Mycoreovirus
Mycoreovirus is a genus of double-stranded RNA viruses in the family Reoviridae and subfamily Spinareovirinae. Fungi serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with this genus include: hypovirulence of the fungal host. The name of the group derives from Ancient Greek myco which means fungus. There are three species in this genus.[1][2]
| Mycoreovirus | |
|---|---|
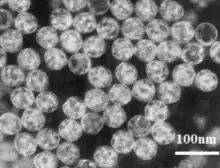 | |
| TEM of SsMYRV4 particles | |
| Virus classification | |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Realm: | Riboviria |
| Kingdom: | Orthornavirae |
| Phylum: | Duplornaviricota |
| Class: | Resentoviricetes |
| Order: | Reovirales |
| Family: | Sedoreoviridae |
| Subfamily: | Spinareovirinae |
| Genus: | Mycoreovirus |
Structure
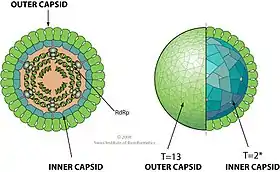
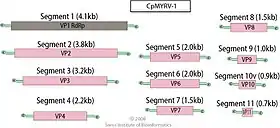
Viruses in genus Mycoreovirus are non-enveloped with icosahedral geometries. The outer capsid has T=13 symmetry and the inner capsid has T=2 symmetry. The diameter is around 80 nm. Genomes are linear and segmented, and around 23 kbp in total length. The genome codes for 12 proteins.[1]
Life cycle
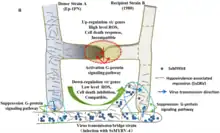
Viral replication is cytoplasmic. Entry into the host cell is achieved by attachment to host receptors, which mediates endocytosis. Replication follows the double-stranded RNA virus replication model. Double-stranded RNA virus transcription is the method of transcription. The virus exits the host cell by cell to cell movement, and monopartite non-tubule guided viral movement. Fungi serve as the natural host.[1]
| Genus | Host details | Tissue tropism | Entry details | Release details | Replication site | Assembly site | Transmission |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mycoreovirus | Fungi | Mycelium | Cell death; cytoplasmic exchange, sporogenesis; hyphal anastomosis | Cell death; cytoplasmic exchange, sporogenesis; hyphal anastomosis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasmic exchange, sporogenesis; hyphal anastomosis |
References
- "Viral Zone". ExPASy. Retrieved 15 June 2015.
- "Virus Taxonomy: 2020 Release". International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV). March 2021. Retrieved 13 May 2021.