Amyl acetate
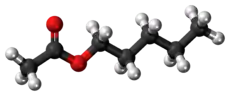
Amyl acetate (pentyl acetate) is an organic compound and an ester with the chemical formula CH3COO[CH2]4CH3 and the molecular weight 130.19 g/mol. It is colorless and has a scent similar to bananas[3][4] and apples.[5] The compound is the condensation product of acetic acid and 1-pentanol. However, esters formed from other pentanol isomers (amyl alcohols), or mixtures of pentanols, are often referred to as amyl acetate. The symptoms of exposure to amyl acetate in humans are dermatitis, central nervous system depression, narcosis and irritation to the eyes and nose.[3]
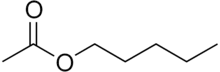 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Pentyl acetate | |
| Other names | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 1744753 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.044 |
| EC Number |
|
| MeSH | Amyl+acetate |
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | UN 1104 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H14O2 | |
| Molar mass | 130.19 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | Banana-like |
| Density | 0.876 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −71 °C (−96 °F; 202 K) |
| Boiling point | 149 °C (300 °F; 422 K) |
| Solubility in other solvents | Water: 1.73 mg/ml (25 °C) |
| Vapor pressure | 4 mmHg[1] |
| −89.06·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards |
Flammable |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 23 °C (73 °F; 296 K) |
| Explosive limits | 1.1–7.5%[1] |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
7400 mg/kg, oral (rabbit) 6500 mg/kg, oral (rat)[2] |
LCLo (lowest published) |
5200 ppm (rat)[2] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible) |
100 ppm, 8 hr TWA (525 mg/m3)[1] |
REL (Recommended) |
TWA 100 ppm (525 mg/m3)[1] |
IDLH (Immediate danger) |
1000 ppm[1] |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Uses
Amyl acetate is a solvent for paints, lacquers, and liquid bandages;[6] and a flavorant. It also fuels the Hefner lamp and fermentative productions of penicillin.
See also
- Isoamyl acetate, also known as banana oil.
- Esters, organic molecules with the same functional groups
References
- NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0031". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- "n-Amyl acetate". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). 4 December 2014. Retrieved 16 February 2015.
- "CDC - NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards - n-Amyl acetate". www.cdc.gov. Retrieved 7 July 2022.
Colorless liquid with a persistent banana-like odor.
- Stark, Norman (1975). The Formula Book. New York: Sheed and Ward. p. 28. ISBN 0-8362-0630-4.
- Thickett, Geoffrey (2006). Chemistry 2: HSC Course. Milton, Queensland, Australia: John Wiley & Sons. p. 227. ISBN 978-0-7314-0415-5.
- "New-Skin® Liquid Bandage—Inactive Ingredients". new-skin. Archived from the original on June 22, 2017. Retrieved July 4, 2017.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
