Longest Rivers". Geoscience Australia. Australian Government. September 2008. Retrieved 18 March 2017.
- Green, D (2011). Water resources and management overview: Murrumbidgee catchment (PDF). NSW Office of Water. p. 14. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 April 2018. Retrieved 4 April 2016.
- "Our Catchment". Murrumbidgee Catchment Management Authority. Government of New South Wales. 2013. Archived from the original on 27 January 2014. Retrieved 22 January 2013.
- "Map of Murrumbidgee River". Bonzle.com. Retrieved 22 January 2013.
- Macquarie ABC Dictionary. The Macquarie Library Pty Ltd. 2003. pp. 647, 853. ISBN 1-876429-37-2.
- "Marrambidya Wetland". Visit Wagga. Retrieved 17 December 2021.
- Booth, Alison (8 May 2021). "An affecting tale of dispossession". Canberra Times. Retrieved 17 December 2021.
- Room, Adrian (2003). Placenames of the World. McFarland. p. 246. ISBN 0-7864-1814-1.
- "Murrumbidgee River Corridor" (PDF). Territory & Municipal Services. Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 April 2015. Retrieved 23 January 2014.
- "Murrumbidgee River Catchment". Catchment Case Studies. NSW Department of Environment and Conservation. 1995. Archived from the original on 19 April 2006. Retrieved 13 July 2006.
- "Interim recreation study for the natural areas of the ACT" (PDF). ACT Government. April 2004. p. 23. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 July 2008. Retrieved 8 June 2008.
- Expert panel environmental flow assessment of the upper Murrumbidgee River (Report). NSW Environmental Protection Authority. 1997.
- Lintermans, Mark. "The re-establishment of endangered Macquarie perch Macquaria australasica in the Queanbeyan River, New South Wales, with an examination of dietary overlap with alien trout" (PDF). Environment ACT and Cooperative Research Centre for Freshwater Ecology. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 August 2008. Retrieved 8 June 2008.
- "eflow panel 1997"
- Lintermans, Mark; Australian Capital Territory. Department of Urban Services; Cooperative Research Centre for Freshwater Ecology (Australia); Australian Capital Territory. Environment ACT (2000). The status of fish in the Australian Capital Territory : a review of current knowledge and management requirements. Environment ACT. ISBN 978-1-86331-473-2.
- Sharp, K. R. (2004). "Cenozoic volcanism, tectonism, and stream derangement in the Snowy Mountains and northern Monaro of New South Wales". Australian Journal of Earth Sciences. 51 (1): 67–83. Bibcode:2004AuJES..51...67S. doi:10.1046/j.1400-0952.2003.01045.x.
- Sustainable Rivers Audit (PDF). Murray-Darling Basin Commission. June 2008. pp. 14, 50. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 July 2008. Retrieved 21 June 2008.
- Official Year Book of the Commonwealth of Australia, 1931 (ABS cat. no. 1301.0)
- Reed, A. W., Place-names of New South Wales: Their Origins and Meanings, (Reed: 1969).
- "Discovery of the Monaro". Cooma-Monaro Shire Council. Archived from the original on 18 October 2015.
- Sturt, Charles (2004) [1833]. Two Expeditions into the Interior of Southern Australia (txt). Project Gutenberg EBook. Retrieved 26 August 2006.
- Favenc, Ernest (2004) [1908]. "Chapter 4". The Explorers of Australia and their Life-work (txt). Project Gutenberg EBook. Retrieved 26 August 2006.
- New bridges Main Roads September 1979 pages 3-5
- Bascule and Swing Span Bridges – Movable Span Bridge Study GHD Group pages 144, 147-149
- "Evacuation begins". The Daily Advertiser. 5 December 2010. Retrieved 5 December 2010.
- Butcher, Cliff (2002). "Chapter 9 Floods". Gundagai: A track winding back. Gundagai, NSW, Australia: A. C. Butcher. pp. 84–98. ISBN 0-9586200-0-8.
- "Murrumbidgee River & Floods". Wagga Wagga City Council. Retrieved 11 March 2012.
- "1852, June, Gundagai flood". Emergency New South Wales. Ministry of Police and Emergency Services. Archived from the original on 27 March 2011. Retrieved 23 April 2013.
- "Disastrous Floods. – Many Families Homeless – Four Men Drowned". The Argus. Melbourne. 29 May 1925. p. 11. Retrieved 18 July 2014 – via National Library of Australia.
- "HEAVY LOSSES AT GUNDAGAI". The Argus. Melbourne. 29 May 1925. p. 11. Retrieved 20 February 2016 – via National Library of Australia.
- Australian Government Emergency Management database Archived 24 September 2006 at the Wayback Machine
- Troy, Michael (23 October 2001). "Report warns of damage to Murrumbidgee River" (transcript). 7.30 Report. Australia: ABC1. Retrieved 22 January 2013.
- Kwek, Glenda (7 March 2012). "Wagga 'dodges a bullet' as severe weather warning issued for Sydney". Sydney Morning Herald. Retrieved 11 March 2012.
- NSW Department of Natural Resources Murrumbidgee Region Archived 23 February 2006 at the Wayback Machine
- "Search Rivers and Creeks". Bonzle Digital Atlas of Australia.
- "Place name search". Geographical Name Register. Geographical Names Board of New South Wales.
- "Gazetteer of Australia Place Name Search". Geoscience Australia. Australian Government.
- "New Bridge for Maude". Hay Shire Council. Retrieved 18 August 2023.
- "Narrandera Rail Bridge". Narrandera Tourism. Narrandera Shire Council. Retrieved 22 July 2020.
- "Wagga's Gobbagombalin bridge proves its worth". The Daily Advertiser. 9 December 2010. Retrieved 2 April 2015.
- Owen, Brodie (20 August 2014). "Hampden Bridge erased from Wagga's landscape". The Daily Advertiser. Retrieved 20 August 2014.
- Transport for NSW, N. S. W. "Sheahan Bridge duplication". Transport for NSW. Retrieved 27 April 2021.
- Heaton, J. H., 1984, The Bedside Book of Colonial Doings, Published in 1879 as Australian Dictionary of Dates containing the History of Australasia from 1542 to May, 1879, Angus & Robertson Publishers Sydney, pp.215-216
External links
- Nomination of Lower Murrumbidgee Catchment for UNESCO's HELP Pilot Demonstration Status by CSIRO
- Murrumbidgee River Flows recorded by NSW Water Archived 11 June 2018 at the Wayback Machine
- River pilot maps 1880-1918 / Echuca Historical Society
- Snowy Flow Response Monitoring and Modelling
- Murrumbidgee Catchment Management Authority Archived 26 January 2014 at the Wayback Machine website
- Upper Murrumbidgee Demonstration Reach "Map" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 April 2022. Retrieved 17 February 2013. 1.22MB
- "Murrumbidgee and Lake George catchments" (map). Office of Environment & Heritage. Government of New South Wales.
- "Murray River catchment (NSW)" (map). Office of Environment & Heritage. Government of New South Wales.