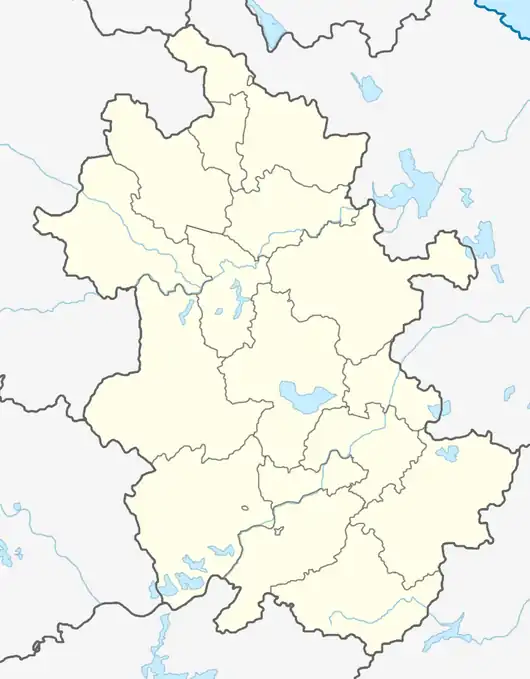
Anhui
Anhui (UK: /ænˈhweɪ/,[5] US: /ɑːnˈhweɪ/)[6] (ⓘ; formerly romanized as Anhwei) is an eastern landlocked province of the People's Republic of China. Its provincial capital and largest city is Hefei. The province is located across the basins of the Yangtze River and the Huai River, bordering Jiangsu to the east, Zhejiang to the southeast, Jiangxi to the south, Hubei to the southwest, Henan to the northwest, and Shandong for a short section in the north.
Anhui
安徽 | |
|---|---|
| Province of Anhui | |
| Name transcription(s) | |
| • Chinese | 安徽省 (Ānhuī Shěng) |
| • Abbreviation | AH / 皖 (pinyin: Wǎn) |
| • Jiang–Huai | Ang1 huei1 Sen3 |
.svg.png.webp) Map showing the location of Anhui Province | |
| Coordinates: 31°50′N 117°0′E | |
| Country | China |
| Named for | 安 Ān: Anqing 徽 Huī: Huizhou |
| Capital (and largest city) | Hefei |
| Divisions | 16 prefectures, 105 counties, 1845 townships |
| Government | |
| • Type | Province |
| • Body | Anhui Provincial People's Congress |
| • CCP Secretary | Han Jun |
| • Congress Chairperson | Han Jun |
| • Governor | Wang Qingxian |
| • Provincial CPPCC Chairperson | Tang Liangzhi |
| • National People's Congress Representation | 111 deputies |
| Area | |
| • Total | 140,200 km2 (54,100 sq mi) |
| • Rank | 22nd |
| Highest elevation | 1,873 m (6,145 ft) |
| Population (2020)[2] | |
| • Total | 61,027,171 |
| • Rank | 9th |
| • Density | 440/km2 (1,100/sq mi) |
| • Rank | 9th |
| Demographics | |
| • Ethnic composition | Han – 99% Hui – 0.6% |
| • Languages and dialects | Jianghuai Mandarin, Zhongyuan Mandarin, Gan, Wu, Huizhou |
| ISO 3166 code | CN-AH |
| GDP[3] | 2022 |
| – Total | ¥4.51 trillion (10th) $670 billion (nominal) |
| – Per capita | ¥73,603 (14th) 10,943 (nominal) |
| – Growth | |
| HDI (2021) | 0.744[4] (20th) – high |
| Website | www |
| Anhui | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
"Anhui" in Chinese characters | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chinese | 安徽 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Literal meaning | "An(qing) and Hui(zhou)" | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
With a population of 61 million, Anhui is the 9th most populous province in China. It is the 22nd largest Chinese province based on area, and the 12th most densely-populated region of all 34 Chinese provincial regions. Anhui's population is mostly composed of Han Chinese. Languages spoken within the province include Jianghuai Mandarin, Wu, Hui, Gan and small portion of Zhongyuan Mandarin Chinese.
The name "Anhui" derives from the names of two cities: Anqing and Huizhou (now Huangshan City).[7] The abbreviation for Anhui is "Chinese: 皖; pinyin: wǎn" after the historical State of Wan, Mount Wan, and the Wan river.
The administration of Anhui is composed of the provincial administrative system, led by the Governor, Provincial Congress, the People's Political Consultative Conference, and the Provincial Higher People's Court. Anhui is known as a province with political tradition in China's government system. Aside from managing provincial government departments, the provincial government manages 16 cities, 62 counties, 43 county-level districts and 1,522 townships. The total GDP of Anhui Province ranked 14th among China's 31 provincial regions as of 2022.
History

Anhui Province was established in the sixth year of the reign of the Kangxi Emperor of the Qing dynasty (1667); before that, there was no coherent concept of "Anhui". The province also has another name, "Wan", because, during the Spring and Autumn Period (722–481 B.C.), a small country named "Wan" was here and a mountain called "Wanshan" (aka Mount Tianzhu) is in the province.
Before Anhui was established, this land had a long history. 20,000 years ago, human beings inhabited this area, proven by some findings in Fanchang County. Archaeologists have identified the cultural domains of Yangshao and Longshan, dated to the Neolithic Age (between 4,000 and 10,000 years ago). In relation to these cultures, archeologists have discovered through excavation a 4500-year-old city called the Nanchengzi Ruins in Guzhen County, after they discovered a Neolithic city wall and a moat that was part of a much larger and integrated city in the region during their 2013 disinterment.[8]
There are many historic sites found in the province from the period of the Xia dynasty (2070 B.C.) to the Warring Kingdoms (475–221 B.C.). After the Qin dynasty unified China, this area belonged to different prefectures such as the Jiujiang, Zhang, Tang and Sishui Prefectures. Anhui became parts of Yang, Yu, and Xu prefectures during Han dynasties. In the period of the Three Kingdoms (222–280 A.D.), Anhui was separately dominated by the Wu State and Wei State. During the Jin dynasty, Northern and Southern dynasties and the Sui dynasty, Anhui was part of Yang, Xu and Yu prefectures, respectively. Later on, the Hui area flourished quickly and the economy and culture of Hui Prefecture created great influence during the Song Dynasty. During the Yuan dynasty, ruled by the Mongolian emperor, Anhui area was a part of Henan province. During the Ming dynasty, the area was directly managed by the administration of the Capital of Nanjing. Shortly after the Qing dynasty was established, this area and Jiangsu province were merged as one province until the sixth year (1666 or 1667) of the Kangxi Emperor's reign in the Qing dynasty.
Later during the Qing dynasty, Anhui played an important role in the Self-Strengthening Movement led by Li Hongzhang, an important Prime Minister during the later Qing Dynasty. At this time, many western weapons, factories and modern government concepts were introduced into China. Over the next 50 years, Anhui became one of the most aggressive areas with liberal thought. Within this environment, many ideologists appeared in Anhui. Several of them impacted the future of China including, Hu Shih, a Chinese philosopher, essayist and diplomat, and Chen Duxiu, founder of the Chinese Communist Party and the first General Secretary of the CCP.
In 1938, the north and central areas of the province were heavily damaged because Chiang Kai-shek, the then-President of the Republic of China, broke the dam of Yellow River, hoping this strategy could slow down the invasion by the Imperial Japanese Army. Within only ten days of the dam breaking, the water and sands drowned all of north and middle area of this province, 500,000 to 900,000 Chinese people died, along with an unknown number of Japanese soldiers. The flood prevented the Japanese Army from taking Zhengzhou.
Following the end of the Second Sino-Japanese War in 1945, the capital city of Anhui province moved to what was then a small town, Hefei. At the same time, the provincial government made significant investments to develop this new capital city, which has become a China Top 25 city (of 660 cities over all of China) in the 2010s. After 1949, the government also launched many Water Projects to repair damage from World War II. In addition, many other areas of China supported Anhui's development.
Anhui developed significantly through the Third Front campaign to build basic industry and national defense industry in protected locations in case of invasion by the Soviet Union or the United States.[9]: xiii–xv The centerpiece of the Shanghai Small Third Front was the "rear base" in Anhui which served as "a multi-function manufacturing base for anti-aircraft and anti-tank weaponry.[10]: xvi
In the later 1990s, Anhui became one of the fastest growing provinces in China. In the 2010s, the province became a part of China Yangtze River Delta Economic Area which is the most developed area of China. And the capital city, Hefei, is set as the sub-central city of this Economic Area, only after Shanghai, Nanjing and Hangzhou.
In terms of culture, Northern Anhui was firmly a part of the North China Plain together with modern-day Henan province, northern Jiangsu and southern Shandong provinces. Central Anhui was densely populated and constituted mostly of fertile land from the Huai River watershed. In contrast, the culture of Southern Anhui, bordered mostly along the Yangtze, was closer to Jiangxi and southern Jiangsu provinces. The hills of southeastern Anhui formed a unique and distinct cultural sphere of its own.
Geography

Anhui is topographically diverse. The north is part of the North China Plain while the north-central areas are part of the Huai River watershed. Both regions are flat, and densely populated. The land becomes more uneven further south, with the Dabie Mountains occupying much of southwestern Anhui and a series of hills and ranges cutting through southeastern Anhui, between which is the Yangtze River. The highest peak in Anhui is Lotus Peak, part of Huangshan in southeastern Anhui. It has an altitude of 1873 m.
Major rivers include the Huai River in the north and the Yangtze in the south. The largest lake is Lake Chaohu situated in the center of the province, with an area of about 800 km2 (310 sq mi). The southeastern part of the province near the Yangtze River has many lakes as well.
As with topography, the province differs in climate from north to south. The north is more temperate with more distinct seasons. January temperatures average at around −1 to 2 °C north of the Huai River, and 0 to 3 °C south of the Huai River; in July temperatures average 27 °C or above. Plum rains occur in June and July and may cause flooding.
Anhui has 16 cities. Economically, top 3 cities are, Hefei, Wuhu and Anqing.
Ecology
The Anhui elm, Ulmus gaussenii W. C. Cheng, is a medium size deciduous tree whose natural range is restricted to the valleys of the Langya limestone mountains of Chu Xian.[11] The tree was most commonly found on the flood plains, indicating a tolerance of periodic inundation. U. gaussenii is now the world's rarest and most endangered elm species, with only approximately 30 trees known to survive in the wild in 2009.[12]
The province is also home to the Chinese alligator (Alligator sinensis, simplified Chinese: 扬子鳄; traditional Chinese: 揚子鱷; pinyin: yángzǐ'è), also known as the Yangtze alligator,[13] China alligator,[14] or historically the muddy dragon,[15] a critically endangered crocodilian.
Administrative divisions
Anhui is divided into sixteen prefecture-level divisions: all prefecture-level cities:
| Administrative divisions of Anhui | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Division code[16] | Division | Area in km2[17] | Population 2020[18] | Seat | Divisions[19] | ||
| Districts | Counties | CL cities | |||||
| 340000 | Anhui Province | 139600.00 | 61,027,171 | Hefei city | 45 | 50 | 9 |
| 340100 | Hefei city | 11,445.06 | 9,369,881 | Shushan District | 4 | 4 | 1 |
| 340200 | Wuhu city | 6,004.97 | 3,644,420 | Jiujiang District | 5 | 1 | 1 |
| 340300 | Bengbu city | 5,950.72 | 3,296,408 | Bengshan District | 4 | 3 | |
| 340400 | Huainan city | 5532.30 | 3,033,528 | Tianjia'an District | 5 | 2 | |
| 340500 | Ma'anshan city | 4,049.13 | 2,159,930 | Yushan District | 3 | 3 | |
| 340600 | Huaibei city | 2,740.91 | 1,970,265 | Xiangshan District | 3 | 1 | |
| 340700 | Tongling city | 2,937.83 | 1,311,726 | Tongguan District | 3 | 1 | |
| 340800 | Anqing city | 13,525.03 | 4,165,284 | Yingjiang District | 3 | 5 | 2 |
| 341000 | Huangshan city | 9,678.39 | 1,330,565 | Tunxi District | 3 | 4 | |
| 341100 | Chuzhou city | 13,515.99 | 3,987,054 | Langya District | 2 | 4 | 2 |
| 341200 | Fuyang city | 10,118.17 | 8,200,264 | Yingzhou District | 3 | 4 | 1 |
| 341300 | Suzhou city | 9,938.77 | 5,324,476 | Yongqiao District | 1 | 4 | |
| 341500 | Lu'an city | 15,450.82 | 4,393,699 | Jin'an District | 3 | 4 | |
| 341600 | Bozhou city | 8,521.23 | 4,996,844 | Qiaocheng District | 1 | 3 | |
| 341700 | Chizhou city | 8,364.81 | 1,342,764 | Guichi District | 1 | 3 | |
| 341800 | Xuancheng city | 12,312.55 | 2,500,063 | Xuanzhou District | 1 | 4 | 2 |
| Administrative divisions in Chinese and varieties of romanizations | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| English | Chinese | Pinyin | Jiang–Huai (Langjin Pinin) | |
| Anhui Province | 安徽省 | Ānhuī Shěng | Ang1 huei1 Sen3 | |
| Hefei city | 合肥市 | Héféi Shì | Ho5 fei2 Shr4 | |
| Wuhu city | 芜湖市 | Wúhú Shì | U2 hu2 Shr4 | |
| Bengbu city | 蚌埠市 | Bèngbù Shì | Bang4 bu4 Shr4 | |
| Huainan city | 淮南市 | Huáinán Shì | Huä2 lang2 Shr4 | |
| Ma'anshan city | 马鞍山市 | Mǎ'ānshān Shì | Ma3 ang1 shang1 Shr4 | |
| Huaibei city | 淮北市 | Huáiběi Shì | Huä2 bä5 Shr4 | |
| Tongling city | 铜陵市 | Tónglíng Shì | Tong2 lin2 Shr4 | |
| Anqing city | 安庆市 | Ānqìng Shì | Ang1 qin4 Shr4 | |
| Huangshan city | 黄山市 | Huángshān Shì | Huang2 shang1 Shr4 | |
| Chuzhou city | 滁州市 | Chúzhōu Shì | Chu2 zhou1 Shr4 | |
| Fuyang city | 阜阳市 | Fùyáng Shì | Fu4 iang2 Shr4 | |
| Suzhou city | 宿州市 | Sùzhōu Shì | Su5 zhou1 Shr4 | |
| Lu'an city | 六安市 | Lù'ān Shì | Lu5 ang1 Shr4 | |
| Bozhou city | 亳州市 | Bózhōu Shì | Bo5 zhou1 Shr4 | |
| Chizhou city | 池州市 | Chízhōu Shì | Chr2 zhou1 Shr4 | |
| Xuancheng city | 宣城市 | Xuānchéng Shì | Süän1 chen2 Shr4 | |
These 16 prefecture-level cities are in turn subdivided into 104 county-level divisions (45 districts, 9 county-level cities, and 50 counties). Those are in turn divided into 1,512 township-level divisions (997 towns, 230 townships, 9 ethnic townships, and 276 subdistricts).
Urban areas
| Population by urban areas of prefecture & county cities | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # | City | Urban area[20] | District area[20] | City proper[20] | Census date |
| 1 | Hefei[lower-alpha 1] | 3,098,727 | 3,310,268 | 7,457,027 | 2010-11-01 |
| 2 | Huainan[lower-alpha 2] | 1,238,488 | 1,666,826 | 3,342,012 | 2010-11-01 |
| 3 | Wuhu[lower-alpha 1] | 1,108,087 | 2,487,111 | 2,263,123 | 2010-11-01 |
| 4 | Huaibei | 854,696 | 1,113,321 | 2,114,276 | 2010-11-01 |
| 5 | Bengbu | 793,866 | 972,784 | 3,164,467 | 2010-11-01 |
| 6 | Fuyang | 780,522 | 1,768,947 | 7,599,913 | 2010-11-01 |
| 7 | Suzhou | 742,685 | 1,647,642 | 5,352,924 | 2010-11-01 |
| 8 | Lu'an[lower-alpha 3][lower-alpha 2] | 661,217 | 1,644,344 | 4,603,585 | 2010-11-01 |
| (8) | Lu'an (new district)[lower-alpha 3] | 134,239 | 134,239 | see Lu'an | 2010-11-01 |
| 9 | Ma'anshan[lower-alpha 4][lower-alpha 1] | 657,847 | 741,531 | 2,304,774 | 2010-11-01 |
| (9) | Ma'anshan (new district)[lower-alpha 4] | 169,888 | 169,888 | see Ma'anshan | 2010-11-01 |
| 10 | Anqing[lower-alpha 5] | 570,538 | 780,514 | 4,472,667 | 2010-11-01 |
| 11 | Bozhou | 474,318 | 1,409,436 | 4,850,657 | 2010-11-01 |
| 12 | Tongling[lower-alpha 5] | 438,981 | 474,363 | 1,562,670 | 2010-11-01 |
| (13) | Chaohu[lower-alpha 1] | 404,789 | 780,711 | see Hefei | 2010-11-01 |
| 14 | Chuzhou | 392,461 | 562,321 | 3,937,868 | 2010-11-01 |
| 15 | Tianchang | 324,625 | 602,840 | see Chuzhou | 2010-11-01 |
| 16 | Xuancheng | 315,058 | 772,490 | 2,532,938 | 2010-11-01 |
| 17 | Chizhou | 289,122 | 595,268 | 1,402,518 | 2010-11-01 |
| 18 | Huangshan | 287,576 | 460,786 | 1,358,980 | 2010-11-01 |
| 19 | Tongcheng | 269,346 | 664,455 | see Anqing | 2010-11-01 |
| 20 | Ningguo | 231,090 | 376,857 | see Xuancheng | 2010-11-01 |
| 21 | Jieshou | 214,776 | 561,956 | see Fuyang | 2010-11-01 |
| 22 | Mingguang | 204,323 | 532,732 | see Chuzhou | 2010-11-01 |
| (23) | Qianshan[lower-alpha 6] | 165,779 | 500,292 | see Anqing | 2010-11-01 |
- Chaohu PLC is currently no longer exist after census it was split among Hefei (Juchao & Lujiang), Wuhu (Wuwei), & Ma'anshan (Hexian & Hanshan); Juchao District is currently known as Chaohu CLC. Chaohu PLC city proper count is reflected among the three PLCs.
- Shouxian County was transferred from Lu'an PLC to Huainan PLC's jurisdiction after census; the City proper count is reflected onto Huainan PLC not Lu'an PLC.
- New district established after census: Yeji by splitting from parts of Huoqiu County. The new district not included in the urban area & district area count of the pre-expanded city.
- New district established after census: Bowang by splitting from parts of Dangtu County. The new district not included in the urban area & district area count of the pre-expanded city.
- Zongyang County was transferred from Anqing PLC to Tongling PLC's jurisdiction after census; the City proper count is reflected onto Tongling PLC not Anqing PLC.
- Qianshan County is currently known as Qianshan CLC after census.
Most populous cities in Anhui Source: China Urban Construction Statistical Yearbook 2018 Urban Population and Urban Temporary Population[21] | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Pop. | Rank | Pop. | ||||||
 Hefei  Wuhu |
1 | Hefei | 4,292,400 | 11 | Tongling | 535,300 | .jpg.webp) Huainan  Bengbu | ||
| 2 | Wuhu | 1,536,700 | 12 | Chuzhou | 507,600 | ||||
| 3 | Huainan | 1,178,200 | 13 | Huangshan | 406,100 | ||||
| 4 | Bengbu | 961,100 | 14 | Bozhou | 365,000 | ||||
| 5 | Fuyang | 907,400 | 15 | Xuancheng | 357,700 | ||||
| 6 | Huaibei | 762,500 | 16 | Chaohu | 357,000 | ||||
| 7 | Ma'anshan | 752,500 | 17 | Chizhou | 310,100 | ||||
| 8 | Anqing | 631,500 | 18 | Tianchang | 196,600 | ||||
| 9 | Lu'an | 607,500 | 19 | Jieshou | 188,600 | ||||
| 10 | Suzhou | 578,600 | 20 | Mingguang | 186,000 | ||||
Government
The Politics of Anhui Province is structured in a dual party-government system like all other governing institutions in mainland China.
The Governor of Anhui (安徽省省长) is the highest-ranking official in the Anhui Provincial People's Government. However, in the province's dual party-government governing system, the Governor has less power than the Anhui Chinese Communist Party Provincial Committee Secretary (安徽省委书记), colloquially termed the "Anhui Party Chief".
Most provincial government departments and the Governor office are located at No.1 Zhongshan Road, moved from old downtown of Hefei since 2016. Provincial government is responsible to manage 16 prefecture-level cities, 105 counties, 1845 townships and different departments in Anhui. The Anhui Provincial People's Congress is just located near provincial government. The Provincial Chinese People's Political Consultative Conference (CPPCC) is located at No.317, Suzhou Road. The Provincial Higher People's Court is located at no. 472 Changjiang Rd.
Typically, annual provincial congress meeting is held in the first quarter of each year shortly before national congress meeting and the annual meeting of CPPCC is held in the first quarter or the fourth quarter of each year.
Economy
.svg.png.webp)
Agriculture in Anhui varies according to the climate zones. To the north of the Huai River, wheat and sweet potatoes are grown, while to the south it is rice and wheat instead. As of 2022, Anhui's nominal GDP was US$670 billion (CN¥ 4.51 trilion), about 3.72% of the country's GDP and ranked 10th among province-level administrative units; the province's primary, secondary and tertiary industries were worth CN¥351.37 billion (US$52.24 billion), CN¥1.8588 trillion (US$276.36 billion) and CN¥2.29433 trillion (US$341.1 billion) respectively. Its nominal GDP per capita was US$10,943 (CN¥73,603) and ranked the 14th in the country.[3]
Natural resources of Anhui include iron in Ma'anshan, coal in Huainan, and copper in Tongling. There are industries related to these natural resources (e.g. steel industry at Ma'anshan). One of the famous Anhui-based corporations is the automobile company Chery, which is based in Wuhu.

Compared to its more prosperous neighbours to the east, Zhejiang and Jiangsu, Anhui has lagged markedly behind in economic development, with a GDP per capita around half of those two provinces in 2017 rapidly improved from 1/3 of those two provinces in 2010. However, the provincial GDP per capita is based on the population registered in the province (that is, with local Hukou), but not necessarily residing there. There is significant regional disparity, where much of the wealth is concentrated in industrial regions close to the Yangtze River, such as Hefei, Wuhu, and Ma'anshan. The province is home to a large cluster of white goods manufacture such as Haier, Hisense, Whirlpool, Gree, Royalstar, and Meling.
Hefei Economic and Technological Development Zone
Hefei Economic and Technological Development Zone is located in the southwest of Hefei and was established in 1993. It is located close to Hefei Luogang International Airport.[22]
Hefei Hi-Tech Industrial Development Zone
Hefei Hi-Tech Industrial Development Zone was founded in October 1990 and approved by the State Council as a state-level Development Zone in March 1991. In 1997, the Development Zone was ratified as an APEC Science and Technology Industrial Park, with special open policies to APEC and EU members. Hefei High Tech Park was also approved as a National High Tech Export Base in 2000 and obtained the award of an Advanced High Tech Zone under the Torch Program in 2003. So far, more than 100 hi-tech enterprises have entered the zone. Industries encouraged in the zone include chemical production and processing, electronics assembly & manufacturing, instruments & industrial equipment, medical Equipment and telecommunications.[23]
Wuhu Economic and Technological Development Zone
Established in 1993, Wuhu Economic and Technological Development Zone was the first state-level development zone approved by central government in Anhui, utilising the transportation advantage of the Yangtse Delta at Wuhu.[24]
Wuhu Export Processing Zone
Wuhu Export Processing Zone was approved to be a national level export processing zone, with a total planned area of 2.95 km2 (1.14 sq mi).[25]
Transportation



Historically, Anhui's transport network was hampered by the lack of bridges across the Yangtze River, which divides the province into northern and southern regions. The first bridge across the Yangtze in Anhui, the Tongling Yangtze River Bridge, was completed in 1995. As of October 2014, Anhui had four bridges across the Yangtze, at Ma'anshan, Wuhu, Tongling, and Anqing.
Rail
Anhui lacked a developed railway network until this century: most cities are now connected by a high-speed train system. Hefei South railway station is the high-speed train hub.
Highway system
The province set an ambitious plan from 2015 to 2025 for highways including:
G42 Shanghai-Chengdu Expressway
S24 Changshu-Hefei Expressway
Subway
Hefei and Wuhu have subway systems. The Hefei Metro has 2 completed lines, 3 lines under construction and another 10 lines planned. The Wuhu Metro has 2 subway lines under construction and another 3 lines planned.
Aviation
The province has 5 major commercial airports and another 4 are under construction. Hefei Xinqiao International Airport and Huangshan International Airport are the 2 international airports. The 5 airports in operation are:
- Hefei Xinqiao International Airport (IATA: HFE, ICAO: ZSOF)
- Huangshan Tunxi International Airport (IATA: TXN, ICAO: ZSTX)
- Fuyang Xiguan Airport (IATA: FUG, ICAO: ZSFY)
- Anqing Tianzhushan Airport (IATA: AQG, ICAO: ZSAQ)
- Chizhou Jiuhuashan Airport (IATA: JUH, ICAO: ZSJH)
Demographics
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1912[26] | 16,229,000 | — |
| 1928[27] | 21,715,000 | +33.8% |
| 1936–37[28] | 23,354,000 | +7.5% |
| 1947[29] | 22,462,000 | −3.8% |
| 1954[30] | 30,343,637 | +35.1% |
| 1964[31] | 31,241,657 | +3.0% |
| 1982[32] | 49,665,724 | +59.0% |
| 1990[33] | 56,180,813 | +13.1% |
| 2000[34] | 58,999,948 | +5.0% |
| 2010[35] | 59,500,510 | +0.8% |
| 2020[2] | 61,027,171 | +2.6% |
Han Chinese make up the vast majority of the population. The Hui and She are the two largest minorities.
Anhui has a highly unbalanced gender ratio. According to a 2009 study published in the British Medical Journal, in the 1–4 age group, there are 138 boys for every 100 girls, making it among the most unbalanced of provinces in China.[36]
Religion
The predominant religions in Anhui are Chinese folk religions, Taoist traditions and Chinese Buddhism. According to surveys conducted in 2007 and 2009, 4.64% of the population believes and is involved in ancestor veneration, while 5.30% of the population identifies as Christian.[37] According to a 2010 survey, Muslims constitute 0.58% of the population of Anhui.[38]
The reports didn't give figures for other types of religion; 89.48% of the population may be either irreligious or involved in worship of nature deities, Buddhism, Confucianism, Taoism and folk religious sects.





Culture
Anhui spans many geographical and cultural regions. The northern, flatter parts of the province, along the Huai River and further north, are most akin to neighboring provinces like Henan, Shandong and northern Jiangsu. In contrast, the southern, hilly parts of the province are more similar in culture and dialect to other southern, hilly provinces, like Zhejiang and Jiangxi.
Mandarin dialects are spoken over the northern and central parts of the province, north of the Yangtze river. Dialects to the north (e.g. Bengbu dialect) are classified as Zhongyuan Mandarin, together with dialects in provinces such as Henan and Shandong; dialects in the central parts (e.g. Hefei dialect) are classified as Jianghuai Mandarin, together with dialects in the central parts of neighboring Jiangsu province. Non-Mandarin dialects are spoken to the south of the Yangzi: dialects of Wu are spoken in Xuancheng prefecture-level city, though these are rapidly being replaced by Jianghuai Mandarin; dialects of Gan are spoken in a few counties in the southwest bordering Jiangxi province;[39] and the Huizhou dialects are spoken in about ten counties in the far south, a small but highly diverse and unique group of Chinese dialects.
Huangmeixi, which originated in the environs of Anqing in southwestern Anhui, is a form of traditional Chinese opera popular across China. Huiju, a form of traditional opera originating in the Huizhou-speaking areas of southern Anhui, is one of the major precursors of Beijing Opera; in the 1950s, Huiju (which had disappeared) was revived. Luju is a type of traditional opera found across central Anhui, from east to west.
Anhui cuisine is one of the eight great traditions of Chinese cuisine. Combining elements of cooking from northern Anhui, south-central Anhui, and the Huizhou-speaking areas of southern Anhui, Anhui cuisine is known for its use of wild game and herbs, both land and sea, and comparatively simple methods of preparation.
Anhui has a high concentration of traditional products related to calligraphy: Xuanzhou (today Xuancheng) and Huizhou (today Huangshan City) are revered for producing Xuan Paper and Hui Ink, respectively, which are traditionally considered the best types of paper and ink for Chinese calligraphy. She County is famous for the She Inkstone, one of the most preferred types of inkstones (a required tool in traditional calligraphy).
Education



Anhui has some good universities. Most universities in Anhui are located in Hefei, Wuhu, Bengbu, Maanshan, some of them are pretty well known. Specifically, Hefei is one of the most important research central cities in China with leading basic scientific research capability.
Public universities
- University of Science & Technology of China, One of China's top University as well as world renowned research and engineering institution.
- Hefei University of Technology, China well-known Engineering School
- Anhui University, China Key University
- Anhui Agricultural University, in Hefei
- Anhui Medical University
- Anhui Normal University, in Wuhu
- Anhui University of Finance and Economics, in Bengbu
- Anhui University of Technology, in Ma'anshan
- Anhui University of Technology and Science, in Wuhu City
- Anhui University of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- Anhui University of Science & Technology, in Huainan
- Anqing Teachers College, in Anqing
- Fuyang Teachers College, in Fuyang
- Hefei Normal University, in Hefei
- Wannan Medical College, in Wuhu City
- Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences in Hefei
- Beihang University (BUAA) - Hefei Campus
- Beijing Foreign Studies University (BFSU) - Hefei Campus
- Tianjin University (TJU) - Hefei Graduate School
- Peking University (PKU) - Hefei Graduate School
- Tsinghua University (THU) - Hefei Institute of Public Safety Research
Military universities
- National University of Defense Technology (NUDT) - Hefei Campus
- PLA Artillery University
- PLA Armoured Force University
- PLA Vehicle University
- PLA Air Force Flight Academy(13th)
- Armed Police Command College(Hefei)
Tourism
Anhui's principal tourism sites include the following:
- Ancient Villages in Southern Anhui – Xidi and Hongcun (World Heritage Site).
- Chao Lake
- Jing Ting Mountain
- Mount Huangshan (World Heritage Site)
- Mount Jiuhua
- Mount Langya
- Mount Qiyun
- Mount Tianzhu
- Old Town of Tunxi
- Taiji Cave, the longest karst cave in East China.
- Zhenfeng Pagoda, a Ming Dynasty pagoda in Anqing City.
- Zuiweng Pavilion, named after the poet Ouyang Xiu (1007–1072 AD).
Notable people
- Xia Jun, economist, telecom researcher and university professor
- Qiu Jianliang, professional kickboxer
- Fang Bian, sanshou fighter and professional kickboxer
Notes
- The data was collected by the Chinese General Social Survey (CGSS) of 2009 and by the Chinese Spiritual Life Survey (CSLS) of 2007, reported and assembled by Xiuhua Wang (2015)[37] in order to confront the proportion of people identifying with two similar social structures: ① Christian churches, and ② the traditional Chinese religion of the lineage (i. e. people believing and worshipping ancestral deities often organized into lineage "churches" and ancestral shrines). Data for other religions with a significant presence in China (deity cults, Buddhism, Taoism, folk religious sects, Islam, et al.) was not reported by Wang. The number of Muslims is taken from a survey reported in the year 2010.[38]
- This may include:
- Buddhists;
- Confucians;
- Deity worshippers;
- Taoists;
- Members of folk religious sects;
- And people not bounded to, nor practicing any, institutional or diffuse religion.
References
- "Doing Business in China – Survey". Ministry Of Commerce – People's Republic Of China. Archived from the original on 5 August 2013. Retrieved 5 August 2013.
- "Communiqué of the Seventh National Population Census (No. 3)". National Bureau of Statistics of China. 11 May 2021. Retrieved 11 May 2021.
- "National Data". National Bureau of Statistics of China. 1 March 2022. Retrieved 23 March 2022.
- "Sub-national HDI - Subnational HDI - Global Data Lab". globaldatalab.org. Retrieved 2021-12-31.
- "Anhui". Lexico UK English Dictionary. Oxford University Press. Archived from the original on May 18, 2021.
- "Anhui". Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary.
- (in Chinese) Origin of the Names of China's Provinces Archived 2016-04-27 at the Wayback Machine, People's Daily Online.
- "4,500-year-old city discovered in China". NDTV.com. Retrieved 2022-10-14.
- Xu, Youwei; Wang, Y. Yvon (2022). Everyday Lives in China's Cold War Military Industrial Complex: Voices from the Shanghai Small Third Front, 1964-1988. Palgrave MacMillan. ISBN 9783030996871.
- Xu, Youwei; Wang, Y. Yvon (2022). Everyday Lives in China's Cold War Military Industrial Complex: Voices from the Shanghai Small Third Front, 1964-1988. Palgrave MacMillan. ISBN 9783030996871.
- Geographical Names: Chu Xian, Anhui, satellite photograph. National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency, Bethesda, MD, USA
- Grimshaw, J. & Bayton, R. (2009). New Trees - Recent Introductions to Cultivation. RBG Kew, London. ISBN 978-1-84246-173-0
- "The largest group of Chinese alligators released to the wild". UNDP in China. June 8, 2016. Archived from the original on April 24, 2017. Retrieved April 23, 2017.
- Jiang, H.; Wu, X. (2018). "Alligator sinensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2018: e.T867A3146005. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-1.RLTS.T867A3146005.en.
- Perry, Tony (July 4, 2012). "San Diego Zoo gets two Chinese alligators in preservation effort". Los Angeles Times. Archived from the original on March 19, 2018. Retrieved December 9, 2018.
- 中华人民共和国县以上行政区划代码 (in Simplified Chinese). Ministry of Civil Affairs. Archived from the original on 2015-04-02. Retrieved 2015-12-11.
- Shenzhen Bureau of Statistics. 《深圳统计年鉴2014》 (in Simplified Chinese). China Statistics Print.|url=http://www.sztj.gov.cn/nj2014/indexce.htm Archived 2015-05-12 at the Wayback Machine
- Census Office of the State Council of the People's Republic of China; Population and Employment Statistics Division of the National Bureau of Statistics of the People's Republic of China (2012). 中国2010年人口普查分乡、镇、街道资料 (in Chinese (China)) (1 ed.). Beijing: China Statistics Print. ISBN 978-7-5037-6660-2.
- Ministry of Civil Affairs (August 2014). 《中国民政统计年鉴2014》 (in Simplified Chinese). China Statistics Print. ISBN 978-7-5037-7130-9.
- Compiled by 国务院人口普查办公室 [Department of Population Census of the State Council], 国家统计局人口和社会科技统计司编 [Department of Population and Social Science and Statistics, National Bureau of Statistics] (2012). 中国2010年人口普查分县资料. Beijing: China Statistics Print. ISBN 978-7-5037-6659-6.
- Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China(MOHURD) (2019). 中国城市建设统计年鉴2018 [China Urban Construction Statistical Yearbook 2018] (in Chinese). Beijing: China Statistic Publishing House. Archived from the original on 2021-08-10. Retrieved 2021-11-29.
- "Hefei Economic and Technological Development Zone". RightSite.asia. Archived from the original on 2012-07-23. Retrieved 2013-04-10.
- "Hefei Hi-Tech Industrial Development Zone". RightSite.asia. Archived from the original on 2012-07-23. Retrieved 2013-04-10.
- "RightSite.asia | Wuhu Economic & Technological Development Zone". Archived from the original on 2010-04-18. Retrieved 2010-04-15.
- "Wuhu Export Processing Zone". RightSite.asia. Archived from the original on 2012-07-23. Retrieved 2013-04-10.
- 1912年中国人口. Archived from the original on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 6 March 2014.
- 1928年中国人口. Archived from the original on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 6 March 2014.
- 1936–37年中国人口. Archived from the original on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 6 March 2014.
- 1947年全国人口. Archived from the original on 13 September 2013. Retrieved 6 March 2014.
- 中华人民共和国国家统计局关于第一次全国人口调查登记结果的公报. National Bureau of Statistics of China. Archived from the original on 2009-08-05.
- 第二次全国人口普查结果的几项主要统计数字. National Bureau of Statistics of China. Archived from the original on 2012-09-14.
- 中华人民共和国国家统计局关于一九八二年人口普查主要数字的公报. National Bureau of Statistics of China. Archived from the original on 2012-05-10.
- 中华人民共和国国家统计局关于一九九〇年人口普查主要数据的公报. National Bureau of Statistics of China. Archived from the original on 2012-06-19.
- 现将2000年第五次全国人口普查快速汇总的人口地区分布数据公布如下. National Bureau of Statistics of China. Archived from the original on 2012-08-29.
- "Communiqué of the National Bureau of Statistics of People's Republic of China on Major Figures of the 2010 Population Census". National Bureau of Statistics of China. Archived from the original on 2013-07-27.
- Zhu, W. X.; Lu, L.; Hesketh, T. (2009). "China's excess males, sex selective abortion, and one child policy: analysis of data from 2005 national intercensus survey". BMJ. 338: b1211. doi:10.1136/bmj.b1211. PMC 2667570. PMID 19359290. Archived from the original on 2012-01-01. Retrieved 2013-04-10.
- China General Social Survey 2009, Chinese Spiritual Life Survey (CSLS) 2007. Report by: Xiuhua Wang (2015, p. 15) Archived 2015-09-25 at the Wayback Machine
- Min Junqing. The Present Situation and Characteristics of Contemporary Islam in China. JISMOR, 8. 2010 Islam by province, page 29 Archived 2017-04-27 at the Wayback Machine. Data from: Yang Zongde, Study on Current Muslim Population in China, Jinan Muslim, 2, 2010.
- Damian Harper; Chung Wah Chow; David Eimer; Thomas Huhti; Carolyn B. Heller; Robert Kelly (2009). China (11, illustrated ed.). Lonely Planet. p. 437. ISBN 978-1-74104-866-7. Archived from the original on 24 April 2016. Retrieved 23 September 2011.
- "Anhui Cooperates With France To Build Rural Tourism Area". Archived from the original on September 8, 2008.
External links
- Anhui Government website Archived 2015-10-07 at the Wayback Machine
- Anhui Provincial Tourism Administration Official Site
- Economic profile for Anhui Province at HKTDC
- Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
.jpg.webp)