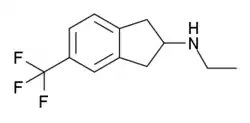
Ethyltrifluoromethylaminoindane
N-Ethyl-5-trifluoromethyl-2-aminoindane (ETAI) is a psychoactive drug and research chemical with putative entactogenic effects. It functions as a selective serotonin releasing agent (SSRA). ETAI is the aminoindane analogue of fenfluramine and is approximately 50% as neurotoxic in comparison.[1]
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H14F3N |
| Molar mass | 229.246 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.