Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast
The Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast (NKAO)[lower-alpha 1] was an autonomous oblast within the Azerbaijan Soviet Socialist Republic that was created on July 7, 1923. Its capital was the city of Stepanakert. The leader of the oblast was the First Secretary of the Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast Committee of the Communist Party of Azerbaijan. The majority of the population were ethnic Armenians.[3][4][5]
| Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Autonomous oblast of the Azerbaijan Soviet Socialist Republic | |||||||||||
| 1923–1991 | |||||||||||
.svg.png.webp) | |||||||||||
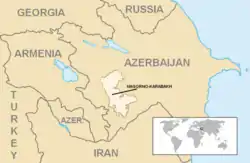 | |||||||||||
| Capital | Stepanakert | ||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||
• 1989[1] | 4,388 km2 (1,694 sq mi) | ||||||||||
| Population | |||||||||||
• 1989[2] | 189,085 | ||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||
| • Type | Autonomous Oblast | ||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||
• Established | 7 July 1923 | ||||||||||
• Abolished | 26 November 1991 | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
History
The area was disputed between Armenia and Azerbaijan during their short-lived independence from 1918 and 1920. After the Sovietization of Armenia and Azerbaijan, the Kavbiuro organisation decided to keep the area within the Azerbaijan SSR whilst granting it broad regional autonomy.[6] Initially, the principal city of Karabakh, Shusha, and its surrounding villages were to be excluded from the autonomy as they were predominantly Azerbaijani, particularly after the massacre and expulsion of the majority Armenian population of Shusha—this decision was later reversed in 1923 when Shusha was decided to join the NKAO despite protests from Muslim villages who favoured its inclusion into the Kurdistan uezd instead.[7]
On July 7, 1923, Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast was created and the capital was moved to Stepanakert.[8] At the time of its formation, its area was 4,161 km2 (1,607 sq mi).[8] According to the 1926 census, the population of the region was 125,200 people, among whom the Armenians accounted for 89.2 percent. However, by 1989, the share of Armenians dropped to 76.9 percent of the population of the autonomous region.[9] Reasons for this include the policy of Soviet Azerbaijani authorities to settle Azerbaijanis in the region and some out-migration of Karabakh Armenians, as well as the generally higher birthrate among Azerbaijanis than among Armenians.[10]
Although the question of Nagorno-Karabakh's status did not become a major public issue until the mid-1980s, Armenian intellectuals, Soviet Armenian and Karabakh Armenian leadership periodically made appeals to Moscow for the region's transfer to Soviet Armenia.[10] In 1945, the leader of Soviet Armenia Grigory Arutinov appealed to Stalin to attach the region to Soviet Armenia, which was rejected.[10] In 1965, thirteen Karabakh Armenian party officials wrote to Soviet leadership with their grievances about the attitude of Soviet Azerbaijani officials towards the NKAO. Many of these Karabakh Armenian officials were dismissed or moved to Armenia.[10] The rise of Heydar Aliyev to the leadership of the Azerbaijani SSR in 1969 saw increasing attempts to tighten Baku's control over the autonomous region. In 1973–74 Aliyev purged the entire leadership of the NKAO, who were regarded as Armenian nationalists. He appointed Boris Kevorkov, an Armenian from outside Karabakh, as the First Secretary of the Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast Committee of the Communist Party of Azerbaijan.[10]
In 1977, the prominent Armenian author Sero Khanzadyan wrote an open letter to Leonid Brezhnev calling for Nagorno-Karabakh's annexation to Soviet Armenia.[11]
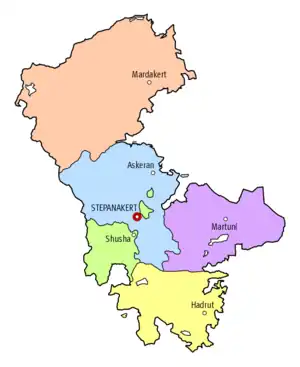
Administrative divisions
There were five administrative divisions or raions in the NKAO :
Demographics
| Ethnic group | 1921[12][13] | 1923[14][12] | 1925[14] | 1926[14][15] | 1939[14][16] | 1959[14][17] | 1970[14][18] | 1979[14][19] | 1989[20] | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | |
| Armenians | 122,426 | 94.73 | 149,600 | 94.8 | 142,470 | 90.28 | 111,694 | 89.24 | 132,800 | 88.04 | 110,053 | 84.39 | 121,068 | 80.54 | 123,076 | 75.89 | 145,450 | 76.92 |
| Azerbaijanis[lower-alpha 2] | 6,550 | 5.07 | 7,700 | 4.9 | 15,261 | 9.67 | 12,592 | 10.06 | 14,053 | 9.32 | 17,995 | 13.80 | 27,179 | 18.08 | 37,264 | 22.98 | 40,688 | 21.52 |
| Russians | 267 | 0.21 | 500 | 0.3 | 46 | 0.03 | 596 | 0.48 | 3,174 | 2.10 | 1,790 | 1.37 | 1,310 | 0.87 | 1,265 | 0.78 | 1,922 | 1.02 |
| Ukrainians | 30 | 0.02 | 35 | 0.03 | 436 | 0.29 | 238 | 0.18 | 193 | 0.13 | 140 | 0.09 | 416 | 0.22 | ||||
| Belarusians | 12 | 0.01 | 11 | 0.01 | 32 | 0.02 | 35 | 0.02 | 37 | 0.02 | 79 | 0.04 | ||||||
| Greeks | 68 | 0.05 | 74 | 0.05 | 67 | 0.05 | 33 | 0.02 | 56 | 0.03 | 72 | 0.04 | ||||||
| Tatars | 6 | 0.00 | 29 | 0.02 | 36 | 0.03 | 25 | 0.02 | 41 | 0.03 | 64 | 0.03 | ||||||
| Georgians | 5 | 0.00 | 25 | 0.02 | 16 | 0.01 | 22 | 0.01 | 17 | 0.01 | 57 | 0.03 | ||||||
| Others | 151 | 0.12 | 235 | 0.16 | 179 | 0.14 | 448 | 0.30 | 285 | 0.18 | 337 | 0.18 | ||||||
| TOTAL | 129,243[lower-alpha 3] | 100.00 | 157,800 | 100.0 | 157,807 | 100.00 | 125,159 | 100.00 | 150,837 | 100.00 | 130,406 | 100.00 | 150,313 | 100.00 | 162,181 | 100.00 | 189,085 | 100.00 |
Abolition
A conflict between the Armenians in the oblast and the government of the Azerbaijan SSR broke out in 1987. The fighting escalated into the First Nagorno-Karabakh War by the end of 1991. On 26 November 1991, the Supreme Soviet of the Azerbaijan Republic abolished the autonomous status of the oblast. Its internal administrative divisions were also abolished, and its territory was split up and redistributed amongst the neighbouring administrative rayons of Khojavend, Tartar, Goranboy, Shusha, and Kalbajar.[21] In response, the majority Armenian population of the oblast declared their independence as the Nagorno-Karabakh Republic which was supported by Armenia.[22][23][24]
See also
Notes
-
- Russian: Нагорно-Карабахская автономная область, НКАО
- Azerbaijani: Dağlıq Qarabağ Muxtar Vilayəti, DQMV
- Armenian: Լեռնային Ղարաբաղի Ինքնավար Մարզ, ԼՂԻՄ
- Until 1936, Azerbaijanis were known as "Tatars" or "Turkish-Tatars".
- With the city of Shusha included, the NKAO's total population was 138,466, the adjusted ethnic composition is as follows:
- Armenians – 122,715 (88.62%)
- Azerbaijanis – 15,444 (11.15%)
- Others – 307 (0.22%)
References
- (in Russian) НАГОРНО-КАРАБАХСКАЯ АО (1989 г.) Archived September 16, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- (in Russian) НАГОРНО-КАРАБАХСКАЯ АО (1989 г.) Archived September 16, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- Ardillier-Carras, Françoise (2006). "Sud-Caucase: conflit du Karabagh et nettoyage ethnique" [South Caucasus: Nagorny Karabagh conflict and ethnic cleansing]. Bulletin de l'Association de Géographes Français (in French). 83 (4): 409–432. doi:10.3406/bagf.2006.2527. Archived from the original on December 12, 2020. Retrieved January 13, 2023.
- "UNHCR publication for CIS Conference (Displacement in the CIS) – Conflicts in the Caucasus". Unhcr. United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees. Archived from the original on September 22, 2020. Retrieved January 13, 2023.
- Yamskov, A. N. (1991). Ethnic Conflict in the Transcausasus: The Case of Nagorno-Karabakh. p. 659.
{{cite book}}:|periodical=ignored (help) - "Q&A with Arsène Saparov: No Evidence that Stalin 'Gave' Karabakh to Aхerbaijan". armenian.usc.edu. December 10, 2018. Archived from the original on December 15, 2020. Retrieved January 13, 2023.
Of all the documents I have seen, there is no direct evidence of Stalin doing or saying something in those 12 days in the summer of 1921 that [resulted in this decision on Karabakh]. A lot of people just assume that since Stalin was an evil person, it would be typical of someone evil to take a decision like that.
- Həmid, Tural (December 15, 2020). "Dağlıq Qarabağın sərhədləri necə cızılırdı?" [How were the borders of Nagorno-Karabakh drawn?]. Azlogos. Archived from the original on January 13, 2023. Retrieved August 23, 2022.
- Атлас Союза Советских Социалистических Республик [Atlas of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics]. Moscow: Central Executive Committee of the USSR. 1928.
The Autonomous Region of Nagorno-Karabakh, which is part of the SSR of Azerbaijan, was formed by the decree of the AzCEC 7 / VI 1923 from Armenian parts of the former Jevanshir, Shulgan, Karyaginsky, and Kubatly uyezds. The territory of the Region is 4.161 sq. km. According to the administrative division on 1 / I of 1927, it is divided into 5 sections or parishes. Its administrative and political center is mountains. Stepanakert (formerly the village of Khankendy). Another city of the Region is Shusha.
- "All-Union Population Census of 1926. Ethnic composition of the population by regions of the republics of the USSR". demoscope.ru. 1926. Archived from the original on November 28, 2020. Retrieved January 13, 2023.
- de Waal, Thomas (2003). Black Garden: Armenia and Azerbaijan through Peace and War. New York and London: New York University Press. pp. 3 & 137–140. ISBN 0-8147-1944-9.
- Sanjian, Ara (January 6, 2021). "The Armenian Diasporan Press on Mountainous Karabagh, 1923-1985". entriessas.com. Entries of the Society for Armenian Studies. Archived from the original on January 13, 2023. Retrieved January 21, 2021.
This 'silence' was only broken in the Diaspora with the publication of Yerevan-based novelist Sero Khanzadyan's open letter to the Soviet leader Leonid Brezhnev in 1977, demanding Mountainous Karabagh's annexation to Soviet Armenia.
- Cory D., Welt (2004). Explaining ethnic conflict in the South Caucasus: Mountainous Karabagh, Abkhazia, and South Ossetia (PDF). Massachusetts Institute of Technology. p. 77. OCLC 59823134. Archived (PDF) from the original on September 11, 2022.
Out of a population of approximately 20,000, at least several hundred were killed; the rest were forced to flee. In the fighting that followed, several nearby villages were also razed.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) - "Перепись населения АзССР в 1921 г." [Census of the population of the AzSSR in 1921]. karabagh.am. Archived from the original on May 26, 2011. Retrieved June 26, 2022.
- Beglaryan, Ashot. "The population of Nagorno-Karabakh for a year. Union of Armenians of Russia - Nagorno-Karabakh Republic. Excursion into history". losevskaya.ru. Stepanakert. Archived from the original on October 31, 2022. Retrieved October 31, 2022.
- Всесоюзная перепись населения 1926 года. Национальный состав населения по регионам республик СССР Archived June 5, 2016, at the Wayback Machine Демоскоп
- Всесоюзная перепись населения 1939 года. Распределение городского и сельского населения областей союзных республик по национальности и полу Archived June 5, 2016, at the Wayback Machine Демоскоп
- Всесоюзная перепись населения 1959 года. Городское и сельское население областей республик СССР (кроме РСФСР) по полу и национальности Archived June 5, 2016, at the Wayback Machine Демоскоп
- Всесоюзная перепись населения 1970 года. Городское и сельское население областей республик СССР (кроме РСФСР) по полу и национальности Archived June 5, 2016, at the Wayback Machine Демоскоп
- Всесоюзная перепись населения 1979 года. Городское и сельское население областей республик СССР (кроме РСФСР) по полу и национальности Archived June 5, 2016, at the Wayback Machine Демоскоп
- Всесоюзная перепись населения 1989 года.Распределение городского и сельского населения областей республик СССР по полу и национальности Archived June 5, 2016, at the Wayback Machine Демоскоп
- Svante Cornell, Turkey and the Conflict in Nagorno Karabakh: A Delicate Balance Archived June 10, 2007, at the Wayback Machine, in Middle Eastern Studies Journal Vol 34, No. 1 (London: Frank Cass Publications, January 1998), pp. 51–72
- Oskanian, Kevork (September 29, 2020). "Nagorno-Karabakh: are Armenia and Azerbaijan sliding towards all-out war?". The Conversation. Archived from the original on November 29, 2020. Retrieved October 19, 2020.
- Minasyan, Karen (October 2, 2020). "Why Nagorno-Karabakh? The history (both ancient and modern) that fuels the deadly conflict between Armenia and Azerbaijan". meduza.io. Archived from the original on December 21, 2020. Retrieved October 19, 2020.
- Department Of State. The Office of Electronic Information, Bureau of Public Affairs. "1993 UN Security Council Resolutions on Nagorno-Karabakh". 2001-2009.state.gov. Archived from the original on January 22, 2020. Retrieved October 19, 2020.