Outline of Macau
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Macau:



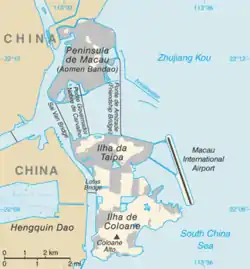
The Macau Special Administrative Region[1] of the People's Republic of China – one of the two special administrative regions of the People's Republic of China, the other being Hong Kong. Macau lies on the western side of the Pearl River Delta, bordering Guangdong province in the north and facing the South China Sea in the east and south.[2] The territory has thriving industries such as textiles, electronics and toys, and a notable tourist industry that boasts a wide range of hotels, resorts, stadiums, restaurants and casinos.[3]
General reference
- Pronunciation:
- Common English country name: Macao
- Official English country name: The Macao Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China
- Common endonym(s): Macau (Portuguese) and 澳門 (Chinese)
- Official endonym(s): Região Administrativa Especial de Macau da República Popular da China (Portuguese) and 中華人民共和國澳門特別行政區 (Chinese)
- Adjectival(s): Macanese
- Demonym(s): Macanese
- Etymology: Name of Macau
- ISO country codes: MO, MAC, 446
- ISO region codes: See ISO 3166-2:MO
- Internet country code top-level domain: .mo
Geography of Macau
- Macau is a:
- City
- Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China
- Peninsula and two islands (one of which is both an artificial island and an airport)
- Population of Macau: 644,900 people (2016 estimate)[4] - 161st most populous country/dependency
- Area of Macau: 29.2 km2 (11.3 sq mi) (about 1⁄6 the size of Washington DC)[5] - not ranked
- Atlas of Macau
- Climate of Macau: subtropical; marine with cool winters and warm summers [5]
Location of Macau
- Geographic coordinates: 22° 10′ 0″ N, 113° 33′ 0″ E
- Macau falls within the following regions:
- Extreme points of Macau:
- High: Coloane Alto 172 m (564 ft)
- Low: South China Sea 0 m
Geographic features of Macau
- Coastline: 41 km[5]
- Terrain: generally flat[5]
- Macau Peninsula - the most populous and historic part of Macau; connected to the Guangdong province of mainland China
- Taipa - connected to Macau Peninsula via Amizade Bridge, Governador Nobre de Carvalho Bridge and Sai Van Bridge
- Coloane - the southernmost island of Macau
- Cotai - a strip of 5.2 km sq. reclaimed land connecting the islands of Taipa and Coloane
- Macau International Airport - artificial island (reclaimed land)
Administrative divisions of Macau
- Capital of Macau: Not applicable. As a semi-autonomous region, Macau does not have a capital, it is its own capital.
- Municipality of Macau (coterminous with Macau Peninsula)
- Municipality of the Islands
- Our Lady of Carmel Parish, coterminous with the island of Taipa
- St. Francis Xavier's Parish, coterminous with the island of Coloane
(Cotai, the reclaimed land between the islands of Taipa and Coloane, had not been assigned to any of the parishes as of 2005).
Demography of Macau
Demographics of Macau Total Population: 644,900 (2016 Qtr4 est.)[4]
- Males: 305,500 (2016 Qtr4 est.) - 47.4% of total population[6]
- Females: 339,400 (2016 Qtr4 est.) - 52.6% of total population[6]
Population density: 21,100 pop./km2 (2015 est.)[6] - dependency with the highest population density in the world
Government and politics of Macau
- Form of government: as a Special administrative region of the People's Republic of China, Macau is a city-state and a multi-party limited democracy
- One country, two systems
- PRC controls the foreign affairs and defense of Macau
- Macau has its own 3-branch government, partly elected, partly appointed
- Empowered by Macau Basic Law until 2049
- One country, two systems
- Capital of Macau: Not applicable. As a semi-autonomous city-state, Macau doesn't have a capital, it is its own capital.
- Elections in Macau
- Mainland and Macau Closer Economic Partnership Arrangement
- Political parties in Macau
Branches of the government of Macau
Executive branch of the government of Macau
- Head of state: President of China, Xi Jinping
- Head of central government: Premier of China, Li Keqiang
- Head of Macau government: Chief Executive of Macau, Ho Iat Seng.
- Cabinet: Executive Council of Macau
- Ho Veng On — Secretary General
- Secretariat for Administration and Justice - André Cheong Weng Chon
- Secretariat for Economy and Finance - Lei Wai Nong
- Secretariat for Security - Wong Sio Chak
- Secretariat for Social Affairs and Culture - Ao Ieong U
- Secretariat for Transport and Public Works - Raimundo Arrais do Rosário
Other departments of the government of Macau
- Commission Against Corruption - Chan Tsz King
- Commission of Audit - Ho Veng On
Legislative branch of the government of Macau
- Parliament of Macau (unicameral): Legislative Assembly of Macau
International organization membership
The Macau Special Administrative Region is a member of:[1]
- International Hydrographic Organization (IHO)
- International Maritime Organization (IMO) (associate)
- International Monetary Fund (IMF)
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO) (correspondent)
- United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) (associate)
- Universal Postal Union (UPU)
- World Customs Organization (WCO)
- World Federation of Trade Unions (WFTU)
- World Meteorological Organization (WMO)
- World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) (associate)
- World Trade Organization (WTO)
Law and order in Macau
Military of Macau
- Macau does not have a military of its own, and is a protectorate of the PRC
- Defense: responsibility of the PLA of the PRC
History of Macau
Culture of Macau

- Architecture of Macau
- Cuisine of Macau
- Events and festivals in Macau
- Gambling in Macau
- Languages of Macau
- Media of Macau
- Museums in Macau
- National symbols of Macau
- Public holidays in Macau
- Religion in Macau
- World Heritage Sites in Macau: Historic Centre of Macau
Art in Macau
Sports in Macau
Economy and infrastructure of Macau
Economy of Macau – Macau's economy has grown dramatically since the opening up of its casino industry to foreign competition in 2001. With the influx of affluent Chinese tourists in the region since its handover in 1999, foreign investments in Macau has transformed the territory into one of the world's largest gaming centres. In 2007, Macau surpassed Las Vegas to be the world's biggest gambling centre.[7] Tourism hence plays a big part of the city's economy, especially since the relaxation of Chinese travel restrictions. In 2015, this city of 646,800 hosted nearly 30.7 million visitors, 67% of which were from mainland China.[5]
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
- Economic rank, by nominal GDP (IMF, 2016): 86th (eighty-sixth)
- GDP PPP(Purchasing Power Parity) per capita: $96,100 (2016 est.) - country comparison to the world: 3rd[5]
- Buildings
- Oldest buildings and structures in Macau
- Tallest buildings in Macau
- All buildings in Macau
- Communications in Macau
- Companies in Macau
- Currency of Macau: Pataca – closely tied to the Hong Kong dollar, which is also freely accepted in the territory.[5]
- ISO 4217: MOP
- Health care in Macau
- Mining in Macau: None (it's a city)
- Tourism in Macau
- Transport in Macau
Education in Macau
See also
References
- "Macau". The World Factbook. United States Central Intelligence Agency. July 15, 2009. Retrieved July 23, 2009.
- Macao Yearbook 2007, 475.
- Chan, 12-13.
- "DSEC - 統計數據庫". www.dsec.gov.mo. Retrieved 2017-04-17.
- "The World Factbook — Central Intelligence Agency". www.cia.gov. Retrieved 2017-04-17.
- "DSEC - 統計數據庫". www.dsec.gov.mo. Retrieved 2017-04-17.
- Barboza, David (2007-01-23). "Macao Surpasses Las Vegas as Gambling Center". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 2017-04-17.
External links
- Business
- MacauHub Archived 2007-12-14 at the Wayback Machine
- Government
- Portal of the government of Macau
- Government Information Bureau
- Cultural Affairs Bureau
- Macau Government Tourist Office
- Guides and directories
- Macau City Guide
 Macau travel guide from Wikivoyage
Macau travel guide from Wikivoyage
- Profiles