Marriage law
Marriage law is the legal requirements, an aspect of family law, that determine the validity of a marriage, and which vary considerably among countries.
| Family law |
|---|
| Family |
Summary table
| Country/territory | Civil marriages | Religious marriages | Customary marriages | Divorce | Same-sex marriages | Polygamous marriages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Foreigners only | Recognized | — | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal[lower-alpha 1] | |
| Performed | Not recognized | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Performed | Not recognized | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal[lower-alpha 1] | |
| Performed | — | Not recognized | Legal | Legal | Illegal | |
| Performed | — | Recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Performed | — | Not recognized | Legal | Legal | Illegal | |
| Performed | Not recognized | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized[lower-alpha 2] | Illegal | |
| Performed | Recognized[1] | Not recognized | Legal | Legal | Illegal | |
| Performed | Not recognized[1] | Not recognized | Legal | Legal | Illegal | |
| Performed | — | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Performed | — | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Foreigners only | Recognized | — | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal[lower-alpha 1] | |
| Performed | Recognized | — | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal[lower-alpha 1] | |
| Performed | Not recognized[1] | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Performed | — | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Performed | — | Recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal | |
| Performed | Not recognized[1] | Not recognized | Legal | Legal | Illegal | |
| Performed | — | Recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Decriminalized | |
| Performed | — | Recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Performed | Not recognized | Not recognized | Legal | Legal | Illegal | |
| Performed | Recognized | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal[lower-alpha 1] | |
| Performed | Not recognized | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Performed | — | Recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal[lower-alpha 3] | |
| Performed | — | — | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Performed | — | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal | |
| Performed | Recognized[1] | Not recognized | Legal | Legal | Illegal | |
| Performed | — | — | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal | |
| Performed | Not recognized | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Performed | Recognized[1] | Not recognized | Legal | Legal | Illegal | |
| Performed | Recognized[2] | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Performed | Recognized | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal[lower-alpha 1] | |
| Performed | — | — | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal | |
| Performed | — | — | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Performed | Not recognized[1] | Not recognized | Legal | Legal | Illegal | |
| Performed | — | — | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal | |
| Performed | — | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Performed | — | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Performed | Recognized[2] | Not recognized | Legal | Legal | Illegal | |
| Performed | — | — | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal | |
| Performed | — | Not recognized | Legal | Legal | Illegal | |
| Performed | — | Recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal[lower-alpha 3] | |
| Performed | — | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Performed | Recognized[2] | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized[lower-alpha 2] | Illegal | |
| Performed | — | Recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal | |
| Performed | Recognized[1] | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Performed | Recognized[2] | Not recognized | Legal | Legal | Illegal | |
| Performed | Not recognized[2] | Not recognized | Legal | Legal | Illegal | |
| Performed | — | — | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal | |
| Performed | Recognized | Recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal | |
| Performed | — | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Performed | — | Not recognized | Legal | Legal | Illegal | |
| Performed | Recognized[1] | Recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal[lower-alpha 3] | |
| Performed | Recognized[2] | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Performed | — | — | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Performed | — | Recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal[lower-alpha 3] | |
| Performed | — | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Performed | Recognized | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Performed | — | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Performed | Recognized[1] | Not recognized | Legal | Legal | Illegal | |
| Performed | Recognized[1] | Recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Muslims only[lower-alpha 1] | |
| Performed | Recognized | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal[lower-alpha 1] | |
| Not performed | Recognized | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal[lower-alpha 1] | |
| Performed | Recognized | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal[lower-alpha 1] | |
| Performed | Recognized[2] | Not recognized | Legal | Legal | Illegal | |
| Not performed | Recognized
|
Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized[lower-alpha 2] | Illegal | |
| Performed | Recognized[2] | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Performed | — | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Performed | Not recognized[3] | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Not performed | Recognized | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal[lower-alpha 1] | |
| Performed | — | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Decriminalized | |
| Performed | Recognized
|
Recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal | |
| Performed | — | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Performed | — | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Foreigners only | — | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal[lower-alpha 1] | |
| Performed | — | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Performed | Recognized[2] | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Not performed | Recognized | — | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal[lower-alpha 1] | |
| Performed | — | Recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal[lower-alpha 3] | |
| Performed | Recognized[1] | Recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal[lower-alpha 3] | |
| Not performed | Recognized | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal[lower-alpha 1] | |
| Performed | Recognized[2] | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Performed | Not recognized[1] | Not recognized | Legal | Legal | Illegal | |
| Performed | — | — | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Performed | — | Recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal[lower-alpha 3] | |
| Non-muslims only | Recognized | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Muslims only | |
| Performed | — | — | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal[lower-alpha 1] | |
| Performed | Recognized | — | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal[lower-alpha 1] | |
| Not performed | Recognized | — | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal[lower-alpha 1] | |
| Performed | — | — | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Performed | Not recognized | Not recognized | Legal | Legal | Illegal | |
| Performed | — | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Performed | — | — | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Performed | — | — | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal[lower-alpha 1] | |
| Performed | — | — | Legal | Unrecognized | Decriminalized | |
| Performed | Not recognized | Recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal[lower-alpha 3] | |
| Performed | — | — | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Performed | Not recognized[1] | Not recognized | Legal | Legal | Illegal | |
| Performed | Recognized[1] | Not recognized | Legal | Legal | Illegal | |
| Performed | — | — | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal[lower-alpha 1] | |
| Performed | Recognized | Recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal (northern regions)[lower-alpha 1] | |
| Performed | Not recognized | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Performed | Recognized[2] | Not recognized | Legal | Legal | Illegal | |
| Performed | — | — | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal[lower-alpha 1] | |
| Performed | — | — | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal[lower-alpha 1] | |
| Not performed | Recognized | — | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal[lower-alpha 1] | |
| Performed | — | — | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Performed | Not recognized[1] | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Performed | Recognized[1] | — | Illegal (except Muslims) | Unrecognized | Muslims only[lower-alpha 1] | |
| Performed | Recognized
10 Christian denominations and Jewish community[5] |
Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Performed | Recognized[1] | — | Legal | Legal | Illegal | |
| Not performed | Recognized | — | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal[lower-alpha 1] | |
| Performed | — | — | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Performed | Not recognized | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Decriminalized | |
| Performed | Not recognized | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Not performed | Recognized | — | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal[lower-alpha 1] | |
| Performed | Recognized | Recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal[lower-alpha 1] | |
| Performed | — | Recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal[lower-alpha 3] | |
| Performed | Muslim marriages only | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Muslims only[lower-alpha 1] | |
| Performed | Recognized[2] | — | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Performed | — | — | Legal | Legal | Illegal | |
| Performed | — | — | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal[lower-alpha 1] | |
| Performed | Recognized | Recognized | Legal | Legal[lower-alpha 4] | Legal[lower-alpha 3] | |
| Performed | — | — | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Performed | — | Recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal | |
| Performed | Recognized[2] | Not recognized | Legal | Legal | Illegal | |
| Performed | Recognized[1] | — | Legal | Unrecognized | Muslims only[lower-alpha 1] | |
| Performed | Recognized[2] | Not recognized | Legal | Legal | Illegal | |
| Performed | — | — | Legal | Legal | Illegal | |
| Performed | — | — | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal[lower-alpha 1] | |
| Performed | — | — | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal[lower-alpha 1] | |
| Performed | — | — | Legal | Legal | Illegal | |
| Performed | Recognized[1] | Recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal | |
| Performed | — | — | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Performed | — | — | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal | |
| Performed | Not recognized[1] | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Performed | — | — | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Performed | Recognized | Recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal | |
| Performed | Not recognized[1] | Not recognized | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Non-muslims only[7] | Recognized | — | Legal | Unrecognized | Legal[lower-alpha 1] | |
| Performed | Recognized[2] | Not recognized | Legal | Legal | Illegal | |
| Performed | — | — | Legal | Legal | Illegal | |
| Performed | — | — | Legal | Legal | Illegal | |
| — | Recognized | Not recognized | Illegal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Performed | — | — | Legal | Unrecognized | Illegal | |
| Performed | — | — | Legal | Not recognized | Illegal | |
| — | — | — | Legal | Not recognized | Legal[lower-alpha 1] | |
| Not performed | Recognized | — | Legal | Not recognized | Legal[lower-alpha 1] | |
| Performed | Recognized | Recognized | Legal | Not recognized | Legal | |
| Performed | Recognized | Recognized | Legal | Not recognized | Legal[lower-alpha 3] | |
- Men can have up to 4 wives
- Foreign same-sex marriages recognized
- Customary marriages only
- Civil marriages only
Rights and obligations

...It (Marriage) does not mean that a man has unfettered right to demand and commit sexual intercourse with his wife without her consent or approval, nor it implies that the husband is in dominant position to impose himself upon the wife. The husband cannot indulge in sexual intimacy in such a manner that is discomforting to the wife to her body, mind and soul.—principal judge Dharmesh Sharma, Delhi court ruling, in lieu of marital rape law in India.[8]
A marriage, by definition, bestows rights and obligations on the married parties, and sometimes on relatives as well, being the sole mechanism for the creation of affinal ties (in-laws). Over 2.3 million weddings take place in the U.S. each year.[9] Historically, many societies have given sets of rights and obligations to husbands that have been very different from the sets of rights and obligations given to wives. In particular, the control of marital property, inheritance rights, and the right to dictate the activities of children of the marriage have typically been given to male marital partners (for more details see coverture and marital power). However, these practices were curtailed to a great deal in many countries, especially Western countries, in the twentieth century, and more modern statutes tend to define the rights and duties of a spouse without reference to gender. In various marriage laws around the world, however, the husband continues to have authority; for instance, the Civil Code of Iran states at Article 1105: "In relations between husband and wife; the position of the head of the family is the exclusive right of the husband".[10]
These rights and obligations vary considerably among legal systems, societies, and groups within a society,[11] and may include:
- Giving a husband/wife or his/her family control over some portion of a spouse's labor or property.
- Giving a husband/wife responsibility for some portion of a spouse's debts.
- Giving a husband/wife visitation rights when his/her spouse is incarcerated or hospitalized.
- Giving a husband/wife control over his/her spouse's affairs when the spouse is incapacitated.
- Establishing the second legal guardian of a parent's child.
- Establishing a joint fund of property for the benefit of children.
- Establishing a relationship between the families of the spouses.
Common law marriage
Common-law marriages were valid in England until Lord Hardwicke's Act of 1753. The act did not apply to Scotland, however, and for many years thereafter couples went north across the border to thwart the ban. On the European continent, common-law marriages were frequent in the Middle Ages, but their legality was abolished in the Roman Catholic countries by the Council of Trent (1545–1563), which required that marriages be celebrated in the presence of a priest and two witnesses.[12]
The Catholic Church forbade clandestine marriage at the Fourth Lateran Council (1215), which required all marriages to be announced in a church by a priest. The Council of Trent (1545–1563) introduced more specific requirements, ruling that future marriages would be valid only if witnessed by the pastor of the parish or the local ordinary (the bishop of the diocese) or by the delegate of one of said witnesses, the marriage being invalid otherwise, even if witnessed by a Catholic priest.This ruling was not accepted in the newly Protestant nations of Europe, nor by Protestants who lived in Roman Catholic countries or their colonies, nor by Eastern Orthodox Christians.
It is sometimes mistakenly claimed[13] that before the Marriage Act 1753 cohabiting couples would enjoy the protection of a "common-law marriage". In fact, neither the name nor the concept of "common-law marriage" was known at this time.[14] Far from being treated as if they were married, couples known to be cohabiting risked prosecution by the church courts for fornication.[15]
The Marriage Act 1753 also did not apply to Britain's overseas colonies of the time, so common-law marriages continued to be recognized in the what became the United States and Canada. Although it is claimed that common-law marriage in the US originated in English common-law, this institution in the United States appears to have originated in the primitive conditions of colonial America where the presence of relatively few clerics or civil officials necessitated a substitute for ceremonial marriage, and the need expanded as the settlers moved into the sparsely populated regions of the West.[16] In the United States, common-law marriages are still recognized in Alabama, Colorado, Iowa, Kansas, Montana, Rhode Island, South Carolina, Texas, Utah and the District of Columbia,[17] (see Common-law marriage in the United States).
All countries in Europe have now abolished "marriage by habit and repute", with Scotland being the last to do so in 2006.[18]
Australia has recognised de facto relationships since the Family Law Act of 2009.
In the United States by the second half of the 20th century, common-law marriages were valid in about one-third of the states, absolutely or conditionally (if entered into before a certain statute-defined date).[19]
Marriage restrictions
Marriage is an institution that is historically filled with restrictions. From age, to gender, to social status, various restrictions are placed on marriage by communities, religious institutions, legal traditions and states.
Marriage age
The minimum age at which a person is able to lawfully marry, and whether parental or other consents are required, vary from country to country. In the U.S. the minimum age for marriage without parental and/or judicial approval is 18 except for Nebraska (19) and Mississippi (21); but most states allow exceptions to the general minimum age in some circumstances (see Marriage age in the United States).[20] In England and Wales the general age at which a person may marry is 18, but 16- or 17-year-olds may get married with their parents' or guardians' consent. If they are unable to obtain this, they can gain consent from the courts, which may be granted by the Magistrates' Courts, or the county or High Court family divisions.
Gender restrictions
Legal, social, and religious restrictions apply in all countries on the genders of the couple.
In response to changing social and political attitudes, some jurisdictions and religious denominations now recognize marriages between people of the same sex. Other jurisdictions have instead "civil unions" or "domestic partnerships", while additional others explicitly prohibit same-sex marriages.
In 1989, Denmark became the first country to legally recognize a relationship for same-sex couples, establishing registered partnerships, which gave those in same-sex relationships "most rights of married heterosexuals, but not the right to adopt or obtain joint custody of a child".[21] In 2001, the Netherlands became the first country in the world to legalize same-sex marriage.[22][23] As of 2023, marriage between same-sex couples is legally performed and recognized in 34 countries, namely the Netherlands, Belgium, Spain, Canada, South Africa, Norway, Sweden, Portugal, Iceland, Argentina, Denmark, Brazil, France, Uruguay, New Zealand, Luxembourg, the United States, Ireland, Colombia, Finland, Malta, Germany, Australia, Austria, Taiwan, Ecuador, United Kingdom, Costa Rica, Chile, Switzerland, Slovenia, Cuba, Mexico and Andorra.[24]
Civil union, civil partnership, domestic partnership and registered partnership statuses offer varying legal benefits of marriage. As of 24 October 2023, countries that have an alternative form of legal recognition other than marriage on a national level are: Bolivia, Croatia, Cyprus, the Czech Republic, Estonia, Greece, Hungary, Italy, Liechtenstein, Monaco, Montenegro and San Marino.[25][26]
Further religious conflicts
These developments have created a political and religious reaction in some countries, including in England, where the Church of England, after long debate, officially banned blessings of gay couples by Church of England clergy,[27] and in the United States, which continues to experience conflicts, based upon religious grounds.
Kinship restrictions
Kinship is two people that are related by blood or adoption, such as brother, sister, mother, father, aunt, uncle etc. No European country prohibits marriage between first cousins. The U.S. is the only western country with cousin marriage restrictions. Societies have often placed restrictions on marriage to relatives, though the degree of prohibited relationship varies widely. In most societies, marriage between brothers and sisters has been forbidden, with ancient Egyptian, Hawaiian, and Inca royalty being prominent exceptions. In many societies, marriage between first cousins is preferred, while at the other extreme, the medieval Catholic Church prohibited marriage even between distant cousins.
In the United Kingdom, the Deceased Wife's Sister's Marriage Act 1907 removed the previous prohibition for a man to marry the sister of his deceased wife. In Australia, marriage with an ancestor or descendant is prohibited, as is a marriage between a brother and a sister, whether of whole blood or half-blood and even if the brother or sister has been adopted.
All mainstream religions prohibit some marriages on the basis of the consanguinity (lineal descent) and affinity (kinship by marriage) of the prospective marriage partners, though the standards vary.
Social restrictions
In the Indian Hindu community, especially in the Brahmin caste, marrying a person of the same gotra was prohibited, since persons belonging to the same gotra are said to have identical patrilineal descent. In ancient India, when gurukuls existed, the shishyas (pupils) were advised against marrying any of guru's children, as shishyas were also considered the guru's children and it would be considered marriage among siblings. However, there were exceptions, including Arjuna's son Abhimanyu's marriage to Uttra, the dance student of Arjuna in Mahabharata. The Hindu Marriage Act, 1955 brought reforms in the area of same-gotra marriages, which were banned prior to the act's passage. Now the Indian constitution allows any consenting adult heterosexual couple (women 18 or older and men 21 or older) from any race, religion, caste, or creed to marry.
Many societies have also adopted other restrictions on whom one can marry, such as prohibitions of marrying persons with the same surname, or persons with the same sacred animal. Anthropologists refer to these sorts of restrictions as exogamy. One example is South Korea's general taboo against a man marrying a woman with the same family name. The most common surname in South Korea is Kim (almost 20%); however, there are several branches (or clans) in the Kim surname. (Korean family names are divided into one or more clans.) Only intra-clan marriages are prohibited, as they are considered one type of endogamy. Thus, many "Kim-Kim" couples can be found.
Societies have also at times required marriage from within a certain group. Anthropologists refer to these restrictions as endogamy. An example of such restrictions would be a requirement to marry someone from the same tribe. Racist laws adopted by some societies in the past—such as Nazi-era Germany, apartheid-era South Africa, and most of the United States in the nineteenth and the first half of the 20th century—and which prohibited marriage between persons of different races could also be considered examples of endogamy.
In modern Israel, the status of marriage is the same as it was historically under the Ottoman Empire and the British mandate, where civil marriage does not exist and authority for marriage is given by the state solely to the recognized religious denominations (Orthodox Judaism, Islam, Druze, and ten Christian denominations (primarily Orthodox Christianity and Catholicism, but also including the Episcopal Church).[28] Israeli couples who wish to contract a marriage that are not allowed under the auspices of any of these religious denominations (including same-sex marriages, marriages involving Israelis of Jewish descent who are not recognized by the state as Jewish and marriages between non-Jewish Arab citizens of Israel and Israeli Jews) or simply wish to get legally married outside the auspices of one of these institutions cannot do so in Israel itself. However, Israel does recognize civil marriages between Israeli citizens that are contracted abroad, including same-sex marriage, so couples in these situations will often hold a non-binding ceremony in Israel and fly abroad (often to nearby Cyprus) to contract a legal marriage that is then recognized in Israel.[29]
In the U.S., many laws banning interracial marriage, which were state laws, were gradually repealed between 1948 and 1967. The U.S. Supreme Court declared all such laws unconstitutional in the case of Loving v. Virginia in 1967.[30]
Polygamy
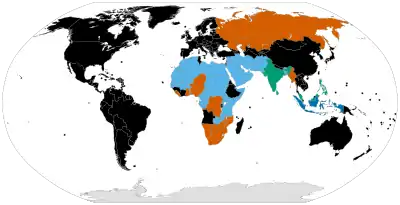
- In India, Malaysia, Philippines and Singapore polygamy is only legal for Muslims.
- In Nigeria and South Africa, polygamous marriages under customary law and for Muslims are legally recognized.
- In Mauritius, polygamous unions have no legal recognition. Muslim men may, however, "marry" up to four women, but they do not have the legal status of wives.
Polygamy—being married to more than one spouse—is illegal in most countries. Where polygamous marriages are allowed, it is typically polygyny that is permitted. While accepted by some societies, it is far less common than monogamy.[31]
Polygamy is normally not permitted in most western countries, although some recognize bona fide polygamous marriages that were performed in other countries. Polygamy is practiced illegally by some groups in the United States and Canada, primarily by certain Mormon fundamentalist sects that separated from the mainstream Latter Day Saints movement after the practice was renounced in 1890.[32]
Many societies, even some with a cultural tradition of polygamy, recognize monogamy as the only valid form of marriage. For example, People's Republic of China shifted from allowing polygamy to supporting only monogamy in the Marriage Act of 1950 after the Communist revolution.
In Islam, polygamy is permitted by the Quran (4:3) which states "If you fear you might fail to give orphan women their ˹due˺ rights ˹if you were to marry them˺, then marry other women of your choice—two, three, or four. But if you are afraid you will fail to maintain justice (between your wives) then ˹content yourselves with˺ one or those ˹bondwomen˺(slaves) in your possession. This way you are less likely to commit injustice (to the orphan girls in your care)." [This verse is from a para which is setting out rules for adoption of orphans.] [33]
Africa has the highest rate of polygamy in the world.[34] In India, only Muslims are allowed to practice polygamy.[35]
Polygamy, taking the form of polygyny, is most common in a region known as the "polygamy belt" in West Africa and Central Africa, with the countries estimated to have the highest polygamy prevalence in the world being Burkina Faso, Mali, Gambia, Niger and Nigeria.[36] In the region of sub-Saharan Africa, polygyny is common and deeply rooted in the culture, with 11% of the population of sub-Saharan Africa living in such marriages (25% of the Muslim population and 3% of the Christian population, as of 2019).[36] Polygyny is especially widespread in West Africa, with the countries estimated to have the highest polygyny prevalence in the world as of 2019 being Burkina Faso (36%), Mali (34%) and Gambia (30%).[36] Outside of Africa, the highest prevalence is in Afghanistan, Yemen and Iraq. [36]
Medical examination
Beginning in the early 20th century, a number of jurisdictions have mandated premarital medical testing or examinations for one or both parties. One of the most commonly mandated was a blood test for syphilis. Between the 1930s and 1950s, most US states passed laws requiring both parties to a marriage to undergo a Wassermann test (or equivalent) for syphilis. If one of the parties was found to have communicable syphilis, they would generally be prevented from marrying until they underwent treatment to resolve the infection. Before the availability of penicillin after World War II, the treatment of syphilis entailed a course of arsenic-based drugs for up to a year or more. These statutes were eventually repealed between the 1970s and 2000s, because they were considered to no longer be a cost-effective public health measure.[37]
In the 1980s and 1990s, many US state legislatures considered laws requiring premarital HIV testing, though only a small number were adopted, and were only briefly active before being repealed.[38] As of 2010, premarital HIV testing is legally mandated in Bahrain, certain provinces of China, Libya, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Uzbekistan.[39]
State recognition
In many jurisdictions, a civil marriage may take place as part of the religious marriage ceremony, although they are theoretically distinct. In most American states, a wedding must be officiated by the justice of the peace in order for it to be recognized. However, priests, ministers, rabbis, and many other religious authorities can act as viable agents of the state. In some countries, such as France, Spain, Germany, Turkey, Argentina, Japan and Russia, it is necessary to be married by government authority separately from any religious ceremony, with the state ceremony being the legally binding one. In those cases, the marriage is usually legalized before the ceremony. Some jurisdictions allow civil marriages in circumstances which are notably not allowed by particular religions, such as same-sex marriages or civil unions.
In a few jurisdictions, a marriage relationship may also be created by the operation of the law alone, as in common-law marriage, sometimes called "marriage by habit and repute." However, the term "common-law marriage" has wider informal use, and is commonly used to refer to cohabiting couples, regardless of any rights they may have. The institution of common-law marriage, in its original legal meaning, has been abolished in almost all jurisdictions that used to have it, and only survives in a few US states. In several jurisdictions, such as parts of Canada, while the law recognizes unmarried couples for various purposes, such relations are not common-law marriages within the original meaning of this legal concept. (see common-law marriage vs. cohabitation). The informal use of the term "common-law marriage" has given rise to many public misconceptions regarding this legal institution.[40]
The status in the eyes of one authority may not be the same as for another. For example, a marriage may be recognised civilly, but not by a church, and vice versa. Normally a marriage entered into in one country will be recognised in other countries. Sometimes, however, a religious ceremony or a marriage entered into in one country is not recognized by another, such as a same-sex marriage.[41]
International recognition
Some countries give legal recognition to marriages performed in another country under the Hague Convention on Marriages (1978).[42] For this to apply, both the country of marriage and the country where recognition is sought need to be members of this convention.
If the country of marriage is not a member of the Hague Convention on Marriages (1978), then the marriage documents will need to be certified following the Apostille convention. This certification is usually performed in the country of marriage by the embassy of the country whose recognition is sought.
License
A marriage license is a document issued, either by a church or state authority, authorizing a couple to marry. The procedure for obtaining a license varies between jurisdictions and has changed over time.
Notice
In many countries there is a requirement to give notice of an impending marriage to the community so that objections to the marriage can be raised. This custom was in place as a mechanism to necessitate the consent of parents as well as the wider community.
Formality

While some countries, such as Australia, permit marriages to be held in private and at any location, others, including England, require that the civil ceremony be conducted in a place specially sanctioned by law (e.g., a church or register office), and be open to the public. An exception can be made in the case of marriage by special emergency license, which is normally granted only when one of the parties is terminally ill. Rules about where and when persons can marry vary from place to place. Some regulations require that one of the parties reside in the locality of the registry office.
Ending a marriage
A marriage can end when one partner dies, by divorce or by annulment. Divorce laws vary significantly by country. The only countries that do not allow divorce are the Philippines and the Vatican City, an ecclesiastical state, which has no procedure for divorce. Countries that have relatively recently legalized divorce are Italy (1970), Portugal (1975), Brazil (1977), Spain (1981), Argentina (1987),[43] Paraguay (1991),[44] Colombia (1991)[lower-alpha 1][44] Ireland (1996), Chile (2004)[45] and Malta (2011).
Notes
- Divorce between 1976-1991 was allowed only for non-Catholics.
References
- Tomkiewicz, Małgorzata. "Skutki cywilne małżeństwa wyznaniowego zawartego przez obywateli polskich przed duchownymi Kościoła Rzymskokatolickiego za granicą" (PDF) (in Polish). p. 3. Retrieved 2019-05-18.
- "Glossary:Marriage".
- "Getting Married in Japan as a Foreigner". August 8, 2017.
- "Marriage Act, 2014" (PDF).
- "Procedura zawierania małżeństwa "konkordatowego" w kontekście polskiego prawa administracyjnego" (PDF).
- Ntampaka, Charles. "Family Law in Rwanda" (PDF).
- "Marriage". The Official Portal of the UAE Government. Retrieved 2022-11-21.
- Agarwal, Sneha (February 25, 2018). "Marriage not a contract for legal sexual pleasure: Delhi court". India Today.
- "Wedding statistics in the United States". SoundVision.com.
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-03-11. Retrieved 2015-07-17.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - Leach, Edmund (1968). Paul Bonannan and John Middleton (ed.). Marriage, Family, and Residence. The Natural History Press. ISBN 1-121-64470-8.
- "Common Law Marriages". Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. Retrieved 24 August 2023.
- Barlow, A., Duncan, S., James, G., and Park, A., (2005) Cohabitation, Marriage and the Law: Social Change and Legal Reform in the 21st Century (Oxford: Hart), p.53
- Probert, R., "Common-Law Marriage: Myths and Misunderstandings", Child & Family Law Quarterly vol.20 issue 1 p.1
- Probert, R. (2012) The Legal Regulation of Cohabitation, 1600–2012: From Fornicators to Family (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press), ch. 2.
- https://scholar.smu.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=3703&context=smulr
- "Marriage Laws of the Fifty States, District of Columbia and Puerto Rico". Legal Information Institute. 14 April 2008. Retrieved 20 April 2015.
- Family Law (Scotland) Act 2006.
- "Common Law Marriages". Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. Retrieved 24 August 2023.
- "At What Age Do People Get Married Around the World?". Priceonomics. 16 May 2016. Retrieved 2022-01-10.
- Rule, Sheila (2 October 1989). "Rights for Gay Couples in Denmark". New York Times. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 19 August 2013.
- Winter, Caroline (December 4, 2014). "In 14 years, same-sex marriage has spread round the world". Bloomberg. Archived from the original on 13 January 2022. Retrieved 2022-02-20.
- "Same-sex marriage around the world". CBC News. Toronto. 26 May 2009. Archived from the original on 25 November 2010. Retrieved 6 October 2009.
- "The Freedom to MarryInternationally". Freedom To Marry. Archived from the original on 23 September 2015. Retrieved 23 September 2015.
- Pearson, Mary. "Where is Gay Marriage Legal?". christiangays.com. Archived from the original on 1 March 2012. Retrieved 20 February 2012.
- Williams, Steve. "Which Countries Have Legalized Gay Marriage?". Care2.com (news.bbc.co.uk as source). Archived from the original on 29 April 2019. Retrieved 20 February 2012.
- "House of Bishops issues pastoral statement on Civil Partnerships". Church of England press release. 2005-07-25. Archived from the original on 2008-06-20. Retrieved 2006-12-05.
- Miller, Akiva. "THE POLICING OF RELIGIOUS MARRIAGE PROHIBITIONS IN ISRAEL: RELIGION, STATE, AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY". Retrieved 8 February 2022.
- Sommer, Allison (15 November 2018). "When Lucy Met Tzachi". Foreign Policy. Retrieved 8 February 2022.
- Loving v. Virginia, 388 U.S. 1 (1967).
- Murdock, George Peter (1949). Social Structure. New York: The MacMillan Company. ISBN 0-02-922290-7. See also: Kaingang.
- "Plural Marriage and Families in Early Utah", churchofjesuschrist.org.
- "Surah An-Nisa - 3". Quran.com. Retrieved 2022-06-14.
- "Social and Cultural Issues" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-06-14. (116 KiB)
- Muslim Marriage Act, 1956
- "Polygamy is rare around the world and mostly confined to a few regions".
- Doroshow, Deborah B (2019). "Wassermann Before Wedding Bells: Premarital Examination Laws in the United States, 1937–1950". Social History of Medicine. 34 (1): 141–169. doi:10.1093/shm/hkz057.
- Closen, Michael; Gamrath, Robert; Hopkins, Dem (1994). "Mandatory Premarital HIV Testing: Political Exploitation of the AIDS Epidemic". Tulane Law Review. 69 (1): 71–115. PMID 11653344.
- Burns, Katya (May 2010). "Mandatory Premarital HIV Testing: An Overview". Open Society Foundations.
- ""Common Law Marriage" myth needs addressing, say MPS - Media centre - Resolution - first for family law". www.resolution.org.uk. Archived from the original on 22 December 2015. Retrieved 1 August 2022.
- "Family Policy - Issues Affecting Gay, Lesbian, Bisexual and Transgender Families" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-11-02. Retrieved 2008-11-25.
- "Convention On Celebration And Recognition Of The Validity Of Marriage". www.legallanguage.com. Retrieved 20 April 2015.
- "Divorce Is Now Legal in Argentina but, So Far, Few Couples Have Taken the Break". Los Angeles Times. 12 July 1987.
- Sex and the State: Abortion, Divorce, and the Family Under Latin. American Dictatorships and Democracies, by Mala Htun, pp 102
- "Chile introduces right to divorce". BBC News. November 18, 2004. Retrieved 2013-11-01.